doker 1.12-runc源码逻辑跳转流程分析
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了doker 1.12-runc源码逻辑跳转流程分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
入口1–>runc处理(2)中处理-->至libcontainer处理(3)
第一步runc代码处理
checkpoint
checkpointCommand(main.go) —> checkpointCommand(checkpoint.go)
container
createCommand(main.go)—>createCommand(create.go)—>startContainer(untils_linux.go)—>run(untils_linux.go)
deleteCommand(main.go)—>deleteCommand(delete.go)—>destroy(untils_linux.go)
eventsCommand(main.go)—>eventsCommand(events.go)
execCommand(main.go)—>execCommand(exec.go)—>execProcess(exec.go)->run(untils_linux.go)
initCommand(main.go)—>initCommand(main_unix.go)
killCommand(main.go)—>killCommand(kill.go)
listCommand(main.go)—>getContainers(list.go)
pauseCommand(main.go) —>pauseCommand(pause.go)
psCommand(main.go)—>psCommand(ps.go)
restoreCommand(main.go)—>restoreCommand(restore.go)—>restoreContainer(restore.go)
resumeCommand(main.go)—>resumeCommand(pause.go)
runCommand(main.go)—>runCommand(run.go)—>startContainer(untils_linux.go)
specCommand(main.go)—>specCommand(spec.go) end
startCommand(main.go)—>startCommand(start.go)
stateCommand(main.go)—>stateCommand(state.go)
updateCommand(main.go)—>updateCommand(update.go)
第二步从runc代码处理至libcontainer处理
checkpoint
checkpointCommand(checkpoint.go) —>Checkpoint(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
container
run(untils_linux.go)—>Run(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
destroy(untils_linux.go)—>Destroy(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
eventsCommand(events.go)—>Status(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
execProcess(exec.go)—>Status\Stopped\State(libcontainer/container_linux.go) || run(untils_linux.go)—>Start\Run\Destroy(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
initCommand(main_unix.go)—>StartInitialization(libcontainer/factory_linux.go)
killCommand(kill.go)—>Signal(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
getContainers(list.go)—>Status\State\Stopped(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
pauseCommand(pause.go)—>Pause(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
psCommand(ps.go)—>exec.Command("ps", psArgs...).Output()
restoreContainer(restore.go)—>Restore(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
resumeCommand(pause.go)—>Resume(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
startContainer(untils_linux.go)—>Run(libcontainer/factory.go)
startCommand(start.go)—>Exec(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
stateCommand(state.go)—>State(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
updateCommand(update.go)—>Set(libcontainer/container_linux.go)
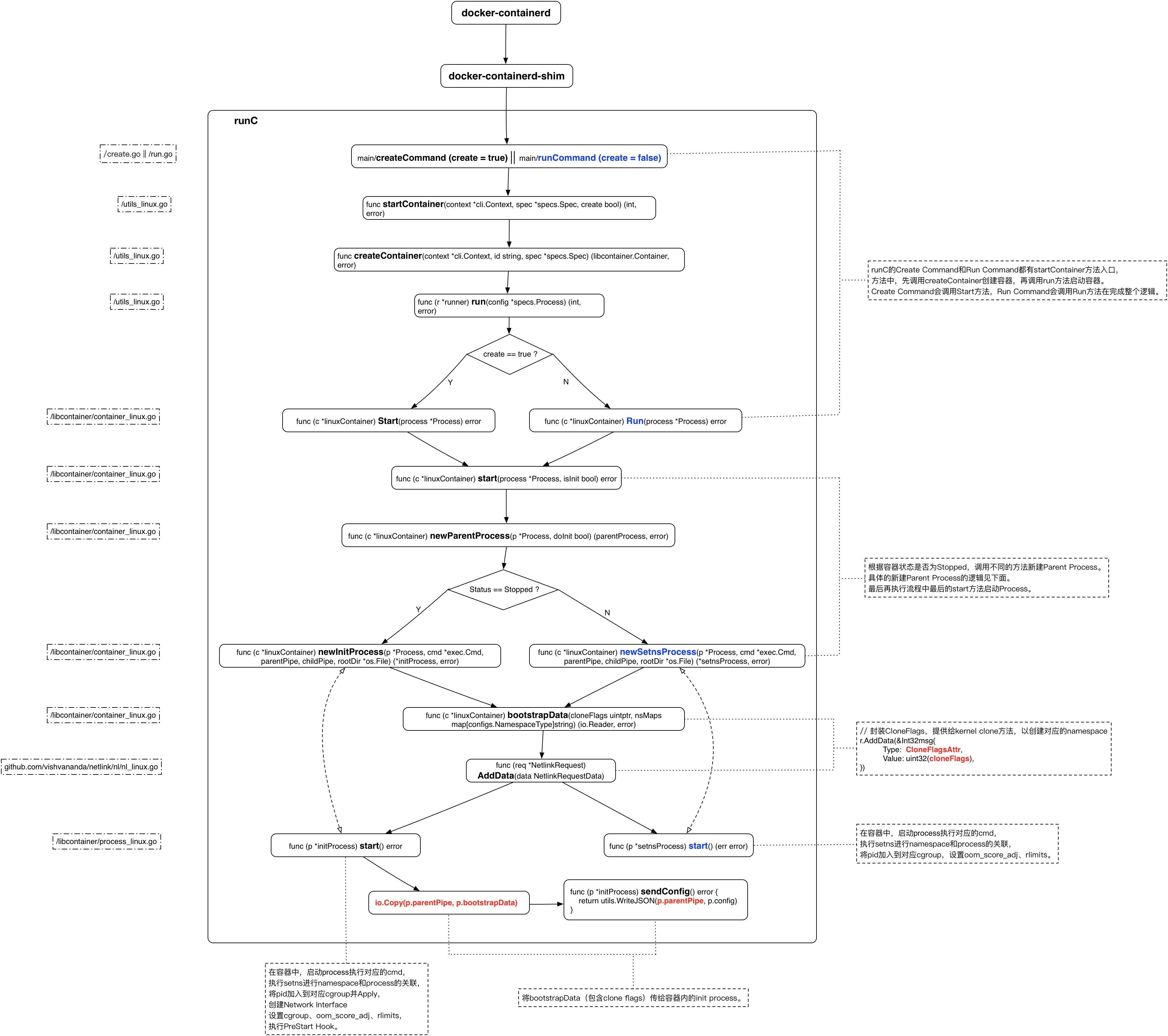
runC源码的核心部分——Create Command & Run Command 进行源码分析。
说明点:
runC create command 和 run command的流程入口统一从/runc/utils_linux.go#334 main.startContainer方法,通过create flag进行区分。
业务逻辑中,主要有两个step构成:
firstly create container filesystem and construct a linuxcontainer object by creatContainer function.
secondly start process in container by runner.run function.
主要的逻辑在process的启动过程,注意以下几点:
对于namespace的隔离,主要通过bootstrapData封装好clone flags。
由sendconfig将bootstrapData封装的config传给容器起的init process。
调用系统setns进行namespace和process 的associate。
cgroup的管理由cgroups.Manager interface进行操作,具体由各个cgroup subsystem各自实现该interface。
oom_score_adj and rlimits等都在这里完成设置。
本文出自 “虫子” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://bingdian.blog.51cto.com/94171/1893657
以上是关于doker 1.12-runc源码逻辑跳转流程分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章