链表的一些基本操作
Posted 哦摩西罗伊
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了链表的一些基本操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
苦逼的大三狗,现在面临升学和找工作的双重压力,没办法只有把原来写的烂代码重新找出来,整理一下,复习复习(o(╯□╰)o)。
代码:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 struct node{
4 int res;
5 struct node *next;
6 };
7 struct node *Creat_link_list(int n){//用尾插法建立一个带有头结点的单链表
8 struct node *head,*p,*q;
9 int i;
10 q=head=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
11 for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
12 p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
13 p->res=rand()%1000+1;
14 q->next=p;
15 q=p;
16 }
17 p->next=NULL;
18 return head;
19 }
20 void Read_link_list(struct node *head){//遍历单链表并输出每个节点
21 while(head->next){
22 printf("%d ",head->next->res);
23 head=head->next;
24 }
25 printf("\\n");
26 }
27 struct node *Opposite_link_list(struct node *head){//倒置带有头结点的单链表,不开辟新内存
28 struct node *Newhead,*tmp,*q;
29 Newhead=NULL;
30 q=head;//由于带有头结点需要额外的指针指向头结点(存放头结点)
31 head=head->next;//首元结点
32 while(head){
33 tmp=head->next;
34 head->next=Newhead;
35 Newhead=head;
36 head=tmp;
37 }
38 q->next=Newhead;
39 Newhead=q;
40 return Newhead;
41 }
42 struct node *Delete_even(struct node *head){//删除单链表中为偶数的全部节点
43 struct node *q,*tmp;
44 tmp=head;
45 while(head->next){
46 if(head->next->res%2==0)
47 {
48 q=head->next;
49 head->next=q->next;//删除节点后,相当于后移了一个节点
50 free(q);
51 }
52 else
53 head=head->next;
54 }
55 return tmp;
56 }
57 struct node *Creat_up_list(int n){//创建一个递增的单链表
58 struct node *head,*p,*tmp;
59 int i;
60 head=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
61 head->next=NULL;
62 for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
63 if(i==1)
64 {
65 p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
66 p->res=rand()%1000+1;
67 p->next=head->next;
68 head->next=p;
69 }
70 else
71 {
72 p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
73 p->res=rand()%1000+1;
74 tmp=head;
75 while(tmp->next&&(tmp->next->res<=p->res)){//两个判断条件不能交换顺序
76 tmp=tmp->next;
77 }
78 p->next=tmp->next;
79 tmp->next=p;
80 }
81 }
82 return head;
83 }
84 struct node *Merge_up_list(struct node *head_a,struct node *head_b){//将两个递增的单链表,合并成一个递增的单链表
85 struct node *head_c,*la,*lb,*lc;
86 lc=head_c=head_a;
87 la=head_a->next;
88 lb=head_b->next;
89 while(la&&lb){
90 if(la->res<=lb->res){
91 lc->next=la;
92 lc=la;
93 la=la->next;
94 }
95 else{
96 lc->next=lb;
97 lc=lb;
98 lb=lb->next;
99 }
100 }
101 lc->next=la?la:lb;
102 free(head_b);
103 return head_c;
104 }
105 struct node *Merge_down_list(struct node *head_a,struct node *head_b){//合并两个递减的单链表,合并合并成一个递减的单链表
106 struct node *head_c,*la,*lb,*lc;
107 lc=head_c=head_a;
108 la=head_a->next;
109 lb=head_b->next;
110 while(la&&lb){
111 if(la->res>=lb->res){
112 lc->next=la;
113 lc=la;
114 la=la->next;
115 }
116 else{
117 lc->next=lb;
118 lc=lb;
119 lb=lb->next;
120 }
121 }
122 lc->next=la?la:lb;
123 free(head_b);
124 return head_c;
125 }
126 struct node *Divide(struct node *head){//将一个单链表分解成两个链表,一个节点全为奇数,另一个全为偶数
127 struct node *Newhead,*q,*p;
128 q=Newhead=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
129 while(head->next){
130 if(head->next->res%2==0){
131 p=head->next;
132 head->next=p->next;
133 q->next=p;
134 q=p;
135 }
136 else
137 head=head->next;
138 }
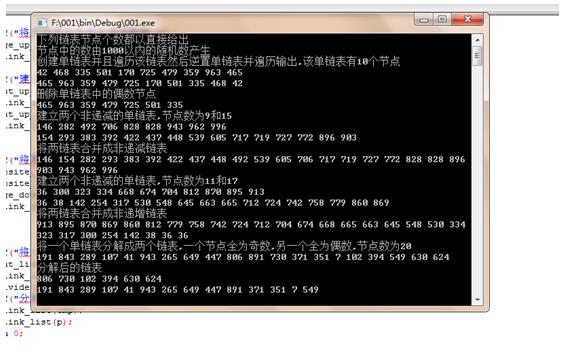
139 q->next=NULL;
140 return Newhead;
141 }
142 int main(){
143 struct node *p,*q,*t,*r,*s,*u,*tmp;
144 printf("下列链表节点个数都以直接给出\\n");
145 printf("节点中的数由1000以内的随机数产生\\n");
146
147
148 printf("创建单链表并且遍历该链表然后逆置单链表并遍历输出,该单链表有10个节点\\n");
149 p=Creat_link_list(10);
150 Read_link_list(p);
151 q=Opposite_link_list(p);
152 Read_link_list(q);
153
154 printf("删除单链表中的偶数节点\\n");
155 t=Delete_even(p);
156 Read_link_list(t);
157
158 printf("建立两个非递减的单链表,节点数为9和15\\n");
159 r=Creat_up_list(9);
160 Read_link_list(r);
161 s=Creat_up_list(15);
162 Read_link_list(s);
163
164 printf("将两链表合并成非递减链表\\n");
165 u=Merge_up_list(r,s);
166 Read_link_list(u);
167
168 printf("建立两个非递减的单链表,节点数为11和17\\n");
169 r=Creat_up_list(11);
170 Read_link_list(r);
171 s=Creat_up_list(17);
172 Read_link_list(s);
173
174
175 printf("将两链表合并成非递增链表\\n");
176 r=Opposite_link_list(r);
177 s=Opposite_link_list(s);
178 u=Merge_down_list(r,s);
179 Read_link_list(u);
180
181
182
183 printf("将一个单链表分解成两个链表,一个节点全为奇数,另一个全为偶数,节点数为20\\n");
184 p=Creat_link_list(20);
185 Read_link_list(p);
186 tmp=Divide(p);
187 printf("分解后的链表\\n");
188 Read_link_list(tmp);
189 Read_link_list(p);
190 return 0;
191 }
测试结果:
还添加两个基本的功能:
链表的排序。
以及链表节点的删除。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int res;
struct node *next;
};
void create(struct node * &head,int n){
head=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *p,*q;//前一个节点和当前节点
p=head;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
q=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
scanf("%d",&q->res);
p->next=q;
p=q;
}
p->next=NULL;
}
void Show(struct node *head){
struct node *tmp;
tmp=head;
while(tmp->next){
printf("%d ",tmp->next->res);
tmp=tmp->next;
}
printf("\\n");
}
void Delete(struct node *head,int x){
struct node *tmp=head,*p;
while(tmp->next&&tmp->next->res!=x){//两者的顺序不能够交换
tmp=tmp->next;
}
if(tmp->next==NULL)
printf("链表中不存在该元素\\n");
else{
p=tmp->next;
tmp->next=p->next;
free(p);
}
}
void Sort(struct node *head){
struct node *tmp1,*tmp2;//额外申请的两个指针
int ans;
for(tmp1=head->next;tmp1->next;tmp1=tmp1->next)
for(tmp2=head->next;tmp2->next;tmp2=tmp2->next){
if(tmp2->res>tmp2->next->res){
ans=tmp2->res;
tmp2->res=tmp2->next->res;
tmp2->next->res=ans;
}
}
}
int main()
{
struct node *head=NULL;
int n,x;
scanf("%d",&n);
create(head,n);
Show(head);
scanf("%d",&x);
Delete(head,x);
Show(head);
Sort(head);
Show(head);
return 0;
}
以上是关于链表的一些基本操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章