bfs
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了bfs相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。




如果要求走出迷宫的所有方案数,则可以采用dfs。如果要求最短步数,采用bfs更好。
因为bfs不需要搜索所有的路径,它的层数是由小到大的特点,它的步数一定是最少的,也就是最优解。
先看两个简单题

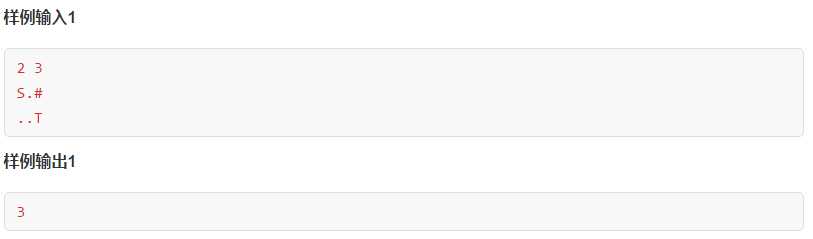
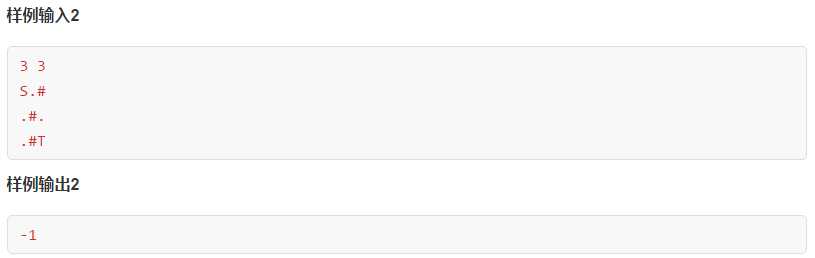

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 int dir[4][2]={{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; 6 char mat[105][105]; 7 int vis[105][105]; 8 int n,m,ans=-1; 9 struct point 10 { 11 int x,y,step; 12 point(int xx,int yy,int ss) 13 { 14 x=xx; 15 y=yy; 16 step=ss; 17 } 18 }; 19 void bfs(int x,int y,int step) 20 { 21 vis[x][y]=1; 22 queue<point> q; 23 q.push(point(x,y,step)); 24 while(!q.empty()) 25 { 26 point dp=q.front(); 27 q.pop(); 28 int dx=dp.x; 29 int dy=dp.y; 30 int dstep=dp.step; 31 32 if(mat[dx][dy]==‘T‘) 33 { 34 ans=dstep; 35 return; 36 } 37 38 for(int i=0;i<4;i++) 39 { 40 int nx=dx+dir[i][0]; 41 int ny=dy+dir[i][1]; 42 if(nx<0||ny<0||nx>=n||ny>=m||mat[nx][ny]==‘#‘||vis[nx][ny]) continue; 43 vis[nx][ny]=1; 44 q.push(point(nx,ny,dstep+1)); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 int main() 49 { 50 cin>>n>>m; 51 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); 52 int index=0; 53 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 54 { 55 cin>>mat[i]; 56 } 57 int start_x,start_y; 58 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 59 { 60 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) 61 { 62 if(mat[i][j]==‘S‘) 63 { 64 start_x=i; 65 start_y=j; 66 } 67 } 68 } 69 bfs(start_x,start_y,0); 70 cout<<ans<<endl; 71 return 0; 72 }

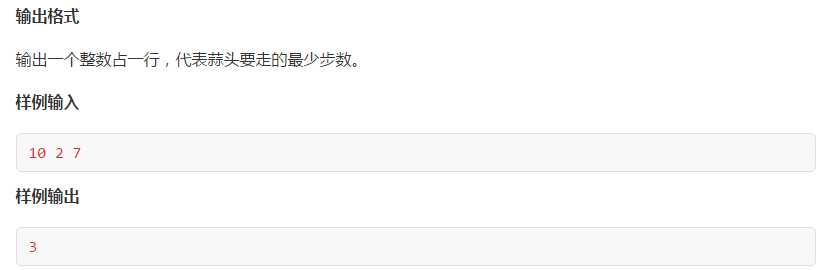

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int dir[4][2]={{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; 4 //char mat[105][105]; 5 int vis[5005]; 6 int n,a,b; 7 int ans; 8 struct point 9 { 10 int index,step; 11 point(int ii,int ss) 12 { 13 index=ii; 14 step=ss; 15 } 16 }; 17 void bfs(int index,int step) 18 { 19 vis[index]=1; 20 queue<point> q; 21 q.push(point(index,step)); 22 while(!q.empty()) 23 { 24 point dp=q.front(); 25 q.pop(); 26 int di=dp.index; 27 int ds=dp.step; 28 29 if(di==b) 30 { 31 ans=ds; 32 return; 33 } 34 35 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) 36 { 37 int ni=di; 38 if(i==0) ni+=1; 39 else if(i==1) ni-=1; 40 else if(i==2) ni*=2; 41 if(ni>=0&&ni<=n&&!vis[ni]) 42 { 43 vis[ni]=1; 44 q.push(point(ni,ds+1)); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 int main() 50 { 51 cin>>n>>a>>b; 52 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); 53 bfs(a,0); 54 cout<<ans<<endl; 55 return 0; 56 }
看个比较神奇的题目

输出格式
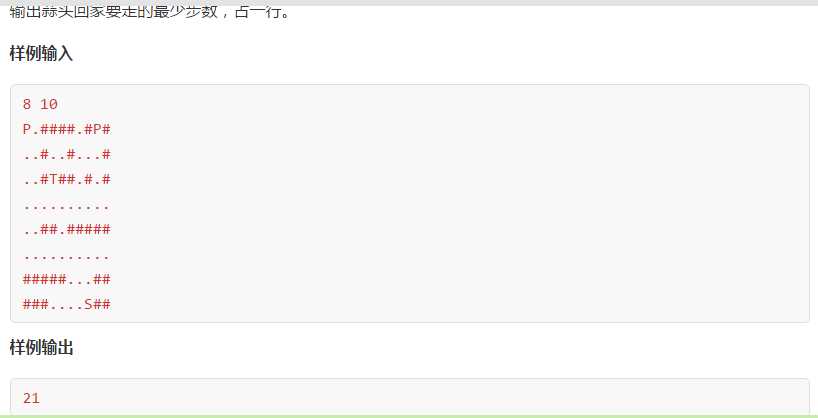

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int dir[4][2]= {{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; 4 int n,m; 5 char mat[2005][2005]; 6 int vis[2005][2005][2]; 7 int ans; 8 struct point 9 { 10 int x,y,step; 11 point(int xx,int yy,int ss) 12 { 13 x=xx; 14 y=yy; 15 step=ss; 16 } 17 }; 18 void dfs(point p) 19 { 20 queue<point> q; 21 q.push(p); 22 vis[p.x][p.y][0]=1; 23 vis[p.x][p.y][1]=0; 24 while(!q.empty()) 25 { 26 point dp=q.front(); 27 //cout<<"访问"<<"x:"<<dp.x<<"y:"<<dp.y<<"step:"<<dp.step<<endl; 28 q.pop(); 29 if(mat[dp.x][dp.y]==‘P‘) 30 { 31 //cout<<"钥匙"<<"x:"<<dp.x<<"y:"<<dp.y<<endl; 32 vis[dp.x][dp.y][1]=1; 33 } 34 if(mat[dp.x][dp.y]==‘T‘&&vis[dp.x][dp.y][1]) 35 { 36 //cout<<"终点:"<<dp.x<<" "<<dp.y<<endl; 37 ans=dp.step; 38 return; 39 } 40 for(int i=0; i<4; i++) 41 { 42 int nx=dp.x+dir[i][0]; 43 int ny=dp.y+dir[i][1]; 44 int nstep=dp.step+1; 45 if(nx>=0&&ny>=0&&nx<n&&ny<m&&mat[nx][ny]!=‘#‘) 46 { 47 if(!vis[dp.x][dp.y][1])//没拿到钥匙 48 { 49 if(!vis[nx][ny][0])//没拿到钥匙时未访问过 50 { 51 vis[nx][ny][0]=1; 52 q.push(point(nx,ny,nstep)); 53 } 54 } 55 else//拿到了钥匙 56 { 57 if(!vis[nx][ny][1]) 58 { 59 vis[nx][ny][1]=1; 60 q.push(point(nx,ny,nstep)); 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 int main() 68 { 69 cin>>n>>m; 70 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); 71 for(int i=0; i<n; i++) 72 { 73 cin>>mat[i]; 74 } 75 int start_x,start_y; 76 for(int i=0; i<n; i++) 77 { 78 for(int j=0; j<m; j++) 79 { 80 if(mat[i][j]==‘S‘) 81 { 82 //cout<<"起点:"<<i<<" "<<j<<endl; 83 start_x=i; 84 start_y=j; 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 dfs(point(start_x,start_y,0)); 89 cout<<ans<<endl; 90 return 0; 91 }
要点是bfs 的时候标记数组多开一维度表示是否已经取得了钥匙的状态。如果到达终点并且取得钥匙的状态被标记,bfs 结束。
以上是关于bfs的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
