信号处理——Hilbert端点效应浅析
Posted 桂。
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了信号处理——Hilbert端点效应浅析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
作者:桂。
时间:2017-03-05 19:29:12
链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/6506405.html
声明:转载请注明出处,谢谢。

前言
|
本文为Hilbert变换分析的补充,主要介绍Hilbert变换中的端点效应,内容拟分两部分展开: 1)Gibbs现象介绍; 2)端点效应分析; 内容为自己一家之言,其中不合理的地方,希望各位告诉我,反正改不改是我的事(●\'◡\'●) |
一、Gibbs现象
关于Gibbs的理论推导,可以参考郑君里的《信号与系统》上册(第二版,P97~101),里边有详细的理论分析。也可参考:维基百科,里边有一张图很形象:
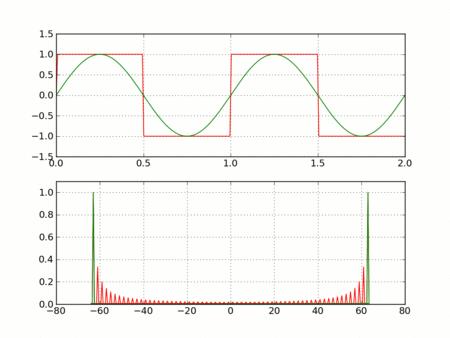
给出对应的代码(用该程序,借助MATLAB便可以生成.gif图):
%% 代码介绍======================================================================== %% Title: % 1) Fourier series approximation of square wave. % 2) Demonstration of Gibbs phenomenon (verification of Fig. 3.9 of [1]) %% Author: % Ankit A. Bhurane (ankit.bhurane@gmail.com) %% Expression: % The Fourier series approximation of a square wave signal existing between % -Tau/2 to Tau/2 and period of T0 will have the form: % % Original signal to be approximated: % : % __________:__________ A % | : | % | : | % | : | % __________| : |__________ % -T0/2 -Tau/2 0 Tau/2 T0/2 % : % : % % Its Fourier series approximation: % % Inf % ___ % A*Tau \\ / sin(pi*n*Tau/T0) \\ % r(t) = ------- | | ------------------ exp^(j*n*2*pi/T0*t) | % T0 /___ \\ (pi*n*Tau/T0) / % n = -Inf % % The left term inside summation are the Fourier series coeffs (Cn). The % right term is the Fourier series kernel. % Tau: range of square wave, T: period of the square wave, % t: time variable, n: number of retained coefficients. % %% Observations: % 1) As number of retained coefficients tends to infinity, the approximated % signal value at the discontinuity converge to half the sum of values on % either side. % 2) Ripples does not decrease with increasing coefficients with % approximately 9% overshoot. % 3) Energy in the error between original and approximated signal, reduces % as the number of retained coefficients are increased. % %% References: % [1] Oppenheim, Willsky, Nawab, "Signals and Systems", PHI, Second edition % [2] Dean K. Frederick and A. Bruce Carlson, "Fourier series" section in % Linear systems in communication and control %% Last Modified: Sept 24, 2013. %% Copyright (c) 2013-2014 | Ankit A. Bhurane %%
clc; clear all; close all;
% Specification
A = 1; % Peak-to-peak amplitude of square wave
Tau = 10; % Total range in which the square wave is defined (here -5 to 5)
T0 = 20; % Period (time of repeatation of square wave), here 10
C = 200; % Coefficients (sinusoids) to retain
N = 1001; % Number of points to consider
t = linspace(-(T0-Tau),(T0-Tau),N); % Time axis
X = zeros(1,N); X(t>=-Tau/2 & t<=Tau/2) = A; % Original signal
R = 0; % Initialize the approximated signal
k = -C:C; % Fourier coefficient number axis
f = zeros(1,2*C+1); % Fourier coefficient values
% Loop for plotting approximated signals for different retained coeffs.
for c = 0:C % Number of retained coefficients
for n = -c:c % Summation range (See equation above in comments)
% Sinc part of the Fourier coefficients calculated separately
if n~=0
Sinc = (sin(pi*n*Tau/T0)/((pi*n*Tau/T0))); % At n NOTEQUAL to 0
else
Sinc = 1; % At n EQUAL to 0
end
Cn = (A*Tau/T0)*Sinc; % Actual Fourier series coefficients
f(k==n) = Cn; % Put the Fourier coefficients at respective places
R = R + Cn*exp(1j*n*2*pi/T0.*t); % Sum all the coefficients
end
R = real(R); % So as to get rid of 0.000000000i (imaginary) factor
Max = max(R); Min = min(R); M = max(abs(Max),abs(Min)); % Maximum error
Overshoot = ((M-A)/A)*100; % Overshoot calculation
E = sum((X-R).^2); % Error energy calculation
% Plots:
% Plot the Fourier coefficients
subplot 211; stem(k,f,\'m\',\'LineWidth\',1); axis tight; grid on;
xlabel(\'Fourier coefficient index\');ylabel(\'Magnitude\');
title(\'Fourier coefficients\');
% Plot the approximated signal
subplot 212; plot(t,X,t,R,\'m\',\'LineWidth\',1); axis tight; grid on;
xlabel(\'Time (t)\'); ylabel(\'Amplitude\');
title([\'Approximation for N = \', num2str(c),...
\'. Overshoot = \',num2str(Overshoot),\'%\',\'. Error energy: \',num2str(E)])
pause(0.1); % Pause for a while
R = 0; % Reset the approximation to calculate new one
end
简而言之:
- 对于跳变的点,傅里叶变换的分量只能是能量收敛,而不是一致(幅度)收敛;
- 对于跳变的点,如门函数/方波,信号由低频到高频众多分量组合而成。
故对于连续时域信号,Fourier级数只能无限项逼近,不能完全一致。
二、端点效应
A-理论解释
借用之前博文的一张图:
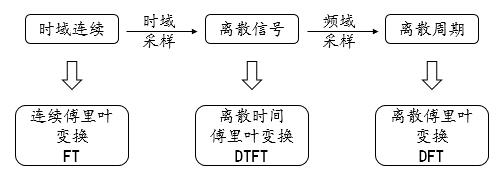
连续信号到离散信号需要进行采样,由于有无穷多项,采样率对于高频的部分(因为无穷多项)难以满足Nyquist采样定理,因此会出现失真,这也就是端点效应的理论解释。失真的根本原因在时域采样,频域采样步骤只不过影响频域分辨率,即所谓的栅栏效应,但不是造成失真的根本原因。
B-现象分析
为了验证理论,此处采样一个正弦信号进行分析,按连续信号来看其Hilbert变换应该是余弦信号。
给出代码:
clc;clear all;close all; fs = 2000; f0 = 80; t = 0:1/fs:.1; sig = sin(2*pi*f0*t); sig_ref = -cos(2*pi*f0*t); sig_hilbert = hilbert(sig); figure; subplot 311 plot(t,sig,\'k\',\'linewidth\',2);hold on; plot(t,sig_ref,\'r.-\',\'linewidth\',2);hold on; plot(t,imag(sig_hilbert),\'b\',\'linewidth\',2);hold on; legend(\'原信号\',\'余弦信号\',\'Hilbert变换信号\',\'localization\',\'best\'); ylim([-2,2]); grid on; %频谱 f = linspace(0,fs,length(t)); subplot 312 plot(f,abs(fft(sig)),\'k\');hold on; plot(f,abs(fft(sig_hilbert)),\'r\');hold on; legend(\'原信号\',\'Hilbert变换信号\',\'localization\',\'best\'); grid on;
对应的结果图:
时域:
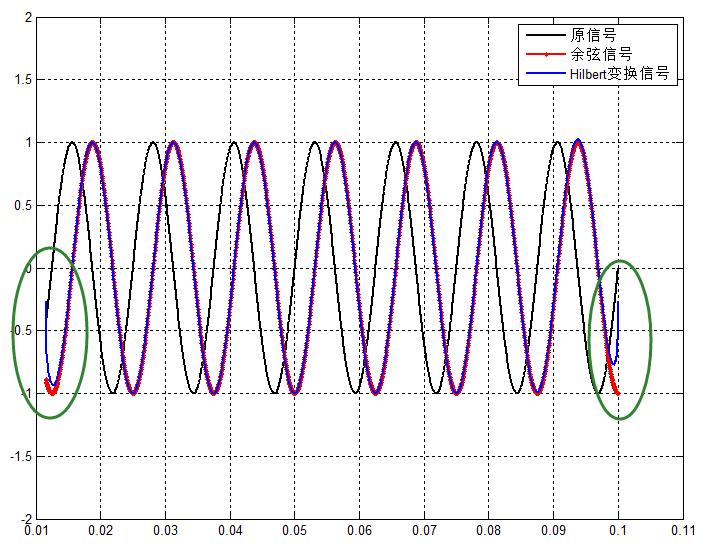
可以看到明显的端点效应(说是端点效应,如果间断点在中间位置,一样会有该效应,毕竟都是Nyquist定理下的误差嘛)。
频域:
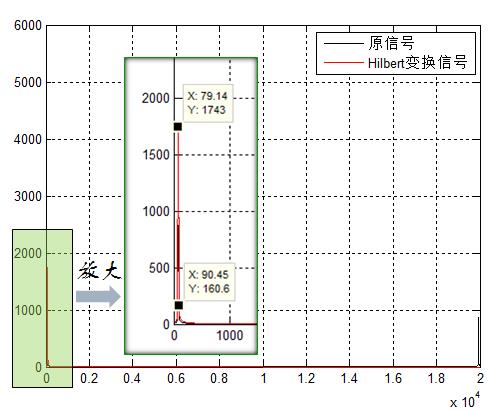
采样率取得够大了,理论上正弦信号Hilbert之后应该是一个单边的冲击。但频谱显示,峰值旁边的一个点,幅度达到160.6,这也印证了能量的泄露。
发现端点效应,与前文理论对应:Hilbert就是一个频域的变相器,本质也是fourier变换,是不是也因为跳变点(即信号中的Gibbs问题)?观察频谱,峰值旁边的点,幅值有160.5大小,我们计算原信号
2*sig(1)-sig(2)
得到结果是:-0.4820,而对于没有的点,应该是默认是0的,因此端点算是一个跳变点了。
注意:端点效应是相对于连续信号来讲,存在失真,从而出现误差。对于数字信号,Hilbert变换结果就是该正弦数字信号的精确表达,即逆Hilbert可以完全恢复出正弦信号。给一张Hilbert变换后,进行逆Hilbert变换的code及示意图:
clc;clear all;close all; fs = 2000; f0 = 40; t = 0:1/fs:.1; sig = sin(2*pi*f0*t); sig_hilbert = -imag(hilbert(imag(hilbert(sig)))); figure; plot(t,sig,\'k\',\'linewidth\',2);hold on; plot(t,sig_hilbert,\'r--\',\'linewidth\',2); ylim([-2,2]); grid on;
从图中,可以看到从Hilbert结果恢复的信号与原信号完全一致!这也印证了上文的观点:失真在时域采样,而不在频域采样。
下面再做一组实验,验证推断:
思路——只要保证2sig(1)-sig(2)逼近0,理论上是不是就没有边界效应了?
此时:2*sig(1)-sig(2)=1.5873e-05,再来看看结果图: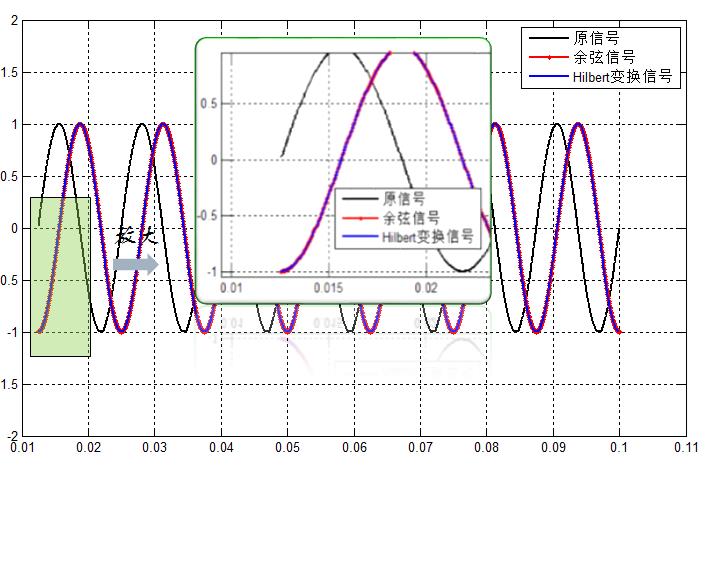
再来看看频谱,没错,峰值旁边的点压的很小(6.183e-13),符合预期。
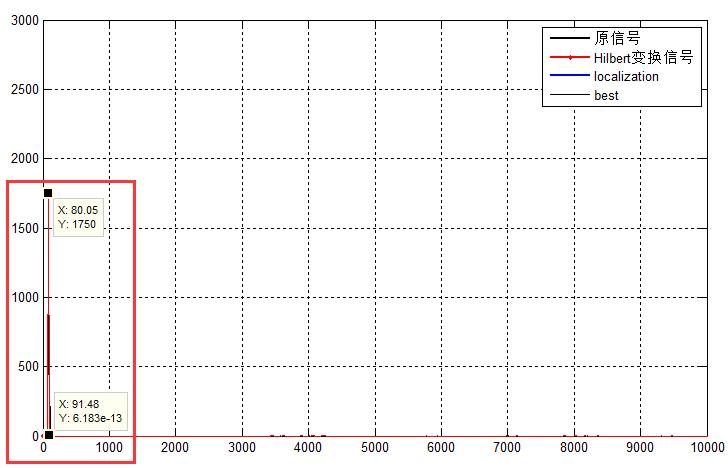
此处代码:
clc;clear all;close all; fs = 20000; f0 = 80; t = 0.01255:1/fs:.1;%t = 0.0252:1/fs:.1则没有跳变。 sig = sin(2*pi*f0*t); 2*sig(1)-sig(2) sig_ref = -cos(2*pi*f0*t); sig_hilbert = hilbert(sig); figure; subplot 211 plot(t,sig,\'k\',\'linewidth\',2);hold on; plot(t,sig_ref,\'r.-\',\'linewidth\',2);hold on; plot(t,imag(sig_hilbert),\'b\',\'linewidth\',2);hold on; legend(\'原信号\',\'余弦信号\',\'Hilbert变换信号\',\'localization\',\'best\'); ylim([-2,2]); grid on; %频谱 f = linspace(0,fs,length(t)); subplot 212 plot(f,abs(fft(sig)),\'k\');hold on; plot(f,abs(fft(sig_hilbert)),\'r\');hold on; legend(\'原信号\',\'Hilbert变换信号\',\'localization\',\'best\'); ylim([0 6000]); grid on;
基于这个基本要点,很多方法对信号:预测、延拓、镜像等操作,以消除或者降低端点效应。为什么用2*sig(1)-sig(2)呢,这是因为实验的函数为sin,在0附近sinx~x ,严格意义上应该是2*f(1)-f(2)≈ 0 。f是函数表达式,而且实际中信号不是单一频点,仅仅通过两个点判断也是不够的。
只是消除端点方法不同,但端点现象的本质一致。
多说一句:Hilbert将双边谱压成单边,这让频域滤波等操作方便了不少。

参考:
Gibbs phenomen:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gibbs_phenomenon
以上是关于信号处理——Hilbert端点效应浅析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章