文件存储结构inode与RAM结构建立联系
Posted yuxi_o
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了文件存储结构inode与RAM结构建立联系相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
linux下一切皆文件,大致可分为以下几类:目录、普通文件、硬连接、软连接、字符设备、块设备、FIFO、Socket,其在物理存储体内存储按inode和数据块存储,inode代表元数据,是除实际数据外的所有(属性)数据。根据不同的文件类型有以下几种情况:
》对于常规文件,文件的数据存储在数据块中,其他数据(即属性)存储在inode中。
》对于目录,该目录下的所有文件名和目录名存储在数据块中,注意文件名保存在它所在目录的数据块中,除文件名之外,ls -l命令看到的其它信息都保存在该文件的inode中。注意这个概念:目录也是一种文件,是一种特殊类型的文件。
》对于硬链接,其只是在硬链接所在目录的数据块中增加或修改文件名,并修改硬链接目标inode的链接数(ls显示属性的第二项),并不会增加inode或数据块。
》对于符号链接,如果目标路径名较短则直接保存在inode中以便更快地查找,如果目标路径名较长则分配一个数据块来保存。
》设备文件、FIFO和socket等特殊文件没有数据块,设备文件的主设备号和次设备号保存在inode中。
inode结构体定义在linux/fs.h中:
/* * Keep mostly read-only and often accessed (especially for * the RCU path lookup and \'stat\' data) fields at the beginning * of the \'struct inode\' */ struct inode { umode_t i_mode; unsigned short i_opflags; uid_t i_uid; gid_t i_gid; unsigned int i_flags; #ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL struct posix_acl *i_acl; struct posix_acl *i_default_acl; #endif const struct inode_operations *i_op; struct super_block *i_sb; struct address_space *i_mapping; #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY void *i_security; #endif /* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */ unsigned long i_ino; /* * Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the * following functions for modification: * * (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink * inode_(inc|dec)_link_count */ union { const unsigned int i_nlink; unsigned int __i_nlink; }; dev_t i_rdev; /* 若是设备文件,此字段将记录设备的设备号 */ struct timespec i_atime; struct timespec i_mtime; struct timespec i_ctime; spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */ unsigned short i_bytes; blkcnt_t i_blocks; loff_t i_size; #ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED seqcount_t i_size_seqcount; #endif /* Misc */ unsigned long i_state; struct mutex i_mutex; unsigned long dirtied_when; /* jiffies of first dirtying */ struct hlist_node i_hash; struct list_head i_wb_list; /* backing dev IO list */ struct list_head i_lru; /* inode LRU list */ struct list_head i_sb_list; union { struct list_head i_dentry; struct rcu_head i_rcu; }; atomic_t i_count; unsigned int i_blkbits; u64 i_version; atomic_t i_dio_count; atomic_t i_writecount; const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */ struct file_lock *i_flock; struct address_space i_data; #ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA struct dquot *i_dquot[MAXQUOTAS]; #endif struct list_head i_devices; union { struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; struct block_device *i_bdev; /* 若是块设备,为其对应的block_device结构体指针 */ struct cdev *i_cdev; /* 若是字符设备,为其对应的cdev结构体指针 */ }; __u32 i_generation; #ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY __u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */ struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_marks; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_IMA atomic_t i_readcount; /* struct files open RO */ #endif void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */ };
inode是linux管理文件系统的最基本单位,也是文件系统连接任何子目录、文件的桥梁。
ls -li显示属性各字段含义介绍
stat函数读取文件的inode,然后把inode中的各种文件属性填入一个struct stat结构体传出给调用者。ls或stat可查看inode属性。
struct stat { dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */ mode_t st_mode; /* protection */ nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */ uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */ gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */ dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */ off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */ blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */ blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */ time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ };
普通文件
~$ls -li wang
588946 -rw-rw-r-- 1 yuxi yuxi 9045 Feb 12 18:37 wang
st_ino file_type st_mode st_nlink st_uid st_gid st_size st_mtime file_name
目录
712708 drwxrwxr-x 2 yuxi yuxi 4096 Oct 6 15:52 file
st_ino file_type st_mode st_nlink st_uid st_gid st_size st_mtime dir_name
硬链接
~$ln wang hard_wang
~$ls -li wang hard_wang
588946 -rwxrwxr-x 2 yuxi yuxi 9045 Feb 12 18:37 hard_wang
588946 -rwxrwxr-x 2 yuxi yuxi 9045 Feb 12 18:37 wang
st_ino file_type st_mode st_nlink st_uid st_gid st_size st_mtime file_name
符号链接
2011 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 Mar 19 10:01 stdout -> /proc/self/fd/1
st_ino file_type st_mode st_nlink st_uid st_gid st_size(软链接文件名大小) st_mtime file_name
字符设备
1904 crw-rw-rw- 1 root tty 5, 0 Mar 19 10:01 tty
st_ino file_type st_mode st_nlink st_uid st_gid st_rdev st_mtime dev_name
块设备
7502 brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 0 Mar 19 10:01 sda
st_ino file_type st_mode st_nlink st_uid st_gid st_rdev st_mtime dev_name
socket
9252 srw-rw-rw- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 10:01 log
st_ino file_type st_mode st_nlink st_uid st_gid st_size st_mtime file_name
inode与RAM建立连接
所有文件都是通过open或类open函数将inode与file建立联系,release将file结构体的修改更新inode。用inode填充file结构体(file为RAM结构体),实现了物理结构体与RAM结构体的分离,之后的read、write等file_operations函数直接操作file结构体即可完成对文件的所有更改。
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
extern struct file * dentry_open(struct dentry *, struct vfsmount *, int, const struct cred *);
extern int dcache_dir_open(struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
file结构体定义于linux/fs.h,如下:
struct file { /* * fu_list becomes invalid after file_free is called and queued via * fu_rcuhead for RCU freeing */ union { struct list_head fu_list; struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead; } f_u; struct path f_path; #define f_dentry f_path.dentry #define f_vfsmnt f_path.mnt const struct file_operations *f_op; /* * Protects f_ep_links, f_flags, f_pos vs i_size in lseek SEEK_CUR. * Must not be taken from IRQ context. */ spinlock_t f_lock; #ifdef CONFIG_SMP int f_sb_list_cpu; #endif atomic_long_t f_count; unsigned int f_flags; fmode_t f_mode; loff_t f_pos; struct fown_struct f_owner; const struct cred *f_cred; struct file_ra_state f_ra; u64 f_version; #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY void *f_security; #endif /* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */ void *private_data; #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL /* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */ struct list_head f_ep_links; #endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */ struct address_space *f_mapping; #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_WRITECOUNT unsigned long f_mnt_write_state; #endif };
字符文件open函数调用过程记录:
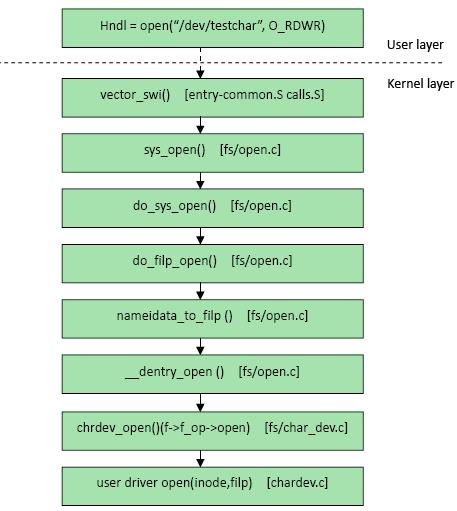
在用户空间调用的open()函数传入的参数是文件路径,通过文件路径可以找到文件的inode节点,实际上inode与文件路径间建立了一一映射关系。
一个路径是/opt/file,则查找的顺序是:
1. 读出inode表中第2项,也就是根目录的inode,从中找出根目录数据块的位置
2. 从根目录的数据块中找出文件名为opt的记录,从记录中读出它的inode号
3. 读出opt目录的inode,从中找出它的数据块的位置
4. 从opt目录的数据块中找出文件名为file的记录,从记录中读出它的inode号
5. 读出file文件的inode
file即表示一个进程内打开的文件,它是与进程对应的。已打开的文件在内核中用file结构体表示,文件描述符表中的指针指向file结构体。
linux文件系统与设备驱动
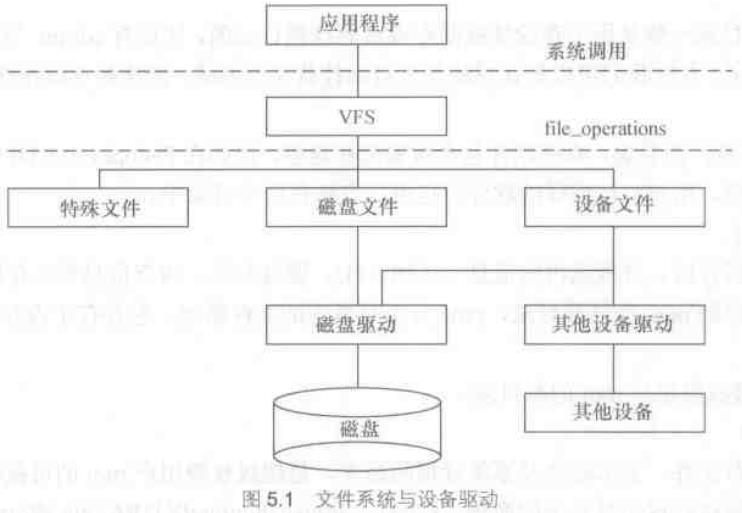
应用程序和VFS之间的接口是系统调用,而VFS与磁盘文件系统以及普通设备之间的接口是file_operations结构体成员函数,这个结构体包含对文件进行打开、关闭、读写、控制的一系列函数。
由于字符设备的上层没有磁盘文件系统,所以字符设备的file_operations成员函数就直接由设备驱动提供,file_operations正是字符设备驱动的核心。
而对于块存储设备而言,ext2、fat、jffs2等文件系统中会实现针对VFS的file_operations成员函数,设备驱动层将看不到file_operations的存在。磁盘文件系统和设备驱动会将对磁盘上文件的访问最终转换成对磁盘上柱面和扇区的访问。
在设备驱动程序的设计中,一般而言,会关心结构体file和inode。
本节摘自《linux设备驱动开发详解》--宋宝华。
参考:
2. ext2文件系统了解
以上是关于文件存储结构inode与RAM结构建立联系的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章