I2C驱动详解
Posted 我有一壶酒
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了I2C驱动详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
I2C讲解:
在JZ2440开发板上,I2C是由两条数据线构成的SCL,SDA;SCL作为时钟总线,SDA作为数据总线;两条线上可挂载I2C设备,如:AT24C08
两条线连接ARM9 I2C控制器,通过控制来控制I2C设备的识别设备地址、读、写操作;如图所示
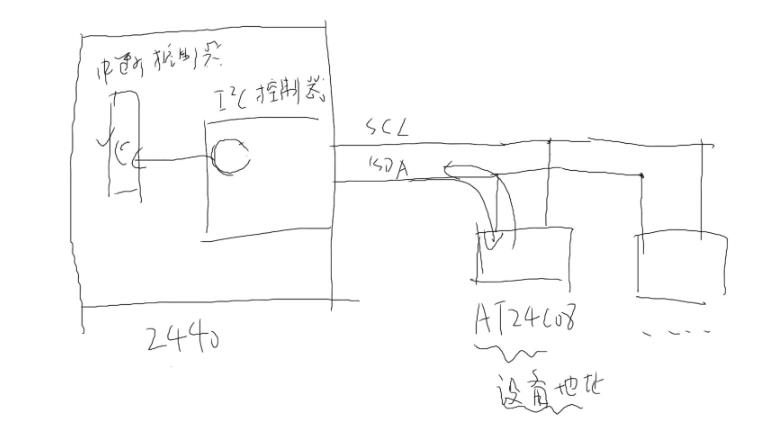
从中所知:I2C线上可以挂载很多个I2C设备;挂载简单,只需要一根数据线和一根时钟线就可以挂载上去,通过地址来去别每个设备的区别;
I2C操作:
对I2C操作主要思想为:1、找到设备 2、进行读写操作 主要原理为:
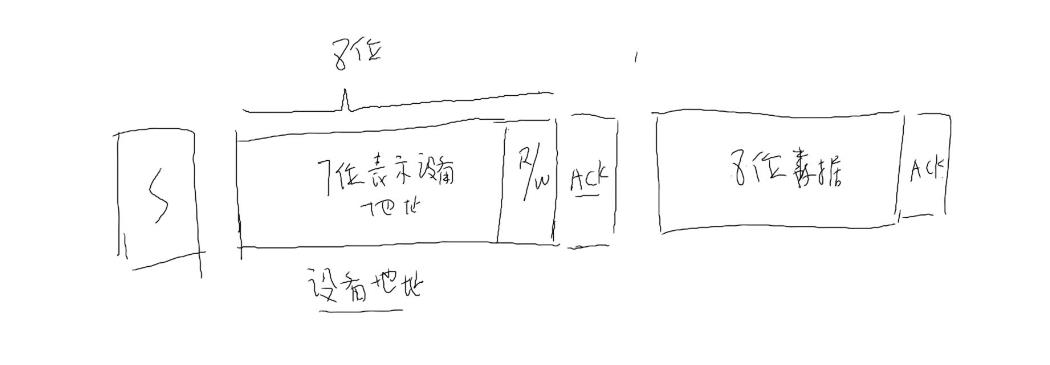
1、发送开始信号S 然后紧接着发生设备8位地址如:0x50,然后等待设备发出一个应答ACK信号
2、当控制器接收到ACK信号后,表面找到这条I2C总线上确实有这个设备,然后发出数据,是进行读还是进行写,由第8位来决定
原理如下图:
JZ2440对I2c驱动框架
正常的设备驱动程序,大体框架为:
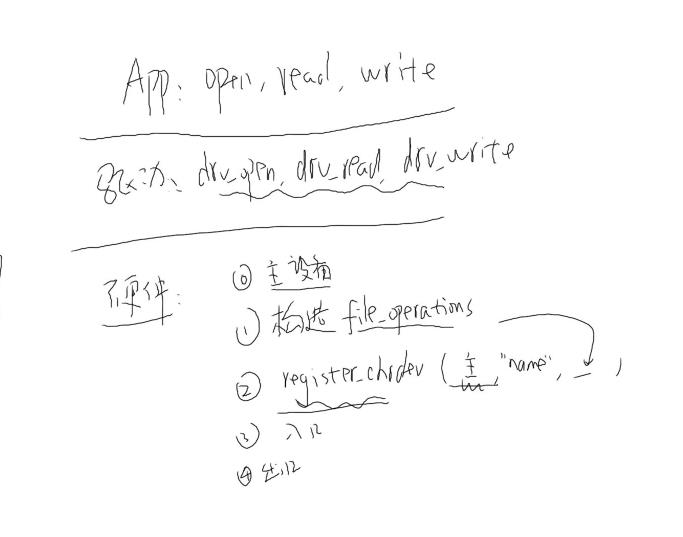
1、通过应用程序open、read、write、ioctl函数去对硬件操作
2、在内核里,接收到应用程序发送过来的open、read、write、ioctl命令,出发中断,进而会跳到一个字符描述符的数组(open时返回值)当中,查找驱动程序ID(驱动程序进行注册);通过该ID找到相对应的drv_open、drv_read、drv_wrte等操作;
3、drv_open、drv_read、drv_wrte等操作跟字符设备的硬件驱动程序紧密相关,会最终会跳到字符设备驱动程序file_operation结构体进行硬件的操作过程。
4、在此之前,需要编写I2C驱动程序,驱动程序要有主入口、出口、file_openration结构体、进行注册等操作;
具体字符设备驱动程序框架为:
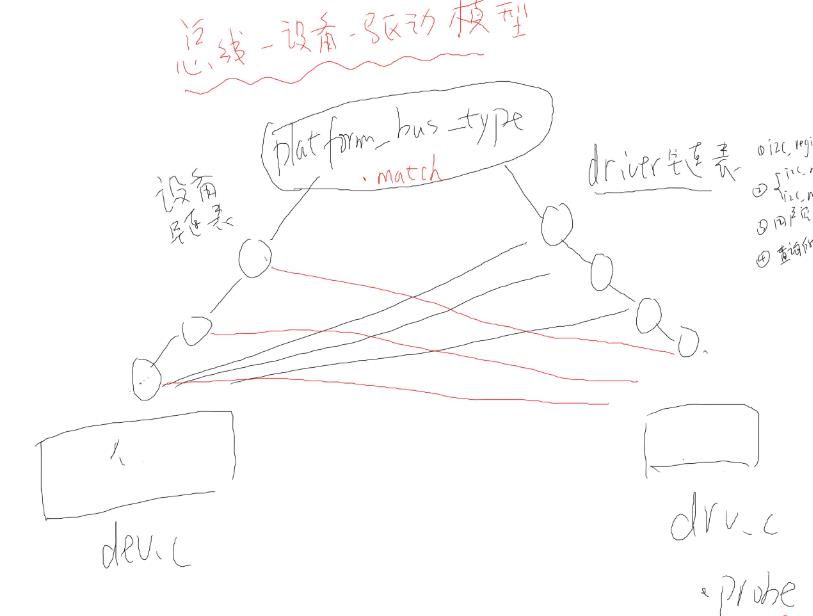
而I2C设备驱动采用的是总线—设备-驱动模型
总线-设备-驱动模型:
总线-设备-驱动模型:其原理为在一条总线上分为两部分,一部分作为设备链表对象的,另一部分作为driver链表;设备链表对象就是
注册一个设备client对象挂载到这条链表上,但注册的设备名需要与右边driver链表注册的驱动名相比配才有意义,才能对进入driver链表
上与设备名相匹配的驱动程序里面的probe函数进行i2c驱动操作;举个例子:将驱动程序比作学生,驱动程序的名字比作学生的宿舍号码
管理员相当于总线,总线知道两个信息:1、学生 2、宿舍号 ;当有一个学生进行入住,学生想住A10-208,好,经过管理员同意好,就
住进A10-208(注册一个i2c_driver)了,当管理员想找到那个学生,则需要通过A10-208这个名字去查找到学生所在住处,通过管理员
管理的学生信息本(注册一个设备)找到名字,进而去到宿舍找到这个学生,让他扫地、打扫卫生什么的;主要原理图如下:
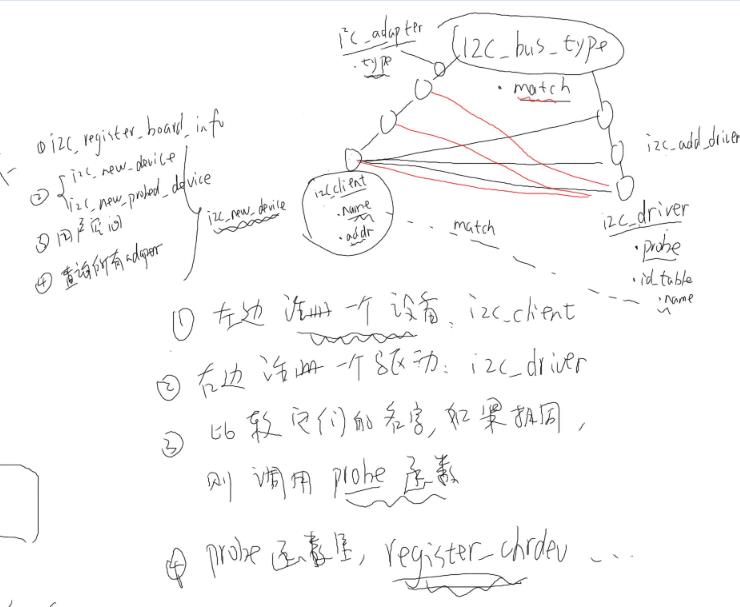
i2c-总线-驱动模型
应用程序是如何调用的呢?如图所示
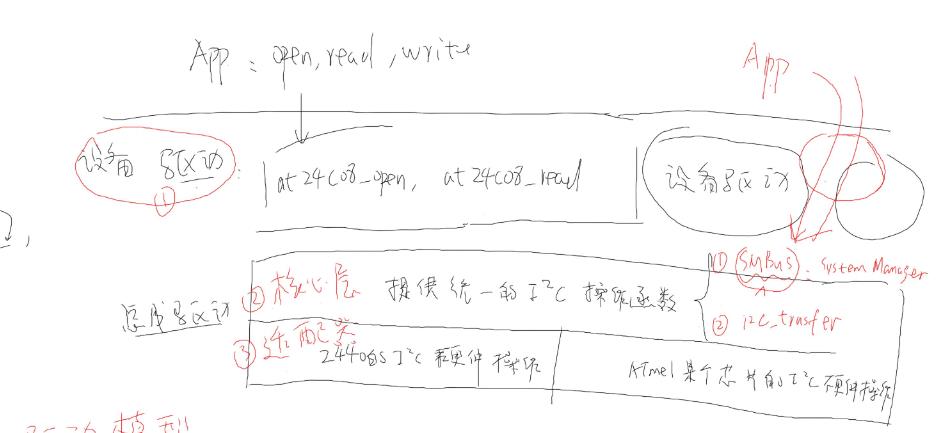
i2c进行open、read、write、ioctl等操作会进入内核太,找到相关设备驱动函数,然后就进入了总线控制层,I2c总线层两部分组成,核心层
里面已经定义了对i2c提供的操作函数,不需要用户自己定义,适配器就是具体的对2440的i2c硬件操作或者定义其它的芯片的硬件操作;
总结:总得来说,我们需要进行的操作为
1、注册一个设备,里面要有设备名,以及该设备id,并挂载到这条设备链表上
2、注册一个驱动,该设备驱动需要有设备名,probe函数、id_table设备地址,然后挂载到驱动链表上
3、比较两条链表上的设备名字是否相同,如果有相同的话,就去到相关的驱动设备上的probe函数,进行
操作
4、probe函数里面就是我们正常的驱动程序的编程程序了,主入口、出口、file_operation结构体的构造等等操作;最终应用程序会进入这里操作硬件对象
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
如图代码所示:新建一个设备有多种方法,该方法为第二种i2c_new_probed_device
at24cxx_dev:注册一个新设备
#include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <linux/i2c.h> #include <linux/err.h> #include <linux/regmap.h> #include <linux/slab.h> static struct i2c_client *at24cxx_client; static const unsigned short addr_list[] = { 0x60, 0x50, I2C_CLIENT_END }; static int at24cxx_dev_init(void) { struct i2c_adapter *i2c_adap; struct i2c_board_info at24cxx_info; memset(&at24cxx_info, 0, sizeof(struct i2c_board_info)); strlcpy(at24cxx_info.type, "at24c08", I2C_NAME_SIZE); i2c_adap = i2c_get_adapter(0); at24cxx_client = i2c_new_probed_device(i2c_adap, &at24cxx_info, addr_list, NULL); i2c_put_adapter(i2c_adap); if (at24cxx_client) return 0; else return -ENODEV; } static void at24cxx_dev_exit(void) { i2c_unregister_device(at24cxx_client); } module_init(at24cxx_dev_init); module_exit(at24cxx_dev_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
at24cxx_drv:注册一个新驱动 注:probe函数并没有进行i2c的·操作,只是打印一些信息而已
#include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <linux/i2c.h> #include <linux/err.h> #include <linux/regmap.h> #include <linux/slab.h> static int __devinit at24cxx_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id) { printk("%s %s %d\\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__); return 0; } static int __devexit at24cxx_remove(struct i2c_client *client) { printk("%s %s %d\\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__); return 0; } static const struct i2c_device_id at24cxx_id_table[] = { { "at24c08", 0 }, {} }; /* 1. 分配/设置i2c_driver */ static struct i2c_driver at24cxx_driver = { .driver = { .name = "100ask", .owner = THIS_MODULE, }, .probe = at24cxx_probe, .remove = __devexit_p(at24cxx_remove), .id_table = at24cxx_id_table, }; static int at24cxx_drv_init(void) { /* 2. 注册i2c_driver */ i2c_add_driver(&at24cxx_driver); return 0; } static void at24cxx_drv_exit(void) { i2c_del_driver(&at24cxx_driver); } module_init(at24cxx_drv_init); module_exit(at24cxx_drv_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile:
KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-3.4.2 all: make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean: make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean rm -rf modules.order obj-m += at24cxx_dev.o obj-m += at24cxx_drv.o #obj-m += i2c_bus_s3c2440.o
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
对I2c驱动的操作
前面已经讲过对于I2c的操作可以调用总线上现成的函数来操作i2c_smbus_write_byte_data
at24cxx_dev:
#include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <linux/i2c.h> #include <linux/err.h> #include <linux/regmap.h> #include <linux/slab.h> static struct i2c_board_info at24cxx_info = { I2C_BOARD_INFO("at24c08", 0x50), }; static struct i2c_client *at24cxx_client; static int at24cxx_dev_init(void) { struct i2c_adapter *i2c_adap; i2c_adap = i2c_get_adapter(0); at24cxx_client = i2c_new_device(i2c_adap, &at24cxx_info); i2c_put_adapter(i2c_adap); return 0; } static void at24cxx_dev_exit(void) { i2c_unregister_device(at24cxx_client); } module_init(at24cxx_dev_init); module_exit(at24cxx_dev_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
at24cxx_drv:注册驱动程序,进行I2c操作
#include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <linux/i2c.h> #include <linux/err.h> #include <linux/regmap.h> #include <linux/slab.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <asm/uaccess.h> static int major; static struct class *class; static struct i2c_client *at24cxx_client; /* 传入: buf[0] : addr * 输出: buf[0] : data */ static ssize_t at24cxx_read(struct file * file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *off) { unsigned char addr, data; copy_from_user(&addr, buf, 1); data = i2c_smbus_read_byte_data(at24cxx_client, addr); copy_to_user(buf, &data, 1); return 1; } /* buf[0] : addr * buf[1] : data */ static ssize_t at24cxx_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *off) { unsigned char ker_buf[2]; unsigned char addr, data; copy_from_user(ker_buf, buf, 2); addr = ker_buf[0]; data = ker_buf[1]; printk("addr = 0x%02x, data = 0x%02x\\n", addr, data); if (!i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(at24cxx_client, addr, data)) return 2; else return -EIO; } static struct file_operations at24cxx_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .read = at24cxx_read, .write = at24cxx_write, }; static int __devinit at24cxx_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id) { at24cxx_client = client; //printk("%s %s %d\\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__); major = register_chrdev(0, "at24cxx", &at24cxx_fops); class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "at24cxx"); device_create(class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "at24cxx"); /* /dev/at24cxx */ return 0; } static int __devexit at24cxx_remove(struct i2c_client *client) { //printk("%s %s %d\\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__); device_destroy(class, MKDEV(major, 0)); class_destroy(class); unregister_chrdev(major, "at24cxx"); return 0; } static const struct i2c_device_id at24cxx_id_table[] = { { "at24c08", 0 }, {} }; /* 1. 分配/设置i2c_driver */ static struct i2c_driver at24cxx_driver = { .driver = { .name = "100ask", .owner = THIS_MODULE, }, .probe = at24cxx_probe, .remove = __devexit_p(at24cxx_remove), .id_table = at24cxx_id_table, }; static int at24cxx_drv_init(void) { /* 2. 注册i2c_driver */ i2c_add_driver(&at24cxx_driver); return 0; } static void at24cxx_drv_exit(void) { i2c_del_driver(&at24cxx_driver); } module_init(at24cxx_drv_init); module_exit(at24cxx_drv_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
应用测试程序i2c_test:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> /* i2c_test r addr * i2c_test w addr val */ void print_usage(char *file) { printf("%s r addr\\n", file); printf("%s w addr val\\n", file); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int fd; unsigned char buf[2]; if ((argc != 3) && (argc != 4)) { print_usage(argv[0]); return -1; } fd = open("/dev/at24cxx", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { printf("can\'t open /dev/at24cxx\\n"); return -1; } if (strcmp(argv[1], "r") == 0) { buf[0] = strtoul(argv[2], NULL, 0); read(fd, buf, 1); printf("data: %c, %d, 0x%2x\\n", buf[0], buf[0], buf[0]); } else if ((strcmp(argv[1], "w") == 0) && (argc == 4)) { buf[0] = strtoul(argv[2], NULL, 0); buf[1] = strtoul(argv[3], NULL, 0); if (write(fd, buf, 2) != 2) printf("write err, addr = 0x%02x, data = 0x%02x\\n", buf[0], buf[1]); } else { print_usage(argv[0]); return -1; } return 0; }
Makefile:
KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-3.4.2 all: make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean: make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean rm -rf modules.order obj-m += at24cxx_dev.o obj-m += at24cxx_drv.o #obj-m += i2c_bus_s3c2440.o
以上是关于I2C驱动详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
RK3399平台开发系列讲解(I2C子系统)4.49I2C驱动详解