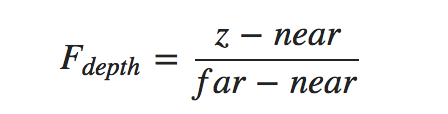OpenGL核心技术之深度测试
Posted 海洋_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了OpenGL核心技术之深度测试相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
笔者介绍:姜雪伟,IT公司技术合伙人,IT高级讲师,CSDN社区专家,特邀编辑,畅销书作者,国家专利发明人;已出版书籍:《手把手教你架构3D游戏引擎》电子工业出版社和《Unity3D实战核心技术详解》电子工业出版社等。
CSDN课程视频网址:http://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/144
深度测试在游戏引擎中使用的非常多,比如在Unity3D引擎中,在UI之间的遮挡设置可以通过其深度值进行设置,在3D场景中也会根据其Z值进行设置其前后关系。这些都会用到深度测试技术,由于Unity3D引擎是跨平台的,它在移动端的渲染使用的是OpenGL,所以后面的系列文章就介绍关于OpenGL使用的核心技术。
深度测试需要一个存储区域,这个存储区域就称为深度缓冲,它就像颜色缓冲用于存储所有的片段颜色,深度缓冲和颜色缓冲区有相同的宽度和高度。深度缓冲由窗口系统自动创建并将其深度值存储为 16、 24 或 32 位浮点数,在大多数系统中深度缓冲区为24位。
使用深度测试就必须要启用它,当深度测试启用的时候, OpenGL 测试深度缓冲区内的深度值。OpenGL 执行深度测试的时候,如果此测试通过,深度缓冲内的值将被设为新的深度值。如果深度测试失败,则丢弃该片段。深度测试在片段着色器运行之后,它是在屏幕空间中执行的。屏幕空间坐标直接有关的视区,由OpenGL的glViewport函数给定,并且可以通过GLSL的片段着色器中内置的 gl_FragCoord变量访问。gl_FragCoord 的 X 和 y 表示该片段的屏幕空间坐标 ((0,0) 在左下角)。gl_FragCoord 还包含一个 z 坐标,它包含了片段的实际深度值。此 z 坐标值是与深度缓冲区的内容进行比较的值。
深度测试默认是关闭的,要启用深度测试的话,我们需要用GL_DEPTH_TEST选项来打开它,函数如下:
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT
清除深度缓冲区,否则深度缓冲区将保留上一次进行深度测试时所写的深度值。函数如下:
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);有时,我们也不需要深度测试,那就关闭它,就是禁止缓冲区写入,函数如下:
glDepthMask(GL_FALSE);glDepthFunc
它包含很多参数:
GL_ALWAYS 永远通过测试
GL_NEVER 永远不通过测试
GL_LESS 在片段深度值小于缓冲区的深度时通过测试
GL_EQUAL 在片段深度值等于缓冲区的深度时通过测试
GL_LEQUAL 在片段深度值小于等于缓冲区的深度时通过测试
GL_GREATER 在片段深度值大于缓冲区的深度时通过测试
GL_NOTEQUAL 在片段深度值不等于缓冲区的深度时通过测试
GL_GEQUAL 在片段深度值大于等于缓冲区的深度时通过测试其中默认 使用
GL_LESS
,它的含义是这将丢弃深度值高于或等于当前深度缓冲区的值的片段。
接下来仔介绍深度值的计算,深度缓冲主要是通过计算深度值来比较大小,在深度缓冲区中包含深度值介于0.0和1.0之间,从观察者看到其内容与场景中的所有对象的 z 值进行了比较。这些视图空间中的 z 值可以在投影平头截体的近平面和远平面之间的任何值。我们因此需要一些方法来转换这些视图空间 z 值到 [0,1] 的范围内,下面的 (线性) 方程把 z 值转换为 0.0 和 1.0 之间的值 :
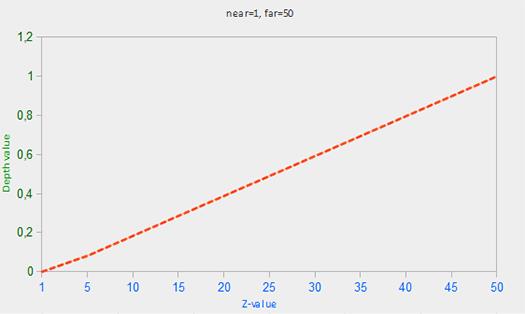
这里far和near是我们用来提供到投影矩阵设置可见视图截锥的远近值。关于这方面技术的讲解,可以查看我之前写的博客,方程带内锥截体的深度值 z,并将其转换到 [0,1] 范围。在下面的图给出 z 值和其相应的深度值的关系:
然而,在实践中是几乎从来不使用这样的线性深度缓冲区。正确的投影特性的非线性深度方程是和1/z成正比的 ,由于非线性函数是和 1/z 成正比,例如1.0 和 2.0 之间的 z 值,将变为 1.0 到 0.5之间, 这样在z非常小的时候给了我们很高的精度。方程如下所示:
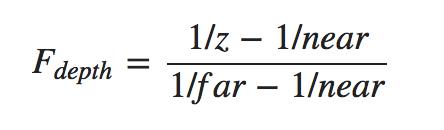
要记住的重要一点是在深度缓冲区的值不是线性的屏幕空间 (它们在视图空间投影矩阵应用之前是线性)。值为 0.5 在深度缓冲区并不意味着该对象的 z 值是投影平头截体的中间;顶点的 z 值是实际上相当接近近平面!你可以看到 z 值和产生深度缓冲区的值在下列图中的非线性关系:
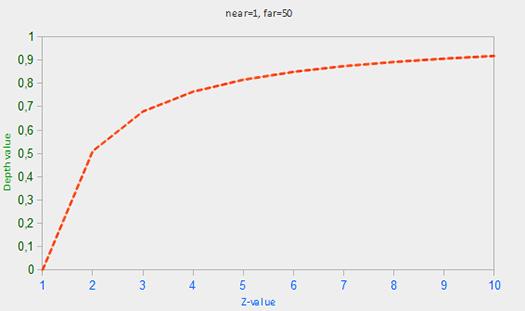
正如你所看到,一个附近的物体的小的 z 值因此给了我们很高的深度精度。变换 (从观察者的角度) 的 z 值的方程式被嵌入在投影矩阵,所以当我们变换顶点坐标从视图到裁剪,然后到非线性方程应用了的屏幕空间中。关于投影矩阵,读者可以查看之前写的博客。
屏幕空间的深度值是非线性的,这个读者可以自己测试,在这里我把原理说一下:屏幕空间的深度值是非线性如他们在z很小的时候有很高的精度,较大的 z 值有较低的精度。该片段的深度值会迅速增加,所以几乎所有顶点的深度值接近 1.0。如果我们小心的靠近物体,你最终可能会看到的色彩越来越暗,意味着它们的 z 值越来越小,这清楚地表明深度值的非线性特性。近的物体相对远的物体对的深度值比对象较大的影响。只移动几英寸就能让暗色完全变亮。
但是我们可以让深度值变换回线性。要实现这一目标我们需要让点应用投影变换逆的逆变换,成为单独的深度值的过程。这意味着我们必须首先重新变换范围 [0,1] 中的深度值为单位化的设备坐标(normalized device coordinates)范围内 [-1,1] (裁剪空间(clip space))。然后,我们想要反转非线性方程 :
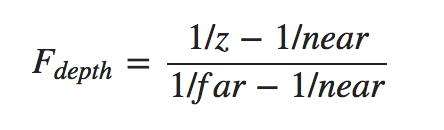
就像在投影矩阵做的那样并将此反转方程应用于所得到的深度值。然后,结果是一个线性的深度值。
首先,我们需要 NDC 深度值转换:
float z = depth * 2.0 - 1.0;
float linearDepth = (2.0 * near) / (far + near - z * (far - near));注意在转换上述方程是并不是从方程:
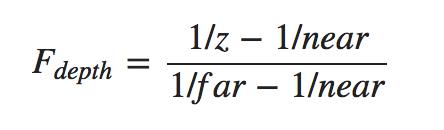
精确的逆方程,这个方程从投影矩阵中导出,可以从新使用等式2将他转换为非线性深度值。这个方程也会考虑使用[0,1] 而不是 [near,far]范围内的 z 值 。
这不是从投影矩阵推导出的准确公式;这个方程是除以far的结果。深度值的范围一直到far,这作为一个介于 0.0 和 1.0 之间的颜色值并不合适。除以far的值把深度值映射到介于 0.0 和 1.0,更适合用于演示目的。
这个能够将屏幕空间的非线性深度值转变为线性深度值的完整的片段着色器如下所示:
#version 330 core
out vec4 color;
float LinearizeDepth(float depth)
{
float near = 0.1;
float far = 100.0;
float z = depth * 2.0 - 1.0; // Back to NDC
return (2.0 * near) / (far + near - z * (far - near));
}
void main()
{
float depth = LinearizeDepth(gl_FragCoord.z);
color = vec4(vec3(depth), 1.0f);
}接下来介绍在程序中经常遇到的问题,深度冲突,就是在物体前后关系设置时会出现重叠现象,导致前后不分,在引擎中通常的做法有几种:
1、也是最重要的技巧是让物体之间不要离得太近,以至于他们的三角形重叠。
2、是尽可能把近平面设置得远一些。
3、是放弃一些性能来得到更高的深度值的精度。大多数的深度缓冲区都是24位。但现在显卡支持32位深度值,这让深度缓冲区的精度提高了一大节。所以牺牲一些性能你会得到更精确的深度测试,减少深度冲突。
最后把实现深度测试的Shader代码给读者展示一下:
首先展示的是片段着色器:
#version 330 core
out vec4 color;
float near = 1.0;
float far = 100.0;
float LinearizeDepth(float depth)
{
float z = depth * 2.0 - 1.0; // Back to NDC
return (2.0 * near * far) / (far + near - z * (far - near));
}
void main()
{
float depth = LinearizeDepth(gl_FragCoord.z) / far; // divide by far to get depth in range [0,1] for visualization purposes.
color = vec4(vec3(depth), 1.0f);
}其次展示的是顶点着色器:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;
layout (location = 1) in vec2 texCoords;
out vec2 TexCoords;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(position, 1.0f);
TexCoords = texCoords;
}下面就是处理Shader脚本的C++代码,在这里把核心代码接口展示一下,代码如下所示:
// 定义视口大小
glViewport(0, 0, screenWidth, screenHeight);
// 启用深度测试
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// glDepthFunc(GL_ALWAYS); // Set to always pass the depth test (same effect as glDisable(GL_DEPTH_TEST))
// 编译shader脚本
Shader shader("depth_testing.vs", "depth_testing.frag"); // 清空缓存
glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// 绘制物体以及传值
shader.Use();
glm::mat4 model;
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(camera.Zoom, (float)screenWidth/(float)screenHeight, 0.1f, 100.0f);
glUniformMatrix4fv(glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "view"), 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(view));
glUniformMatrix4fv(glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "projection"), 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(projection));在这里把Shader类代码展示如下:
#ifndef SHADER_H
#define SHADER_H
#include <GL/glew.h>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
class Shader
{
public:
GLuint Program;
// Constructor generates the shader on the fly
Shader(const GLchar* vertexPath, const GLchar* fragmentPath, const GLchar* geometryPath = nullptr)
{
// 1. Retrieve the vertex/fragment source code from filePath
std::string vertexCode;
std::string fragmentCode;
std::string geometryCode;
std::ifstream vShaderFile;
std::ifstream fShaderFile;
std::ifstream gShaderFile;
// ensures ifstream objects can throw exceptions:
vShaderFile.exceptions (std::ifstream::failbit | std::ifstream::badbit);
fShaderFile.exceptions (std::ifstream::failbit | std::ifstream::badbit);
gShaderFile.exceptions (std::ifstream::failbit | std::ifstream::badbit);
try
{
// Open files
vShaderFile.open(vertexPath);
fShaderFile.open(fragmentPath);
std::stringstream vShaderStream, fShaderStream;
// Read file's buffer contents into streams
vShaderStream << vShaderFile.rdbuf();
fShaderStream << fShaderFile.rdbuf();
// close file handlers
vShaderFile.close();
fShaderFile.close();
// Convert stream into string
vertexCode = vShaderStream.str();
fragmentCode = fShaderStream.str();
// If geometry shader path is present, also load a geometry shader
if(geometryPath != nullptr)
{
gShaderFile.open(geometryPath);
std::stringstream gShaderStream;
gShaderStream << gShaderFile.rdbuf();
gShaderFile.close();
geometryCode = gShaderStream.str();
}
}
catch (std::ifstream::failure e)
{
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::FILE_NOT_SUCCESFULLY_READ" << std::endl;
}
const GLchar* vShaderCode = vertexCode.c_str();
const GLchar * fShaderCode = fragmentCode.c_str();
// 2. Compile shaders
GLuint vertex, fragment;
GLint success;
GLchar infoLog[512];
// Vertex Shader
vertex = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
glShaderSource(vertex, 1, &vShaderCode, NULL);
glCompileShader(vertex);
checkCompileErrors(vertex, "VERTEX");
// Fragment Shader
fragment = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
glShaderSource(fragment, 1, &fShaderCode, NULL);
glCompileShader(fragment);
checkCompileErrors(fragment, "FRAGMENT");
// If geometry shader is given, compile geometry shader
GLuint geometry;
if(geometryPath != nullptr)
{
const GLchar * gShaderCode = geometryCode.c_str();
geometry = glCreateShader(GL_GEOMETRY_SHADER);
glShaderSource(geometry, 1, &gShaderCode, NULL);
glCompileShader(geometry);
checkCompileErrors(geometry, "GEOMETRY");
}
// Shader Program
this->Program = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(this->Program, vertex);
glAttachShader(this->Program, fragment);
if(geometryPath != nullptr)
glAttachShader(this->Program, geometry);
glLinkProgram(this->Program);
checkCompileErrors(this->Program, "PROGRAM");
// Delete the shaders as they're linked into our program now and no longer necessery
glDeleteShader(vertex);
glDeleteShader(fragment);
if(geometryPath != nullptr)
glDeleteShader(geometry);
}
// Uses the current shader
void Use() { glUseProgram(this->Program); }
private:
void checkCompileErrors(GLuint shader, std::string type)
{
GLint success;
GLchar infoLog[1024];
if(type != "PROGRAM")
{
glGetShaderiv(shader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if(!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(shader, 1024, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "| ERROR::::SHADER-COMPILATION-ERROR of type: " << type << "|\\n" << infoLog << "\\n| -- --------------------------------------------------- -- |" << std::endl;
}
}
else
{
glGetProgramiv(shader, GL_LINK_STATUS, &success);
if(!success)
{
glGetProgramInfoLog(shader, 1024, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "| ERROR::::PROGRAM-LINKING-ERROR of type: " << type << "|\\n" << infoLog << "\\n| -- --------------------------------------------------- -- |" << std::endl;
}
}
}
};
#endif另外在处理时需要用到摄像机代码,完整代码如下所示:
#pragma once
// Std. Includes
#include <vector>
// GL Includes
#include <GL/glew.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
// Defines several possible options for camera movement. Used as abstraction to stay away from window-system specific input methods
enum Camera_Movement {
FORWARD,
BACKWARD,
LEFT,
RIGHT
};
// Default camera values
const GLfloat YAW = -90.0f;
const GLfloat PITCH = 0.0f;
const GLfloat SPEED = 3.0f;
const GLfloat SENSITIVTY = 0.25f;
const GLfloat ZOOM = 45.0f;
// An abstract camera class that processes input and calculates the corresponding Eular Angles, Vectors and Matrices for use in OpenGL
class Camera
{
public:
// Camera Attributes
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Front;
glm::vec3 Up;
glm::vec3 Right;
glm::vec3 WorldUp;
// Eular Angles
GLfloat Yaw;
GLfloat Pitch;
// Camera options
GLfloat MovementSpeed;
GLfloat MouseSensitivity;
GLfloat Zoom;
// Constructor with vectors
Camera(glm::vec3 position = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3 up = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), GLfloat yaw = YAW, GLfloat pitch = PITCH) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MovementSpeed(SPEED), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
this->Position = position;
this->WorldUp = up;
this->Yaw = yaw;
this->Pitch = pitch;
this->updateCameraVectors();
}
// Constructor with scalar values
Camera(GLfloat posX, GLfloat posY, GLfloat posZ, GLfloat upX, GLfloat upY, GLfloat upZ, GLfloat yaw, GLfloat pitch) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MovementSpeed(SPEED), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
this->Position = glm::vec3(posX, posY, posZ);
this->WorldUp = glm::vec3(upX, upY, upZ);
this->Yaw = yaw;
this->Pitch = pitch;
this->updateCameraVectors();
}
// Returns the view matrix calculated using Eular Angles and the LookAt Matrix
glm::mat4 GetViewMatrix()
{
return glm::lookAt(this->Position, this->Position + this->Front, this->Up);
}
// Processes input received from any keyboard-like input system. Accepts input parameter in the form of camera defined ENUM (to abstract it from windowing systems)
void ProcessKeyboard(Camera_Movement direction, GLfloat deltaTime)
{
GLfloat velocity = this->MovementSpeed * deltaTime;
if (direction == FORWARD)
this->Position += this->Front * velocity;
if (direction == BACKWARD)
this->Position -= this->Front * velocity;
if (direction == LEFT)
this->Position -= this->Right * velocity;
if (direction == RIGHT)
this->Position += this->Right * velocity;
}
// Processes input received from a mouse input system. Expects the offset value in both the x and y direction.
void ProcessMouseMovement(GLfloat xoffset, GLfloat yoffset, GLboolean constrainPitch = true)
{
xoffset *= this->MouseSensitivity;
yoffset *= this->MouseSensitivity;
this->Yaw += xoffset;
this->Pitch += yoffset;
// Make sure that when pitch is out of bounds, screen doesn't get flipped
if (constrainPitch)
{
if (this->Pitch > 89.0f)
this->Pitch = 89.0f;
if (this->Pitch < -89.0f)
this->Pitch = -89.0f;
}
// Update Front, Right and Up Vectors using the updated Eular angles
this->updateCameraVectors();
}
// Processes input received from a mouse scroll-wheel event. Only requires input on the vertical wheel-axis
void ProcessMouseScroll(GLfloat yoffset)
{
if (this->Zoom >= 1.0f && this->Zoom <= 45.0f)
this->Zoom -= yoffset;
if (this->Zoom <= 1.0f)
this->Zoom = 1.0f;
if (this->Zoom >= 45.0f)
this->Zoom = 45.0f;
}
private:
// Calculates the front vector from the Camera's (updated) Eular Angles
void updateCameraVectors()
{
// Calculate the new Front vector
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(this->Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(this->Pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(this->Pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(this->Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(this->Pitch));
this->Front = glm::normalize(front);
// Also re-calculate the Right and Up vector
this->Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(this->Front, this->WorldUp)); // Normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
this->Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(this->Right, this->Front));
}
};以上就是关于深度测试的介绍,供参考。。。。。。。
以上是关于OpenGL核心技术之深度测试的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章