深入理解Magento - 第六章 - 高级Magento模型
Posted ec04
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深入理解Magento - 第六章 - 高级Magento模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我们讲过Magento有两种模型,简单模型和EAV(Entity Attribute Value)模型。上一章我们讲过所有的Magento模型都是继承自Mage_Core_Model_Abstract / Varien_Object。简单模型和EAV模型的区别在于资源模型(Model Resource)。虽然所有的资源模型都最终继承“Mage_Core_Model_Resrouce_Abstract”,但是简单模型是直接继承“Mage_Core_Model_mysql4_Abstract”,而EAV模型是直接继承“Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Abstract”。
Magento这么做是由它的道理的。对于大部分开发人员或者用户来说,他们只需要知道一系列的方法能够操作模型,获得数据,数据到底是如何存储的并不是很重要。
什么是EAV模型?
Wikipedia是这么定义的:
EAV(Entity-Attribute-Value)模型,也作Object-Attribute-Value模型或者开放模型是一种数据模型。这种数据模型常常用在一个对象的属性数目不是一定的情况下。在数学上,这种模型称为松散矩阵。
换一种方式理解,EAV模型就是数据表的一种泛化。在传统的数据库中,数据表的列的数量是一定的
+——————+
| products |
+——————+
| product_id |
| name |
| price |
| etc.. |
+——————+
+————+—————-+——————+———+
| product_id | name | price | etc… |
+————+—————-+——————+———+
| 1 | Widget A | 11.34 | etc… |
+————+—————-+——————+———+
| 2 | Dongle B | 6.34 | etc… |
+————+—————-+——————+———+
在上面这张表中,每一个商品都有名称,价格等等。
在EAV模型中,每一个模型都有不同的属性。这对于电子商务的应用来说是很合适的。比如说一个网店可以卖笔记本,拥有CPU速度,颜色,内存等属性,但是网店也可以卖衣服,有颜色属性,但是没有CPU速度。即使是卖衣服的网店,也有上衣和裤子之分,它们的属性也是不一样的。
有很多开源的或者商业的数据库是默认使用EAV模型的。但是一般的网站托管平台不提供这些数据库。所以Varien开发了一套基于php和MySQL的EAV系统。换句话说,它们在传统的关系型数据库上面开发了一套EAV数据库系统。
在使用的时候,EAV模型的属性是会分布在不同的MySQL数据表中。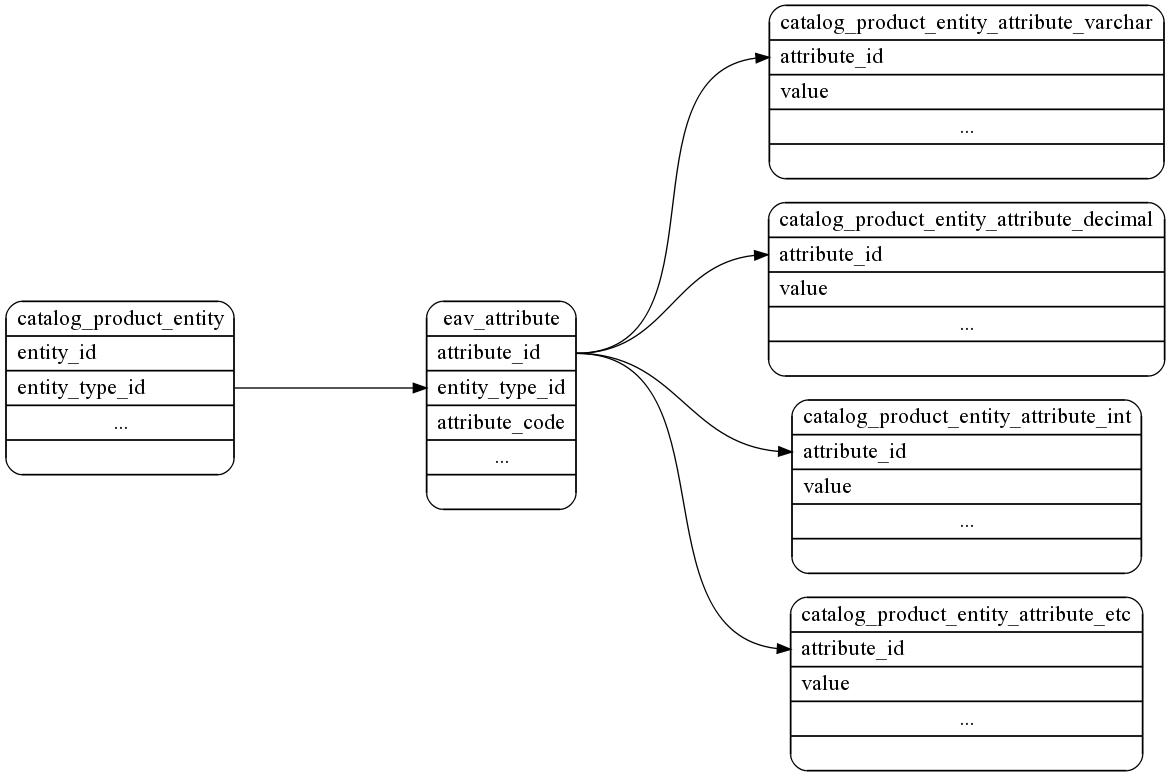
上面的这张图是Magento中关于“catalog_product”的表。每一个产品都是“catalog_product_entity”中的一行。Magento系统中所有的属性(不仅仅是商品)都存放在“eav_attribute”表中,而属性的值都放在类似下面的表中“catalog_product_entity_attribute_varchar”, “catalog_product_entity_attribute_decimal”, “catalog_product_entity_attribute_etc”。【译者注:如果你仔细观察上面这幅数据表结构图,你会发现明显少了一张表,和“entity_type”有关。因为这里有“entity_type_id”出现,但却没有定义这个属性的表。这个表在Magneto中叫做“eav_entity_type”。由于EAV模型中所有的模型数据都混在一套数据表中了,实体类型(entity_type)就是用来把不同的模型区别开来的属性。假如我们要找出系统中所有的产品数据,那么Magento先通过“eav_entity_type”表获得产品模型的“entity_type_id”,然后再通过上面这幅图的关系来拿到所有的数据。】
在EAV系统下面,当你需要添加一个属性的时候,只需要在“eav_attribute”表中添加一行就行了。而传统的关系型数据库则需要修改数据表调用“ALTER TABLE”语句,复杂而且有风险。EAV模型的缺点是你不能通过一个简单的SQL语句就获得一个模型的所有属性。你往往需要调用多个SQL或者一个SQL包干了多个join语句。
实战EAV模型
我们已经介绍了EAV是怎么工作的了。下面我们要通过一个例子来说明要在Magento中创建一个EAV模型所需要的步骤。这部分内容大概是Magento中最令人头疼的部分,95%的Magento用户都不会和这些代码打交道,但是理解EAV模型的原理能够帮助你更好的理解Magento的代码和架构。
因为EAV模型的内容太多了,所以我假设你已经熟悉了前几章的内容,包括Magento MVC,组类名等等。在这一章我不会再重复这些内容。
EAV形式的Hello World
我们将为Hello World模块创建另外一个模型,使用EAV形式的资源模型。首先我们为模块创建一个新的模型叫做“Eavblogpost”。记住,简单模型和EAV模型的区别是资源模型,所以我们创建一个模型的基本步骤是一样的。
<global>
<!– … –>
<models>
<!– … –>
<helloworld-eav>
<class>Zhlmmc_Helloworld_Model</class>
<resourceModel>helloworld-eav_mysql4</resourceModel>
</helloworld-eav>
<!– … –>
</models>
<!– … –>
</global>
我想我不说你也应该知道,我们要创建一个新的模型文件。由于PHP 5.3和命名空间(namespaces)还没有被广泛采用,Magento中的类名仍然和文件的物理路径相关。这就导致了很多时候不知道一个URI所对应的类究竟该放在什么文件夹下面。我发现我们可以利用Magento的异常信息来直接得到一个类的路径。比如,这里我们先不创建模型类,先来修改BlogController来直接使用模型类,这样Magento就会报错说找不到模型类,并给出路径
public function eavReadAction(){
$eavModel = Mage::getModel(\'helloworld-eav/eavblogpost\');
echo get_class($eavModel)."<br/>";
}
清空Magento缓存,访问以下URL
http://127.0.0.1/Magento/helloworld/blog/eavRead
跟预计的一样,你应该得到以下异常
Warning: include(Zhlmmc/Helloworld/Model/Eavblogpost.php) [function.include]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory
所以我们应该创建如下文件
File: app/code/local/Zhlmmc/Helloworld/Model/Eavblogpost.php
class Zhlmmc_Helloworld_Model_Eavblogpost extends Mage_Core_Model_Abstract
{
protected function _construct()
{
$this->_init(\'helloworld-eav/blogpost\');
}
}
刷新页面,你应该看到下面的输出
Zhlmmc_Helloworld_Model_Eavblogpost
下面我们来创建资源模型。先定义资源模型
<helloworld-eav_mysql4>
<class>Zhlmmc_Helloworld_Model_Resource_Eav_Mysql4</class>
<entities>
<blogpost>
<table>eavblog_posts</table>
</blogpost>
</entities>
</helloworld-eav_mysql4>
这里的标签名字和我们上面定义的模型的是一致的。的定义和上一章是一样的。下面的适配器的定义
<resources>
< !– … ->
<helloworld-eav_write>
<connection>
<use>default_write</use>
</connection>
</helloworld-eav_write>
<helloworld-eav_read>
<connection>
<use>default_read</use>
</connection>
</helloworld-eav_read>
</resources>
然后再次利用Magento的异常,先修改“eavReadAction”
public function eavReadAction(){
$eavModel = Mage::getModel(\'helloworld-eav/eavblogpost\');
$params = $this->getRequest()->getParams();
echo("Loading the blogpost with an ID of ".$params[\'id\']."<br />");
$eavModel->load($params[\'id\']);
$data = $eavModel->getData();
var_dump($data);
}
清空Magento缓存,访问URL
http://127.0.0.1/Magento/helloworld/blog/eavRead/id/1
你应该看到如下异常
Warning: include(Wemvc/Helloworld/Model/Resource/Eav/Mysql4/Blogpost.php) [function.include]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory
所以我们创建相应的资源模型类
File: app/code/local/Wemvc/Helloworld/Model/Resource/Eav/Mysql4/Blogpost.php
class Wemvc_Helloworld_Model_Resource_Eav_Mysql4_Blogpost extends Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Abstract
{
public function _construct()
{
$resource = Mage::getSingleton(\'core/resource\');
$this->setType(\'helloworld_eavblogpost\');
$this->setConnection(
$resource->getConnection(\'helloworld-eav_read\'),
$resource->getConnection(\'helloworld-eav_write\')
);
}
}
这个类和简单的资源模型就不一样。首先,我们这里继承的是“Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Abstract”。其次,我们没有调用“_init”方法。在EAV模型中我们需要自己来完成资源模型初始化的过程,包括,告诉资源模型使用哪个适配器,以及实体类型(entity_type)。刷新URL,你应该看到如下异常
Invalid entity_type specified: helloworld_eavblogpost
根据我们上文所讲的内容,那这个异常的原因很明显,那就是“eav_entity_type”表中,没有需要的“helloworld_eavblogpost”的数据。这里的“helloworld_eavblogpost”就是我们“setType”的参数。让我们来看一下这张表长什么样
mysql> select * from eav_entity_type\\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
entity_type_id: 1
entity_type_code: customer
entity_model: customer/customer
attribute_model:
entity_table: customer/entity
value_table_prefix:
entity_id_field:
is_data_sharing: 1
data_sharing_key: default
default_attribute_set_id: 1
increment_model: eav/entity_increment_numeric
increment_per_store: 0
increment_pad_length: 8
increment_pad_char: 0
additional_attribute_table: customer/eav_attribute
entity_attribute_collection: customer/attribute_collection
*************************** 2. row ***************************
entity_type_id: 2
entity_type_code: customer_address
entity_model: customer/customer_address
attribute_model:
entity_table: customer/address_entity
value_table_prefix:
entity_id_field:
is_data_sharing: 1
data_sharing_key: default
default_attribute_set_id: 2
increment_model:
increment_per_store: 0
increment_pad_length: 8
increment_pad_char: 0
additional_attribute_table: customer/eav_attribute
entity_attribute_collection: customer/attribute_collection
正如我们前面讲过的,这张表包含了所有系统中的实体类型。我们的参数“helloworld_eavblogpost”就是实体类型的值,对应数据表列“entity_type_code”。
系统和应用程序
这一章讲的内容是Magento最重要的一个概念,也是很多人觉得头疼的概念。拿电脑来做比方,操作系统,比如Mac OS X,Windows,Linux等等,是软件系统,而浏览器,比如Firefox,Safari,IE等等是应用程序。Magento首先是一个系统,其次才是一个应用程序。你可以在Magento系统之上创建一个电子商务应用。令人感到困惑的是Magento的代码在很多地方是以很原始的方式暴露给应用程序的。EAV系统的配置和你网店的数据存放在统一数据库中就是一个例子。
随着你越来越深入Magento,你需要把Magento当作老式的 IBM 650 机器。也就是说,你必须对Magento有很深的了解才能对它运用自如。【译者注:这一段和上下文没什么关系,大概是作者有感而发】
创建资源配置
从理论上讲,你可以手动的在数据库中插入数据,让我们的EAV模型工作,但我还是不建议你这么做。所幸的是,Magento提供了一个特殊的资源配置类,包含了一些有用的方法能自动的创建一些数据,使得系统能工作。
我们先添加资源配置
<resources>
< !– … –>
<helloworld-eav_setup>
<setup>
<module>Wemvc_Helloworld</module>
<class>Wemvc_Helloworld_Model_Entity_Setup</class>
</setup>
<connection>
<use>core_setup</use>
</connection>
</helloworld-eav_setup>
< !– … –>
</resources>
创建资源配置类文件
File: app/code/local/Wemvc/Helloworld/Model/Entity/Setup.php
class Wemvc_Helloworld_Model_Entity_Setup extends Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Setup {
}
请注意,这里我们继承的父类是“Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Setup”。最后,我们来创建安装脚本。如果你不熟悉这部分内容,请你参考前面章节的内容。
File: app/code/local/Wemvc/Helloworld/sql/helloworld-eav_setup/mysql4-install-0.1.0.php
< ?php
$installer = $this;
throw new Exception("This is an exception to stop the installer from completing");
?>
清空Magento缓存,访问任何页面,你应该看到以上异常。如果你没有看到异常,那说明你哪里配置错了。
请注意:我们将一步一步的创建安装脚本。如果你阅读了前面的章节,你应该知道我们必须删除“core_resource”数据表中的相应数据才能使得安装脚本重新运行。所以在我们下面的例子中,当我们修改了安装脚本,我们都默认会删除“core_resource”表中的数据。正常使用Magento的时候我们不需要这样做的,教程中的例子是极端情况。
添加实体类型
首先我们修改安装脚本如下
$installer = $this;
$installer->addEntityType(\'helloworld_eavblogpost\',Array(
//entity_mode is the URL you\'d pass into a Mage::getModel() call
\'entity_model\' =>\'helloworld-eav/eavblogpost\',
//blank for now
\'attribute_model\' =>\'\',
//table refers to the resource URI helloworld-eav/blogpost
//<helloworld -eav_mysql4>…<blogpost><table>eavblog_posts</table>
\'table\' =>\'helloworld-eav/blogpost\',
//blank for now, but can also be eav/entity_increment_numeric
\'increment_model\' =>\'\',
//appears that this needs to be/can be above "1" if we\'re using eav/entity_increment_numeric
\'increment_per_store\' =>\'0\'
));
我们调用了资源配置对象的“addEntityType”方法。这个方法的参数是实体类型(helloworld_eavblogpost)还有和这个类型相关的参数。当你运行这个脚本以后,你会发现“eav_attribute_group”,“eav_attributeset”还有“eav_entity_type”数据表中有了新的数据。访问以下URL
http://127.0.0.1/Magento/helloworld/blog/eavRead/id/1
你应该看到以下异常
SQLSTATE[42S02]: Base table or view not found: 1146 Table \'eavblog_posts\' doesn\'t exist
创建数据表
我们已经告诉Magento我们的实体类型。接下来,我们要创建用来存储数据的数据表,并配置系统让Magento知道我们要用这些表。
如果你研究过Magento核心模块的资源配置脚本的话,比如core/Mage/CatalogInventory的配置脚本,你会看到很多用来创建数据表的SQL语句。所幸的是,我们已经不必要这样做了。Magento提供的资源配置类有一个方法“createEntityTables”。我们可以用这个方法来创建我们需要的数据表。同时这个方法也会在Magento的系统数据表中添加相应的配置数据。
$installer->createEntityTables(
$this->getTable(\'helloworld-eav/blogpost\')
);
“createEntityTables”有两个参数。第一个参数是基础表名(base table name)。第二个参数是一系列选项。我们这里忽略了第二个参数,这些参数都是一些高级配置,超出了我们讨论的范围。在运行了上述脚本以后,你会发现数据库中添加了如下数据表
eavblog_posts
eavblog_posts_datetime
eavblog_posts_decimal
eavblog_posts_int
eavblog_posts_text
eavblog_posts_varchar
同时,你会发现在“eav_attribute_set”表中多了一条数据
mysql> select * from eav_attribute_set order by attribute_set_id DESC LIMIT 1 \\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
attribute_set_id: 63
entity_type_id: 31
attribute_set_name: Default
sort_order: 3
清空Magento缓存,重新访问如下URL
http://127.0.0.1/Magento/helloworld/blog/eavRead/id/1
你应该看到以下输出
Loading the blogpost with an ID of 1
array(0) { }
添加属性
创建资源配置的最后一步是告诉Magento我们的模型有哪些属性。这就和为单独的数据表添加列是一样的。【注:我们上面的输出是空的就是因为我们虽然创建了EAV数据表,但是却没有创建EAV属性,就像创建了一张没有任何列的数据表,当然是空的。】和上面的步骤一样,Magento的资源配置类提供了相应的帮助函数,“installEntities”和“getDefaultEntities”。
我们之前所做的是告诉Magento,我们创建了一个实体类型(Entity Type),而现在,我们要配置这个实体类型使它能够和我们的模型相符合。这个方法名字有点搞“installEntities”,其实我们要做的是配置这个实体。修改类“Wemvc_Helloworld_Model_Setup_Entity_Setup”
class Wemvc_Helloworld_Model_Setup_Entity_Setup extends Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Setup {
<?php
class Wemvc_Helloworld_Model_Entity_Setup extends Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Setup {
public function getDefaultEntities()
{
return array (
\'helloworld_eavblogpost\' => array(
\'entity_model\' => \'helloworld-eav/eavblogpost\',
\'attribute_model\' => \'\',
\'table\' => \'helloworld-eav/blogpost\',
\'attributes\' => array(
\'title\' => array(
//the EAV attribute type, NOT a mysql varchar
\'type\' => \'varchar\',
\'backend\' => \'\',
\'frontend\' => \'\',
\'label\' => \'Title\',
\'input\' => \'text\',
\'class\' => \'\',
\'source\' => \'\',
// store scope == 0
// global scope == 1
// website scope == 2
\'global\' => 0,
\'visible\' => true,
\'required\' => true,
\'user_defined\' => true,
\'default\' => \'\',
\'searchable\' => false,
\'filterable\' => false,
\'comparable\' => false,
\'visible_on_front\' => false,
\'unique\' => false,
),
\'post\' => array(
//the EAV attribute type, NOT a mysql varchar
\'type\' => \'text\',
\'backend\' => \'\',
\'frontend\' => \'\',
\'label\' => \'Post\',
\'input\' => \'text\',
\'class\' => \'\',
\'source\' => \'\',
// store scope == 0
// global scope == 1
// website scope == 2
\'global\' => 0,
\'visible\' => true,
\'required\' => true,
\'user_defined\' => true,
\'default\' => \'\',
\'searchable\' => false,
\'filterable\' => false,
\'comparable\' => false,
\'visible_on_front\' => false,
\'unique\' => false,
),
),
)
);
}
}
这里我们构建了一个数组,数组的元素是“key/value”对。“key”就是实体类型的名字(以下代码参数是一样的“$installer->addEntityType(‘helloworld_eavblogpost’,…)”),“value”是一个数组,用来描述这个实体类型。“value”数组的元素大部分你应该都见过,就不多解释了。这里要关注的是“attribute”元素,这个元素的值又是一个数组。这个数组的内容就是我们定义的实体类型的属性,相当于普通数据表的列,比如这里的“title”。很可惜,我无法完整解释用来描述一个属性的数组的内容。在这里,我们只要知道“type”就是这个属性的数据类型“varchar”。也就是说,这个属性的值将会被保存到“eavblog_posts_varchar”数据表中。其他的很多元素都是和Magento的后台管理有关。Magento很多地方的UI是由模型控制的,很多这些参数都是用来控制UI显示和系统设置。这样做的优点是灵活性提高,但是缺点是这些内容对于外部开发者都是不透明的。【译者注:我们是可以在这个函数中返回多个实体类型的。如果返回多个实体类型,那就说明模块拥有多个模型。】
顺便说一下,Magento选择使用数组嵌套数组的形式来表示实体类型的属性很奇怪。因为Magento整个架构是非常面向对象的。这里的数据结构和系统的其他部分很不一样。
接下来我们需要修改安装脚本,添加如下代码
$installer->installEntities();
“installEntities”会调用“getDefaultEntities”方法来获取将要被配置的属性。当然你也可以把属性直接作为参数传给“installEntities”,但是我觉得还是按照Magento的习惯来比较好。在调用“installEntitis”以后,Magento会做下面两件事
- 在“eav_attribute”表中添加“title”属性
- 在“eav_entity_attribute”表中添加一行
清空Magento缓存,刷新页面,你应该看到如下异常
SQLSTATE[23000]: Integrity constraint violation: 1217 Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails
那是因为我们之前已经调用过一次“createEntityTables”,再次调用的时候Magento会尝试先删除数据表,然后再创建。但是删除的时候Magento没有考虑到外键的关系,先尝试删除了主表,所以就有了以上异常。为了简化教程的例子,我们暂时把“createEntityTables”语句删了。再次刷新页面,你应该看到正常的输出。
给EAV模型添加数据
到这里为止,我们的EAV模型已经创建好了,下面我们来为模型添加一些数据。在BlogController中添加以下方法
public function eavPopulateEntriesAction() {
for($i=0;$i<10;$i++) {
$weblog2 = Mage::getModel(\'helloworld-eav/eavblogpost\');
$weblog2->setTitle(\'This is a test \'.$i);
$weblog2->save();
}
echo \'Done\';
}
public function eavShowcollectionAction() {
$weblog2 = Mage::getModel(\'helloworld-eav/eavblogpost\');
$entries = $weblog2->getCollection()->addAttributeToSelect(\'title\');
$entries->load();
foreach($entries as $entry)
{
// var_dump($entry->getData());
echo \'<h1>\'.$entry->getTitle().\'</h1>\';
}
echo \'<br />Done<br />\';
}
记得添加模型集合
class Wemvc_Helloworld_Model_Resource_Eav_Mysql4_Blogpost_Collection extends Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Collection_Abstract
{
protected function _construct()
{
$this->_init(\'helloworld-eav/eavblogpost\', \'helloworld-eav/blogpost\');
}
}
访问以下URL
http://127.0.0.1/Magento/helloworld/blog/eavPopulateEntries
你应该看到正确的输出。细心一点的话你应该发现这里有两点比较特殊。第一,“$weblog2->getCollection()->addAttributeToSelect(‘title’)”,这里的“title”是干什么的?因为EAV模型在数据库层面比较复杂,一个简单的查询都需要好多个SQL才能完成。所以在查询的时候你需要指明你想找什么,这样可以节省系统资源。不过你也可以传入“*”,表示查找所有数据。第二,为什么“$this->_init”有两个参数?在我们以前的章节中,简单模型的模型集合初始化的时候只需要传入模型的URI就可以了,为什么这里要两个参数呢?其实如果你仔细看了模型集合抽象类的代码的话,你会发现这样一段
if (is_null($resourceModel)) {
$resourceModel = $model;
}
所以其实是需要模型的URI和资源模型的URI,但是由于我们前面章节的例子,这两个URI是一样的,所以省略了第二个参数。而这里,资源模型的URI和模型的URI是不一样的,所以不能省略。
总结
到这里,你应该对Magento整个系统的运作有所了解了。起码下一次你看到网店里面的某个商品部显示了,或者什么属性不对了,你知道去哪里找问题。除了本章介绍的内容以外EAV模型还有很多东西可以学习。下面是我打算在以后的文章中介绍的一些内容
- EAV属性:EAV模型的属性类型不局限于datatime, decimal, int, text和varchar。你可以创建自定义的数据类型。
- 集合筛选:对EAV模型的数据进行筛选不是看起来的那么简单,特别是当属性是自定义类型的情况下,我们需要在集合装载之前调用“addAttributeToFilter”方法。
- Magento EAV模型继承:Magento在基本的EAV模型之上又创建了模型的继承关系,这些继承关系可以和网店的功能直接相关,也可以优化EAV模型的查询。
毫无疑问,EAV模型是Magento系统中最复杂的部分。不过你要始终相信一点,不管多复杂,它也就是程序。从哲学角度来讲,任何事物的产生都有特定的理由,你只需要搞清楚为什么。
以上是关于深入理解Magento - 第六章 - 高级Magento模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章