android中shape的属性
Posted Z2
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了android中shape的属性相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
<shape> <!– 实心 –> <solid android:color=”#ff9d77″/> <!– 渐变 –> <gradient android:startColor=”#ff8c00″ android:endColor=”#FFFFFF” android:angle=”270″ /> <!– 描边 –> <stroke android:width=”2dp” android:color=”#dcdcdc” /> <!– 圆角 –> <corners android:radius=”2dp” /> <padding android:left=”10dp” android:top=”10dp” android:right=”10dp” android:bottom=”10dp” /> </shape>
solid:实心,就是填充的意思
android:color指定填充的颜色
gradient:渐变
android:startColor和android:endColor分别为起始和结束颜色,ndroid:angle是渐变角度,必须为45的整数倍。
另外渐变默认的模式为android:type=”linear”,即线性渐变,可以指定渐变为径向渐变,android:type=”radial”,径向渐变需要指定半径android:gradientRadius=”50″。
stroke:描边
android:width=”2dp”
描边的宽度,android:color
描边的颜色。
我们还可以把描边弄成虚线的形式,设置方式为:
android:dashWidth=”5dp”
android:dashGap=”3dp”
其中android:dashWidth表示’-‘这样一个横线的宽度,android:dashGap表示之间隔开的距离。
corners:圆角
android:radius为角的弧度,值越大角越圆。
我们还可以把四个角设定成不同的角度,方法为:
<corners android:topRightRadius=”20dp” 右上角 android:bottomLeftRadius=”20dp” 右下角 android:topLeftRadius=”1dp” 左上角 android:bottomRightRadius=”0dp” 左下角 />
这里有个地方需要注意,bottomLeftRadius是右下角,而不是左下角,这个有点郁闷,不过不影响使用,记得别搞错了就行。
还有网上看到有人说设置成0dp无效,不过我在测试中发现是可以的,我用的是2.2,可能修复了这个问题吧,如果无效的话那就只能设成1dp了。
padding:间隔
这个就不用多说了,XML布局文件中经常用到。
大体的就是这样,以下是一个使用的具体示例:用在Selector中作为Button的背景,分别定义了按钮的一般状态、获得焦点状态和按下时的状态,具体代码如下:
main.xml:
<Button android:layout_width=”wrap_content” android:layout_height=”wrap_content” android:text=”TestShapeButton” android:background=”@drawable/button_selector” />
button_selector.xml:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?> <selector xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”> <item android:state_pressed=”true” > <shape> <!– 渐变 –> <gradient android:startColor=”#ff8c00″ android:endColor=”#FFFFFF” android:type=”radial” android:gradientRadius=”50″ /> <!– 描边 –> <stroke android:width=”2dp” android:color=”#dcdcdc” android:dashWidth=”5dp” android:dashGap=”3dp” /> <!– 圆角 –> <corners android:radius=”2dp” /> <padding android:left=”10dp” android:top=”10dp” android:right=”10dp” android:bottom=”10dp” /> </shape> </item> <item android:state_focused=”true” > <shape> <gradient android:startColor=”#ffc2b7″ android:endColor=”#ffc2b7″ android:angle=”270″ /> <stroke android:width=”2dp” android:color=”#dcdcdc” /> <corners android:radius=”2dp” /> <padding android:left=”10dp” android:top=”10dp” android:right=”10dp” android:bottom=”10dp” /> </shape> </item> <item> <shape> <solid android:color=”#ff9d77″/> <stroke android:width=”2dp” android:color=”#fad3cf” /> <corners android:topRightRadius=”5dp” android:bottomLeftRadius=”5dp” android:topLeftRadius=”0dp” android:bottomRightRadius=”0dp” /> <padding android:left=”10dp” android:top=”10dp” android:right=”10dp” android:bottom=”10dp” /> </shape> </item> </selector>
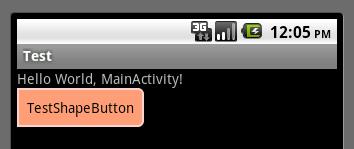
运行效果如下图:
一般状态:
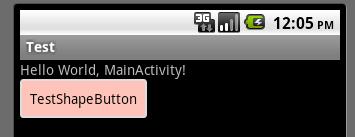
获得焦点状态:
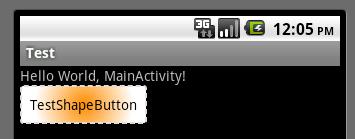
按下状态:
本文章转接于:http://kofi1122.blog.51cto.com/2815761/521605
以上是关于android中shape的属性的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章