OpenCV示例学习笔记-contours2.cpp-通过findContours 函数实现轮廓提取
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了OpenCV示例学习笔记-contours2.cpp-通过findContours 函数实现轮廓提取相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这个系列的目的是通过对OpenCV示例,进一步了解OpenCV函数的使用,不涉及具体原理。
示例代码地址:http://docs.opencv.org/3.0.0/examples.html(安装openCV时可框选)
目录
简介
Example运行截图
Example分析
Example代码
简介
本文记录了对OpenCV示例contours2.cpp的分析。这个示例主要演示了如何使用findContours 对图像进行轮廓检测。
示例涉及到findContours ,approxPolyDP,drawContours,createTrackbar,和on_trackbar等四个函数的使用;
1.findContours函数轮廓检测函数原型:void findContours(InputOutputArray image, OutputArrayOfArrays contours, OutputArray hierarchy, int mode, int method, Point offset=Point());参数说明:
image:输入图像必须为一个2值单通道图像
contours:检测的轮廓数组,每一个轮廓用一个point类型的vector表示
hiararchy:和轮廓个数相同,每个轮廓contours[ i ]对应4个hierarchy元素hierarchy[ i ]
[0 ] ~hierarchy[ i ][ 3 ],分别表示后一个轮廓、前一个轮廓、父轮廓、内
嵌轮廓的索引编号,如果没有对应项,该值设置为负数。
mode:表示轮廓的检索模式
RETR_EXTERNAL表示只检测外轮廓
RETR_LIST检测的轮廓不建立等级关系
RETR_CCOMP建立两个等级的轮廓,上面的一层为外边界,里面的一层为内孔的边 界信息。如果内孔内还有一个连通物体,这个物体的边界也在顶层。
RETR_TREE建立一个等级树结构的轮廓。具体参考contours.c这个demo
method:为轮廓的近似办法
CHAIN_APPROX_NONE存储所有的轮廓点,相邻的两个点的像素位置差不超过1,即max(abs(x1-x2),abs(y2-y1))==1
CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE压缩水平方向,垂直方向,对角线方向的元素,只保留该方向的终点坐标,例如一个矩形轮廓只需4个点来保存轮廓信息
CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,CV_CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS使用teh-Chinl chain 近似算法
offset:代表轮廓点的偏移量,可以设置为任意值。对ROI图像中找出的轮廓,并要在整个图像中进行分析时,这个参数还是很有用的。
CHAIN_APPROX_NONE存储所有的轮廓点,相邻的两个点的像素位置差不超过1,即max(abs(x1-x2),abs(y2-y1))==1
CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE压缩水平方向,垂直方向,对角线方向的元素,只保留该方向的终点坐标,例如一个矩形轮廓只需4个点来保存轮廓信息
CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,CV_CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS使用teh-Chinl chain 近似算法
offset:代表轮廓点的偏移量,可以设置为任意值。对ROI图像中找出的轮廓,并要在整个图像中进行分析时,这个参数还是很有用的。
PS:findContours后会对输入的2值图像改变,所以如果不想改变该2值图像,需创建新mat来存放。
以上描述摘至参考资料3
函数原型:
OutputArray approxCurve:输出的点集,当前点集是能最小包容指定点集的。draw出来即是一个多边形;
double epsilon:指定的精度,也即是原始曲线与近似曲线之间的最大距离。
bool closed:若为true,则说明近似曲线是闭合的,它的首位都是相连,反之,若为false,则断开。
2.approxPolyDP
点集逼近
void approxPolyDP(InputArray curve, OutputArray approxCurve, double epsilon, bool closed);
参数说明:
InputArray curve:输入的点集OutputArray approxCurve:输出的点集,当前点集是能最小包容指定点集的。draw出来即是一个多边形;
double epsilon:指定的精度,也即是原始曲线与近似曲线之间的最大距离。
bool closed:若为true,则说明近似曲线是闭合的,它的首位都是相连,反之,若为false,则断开。
PS:findContours后的轮廓信息contours可能过于复杂不平滑,可以用approxPolyDP函数对该多边形曲线做适当近似。
以上描述摘至参考资料4
3.drawContours
绘制轮廓
函数原型:
void
drawContours(InputOutputArray image, InputArrayOfArrays contours, int contourIdx, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1, int lineType=8, InputArray hierarchy=noArray(), int maxLevel=INT_MAX, Point offset=Point() )
参数说明:
InputOutputArray image:要绘制轮廓的图像
InputArrayOfArrays contours:所有输入的轮廓,每个轮廓被保存成一个point向量
int contourIdx:指定要绘制轮廓的编号,如果是负数,则绘制所有的轮廓
const Scalar& color:绘制轮廓所用的颜色
int thickness=1:绘制轮廓的线的粗细,如果是负数,则轮廓内部被填充
int lineType=8:绘制轮廓的线的连通性
InputArray hierarchy=noArray():关于层级的可选参数,只有绘制部分轮廓时才会用到
int maxLevel=INT_MAX:绘制轮廓的最高级别,这个参数只有hierarchy有效的时候才有效
maxLevel=0,绘制与输入轮廓属于同一等级的所有轮廓即输入轮廓和与其相邻的轮廓
maxLevel=1, 绘制与输入轮廓同一等级的所有轮廓与其子节点。
maxLevel=2,绘制与输入轮廓同一等级的所有轮廓与其子节点以及子节点的子节点
Point offset=Point():
PS:findContours()运行的时候,这个图像会被直接涂改,因此如果是将来还有用的图像,应该复制之后再传给findContours()。
以上描述摘至参考资料54.createTrackbar
窗口中快速创建一个滑动控件,用于手动调节阈值,具有非常直观的效果。
函数原型:
int createTrackbar(const string& trackbarname, const string& winname,
int* value, int count,
TrackbarCallback onChange = 0,
void* userdata = 0);
参数说明:
trackbarname:滑动空间的名称;
winname:滑动空间用于依附的图像窗口的名称;
value:初始化阈值;
count:滑动控件的刻度范围;
TrackbarCallback是回调函数。
5.TrackbarCallback
createTrackbar调用的回调函数,用于响应滑动条的交互消息。
函数原型:
typedef void (CV_CDECL *TrackbarCallback)(int pos, void* userdata);
参数说明:
pos:滑动条当前位置;
userdata:调用滑动条传递的数据。
PS:事实上pos和userdata用得非常少,更多的时候直接使用全局变量完成参数传递。
Example运行截图
原图
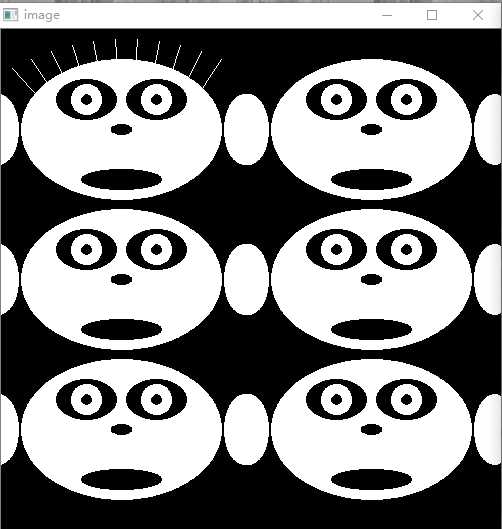
效果图

取消approxPolyDP调用

Example分析
1.申明需要使用的变量
const int w = 500;
int levels = 3;
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
注意:
(1)w:图像的宽度和高度
(2)levels:绘制轮廓的级别和数量
(3)contours:保存轮廓
(4)hierarchy:层级参数
2.主函数
2.1创建一个灰度图像
Mat img = Mat::zeros(w, w, CV_8UC1);
2.2.绘制6个人脸用于测试

for( int i = 0; i < 6; i++ ) { int dx = (i%2)*250 - 30; int dy = (i/2)*150; const Scalar white = Scalar(255); const Scalar black = Scalar(0); if( i == 0 ) { for( int j = 0; j <= 10; j++ ) { double angle = (j+5)*CV_PI/21; line(img, Point(cvRound(dx+100+j*10-80*cos(angle)), cvRound(dy+100-90*sin(angle))), Point(cvRound(dx+100+j*10-30*cos(angle)), cvRound(dy+100-30*sin(angle))), white, 1, 8, 0); } } ellipse( img, Point(dx+150, dy+100), Size(100,70), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+115, dy+70), Size(30,20), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+185, dy+70), Size(30,20), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+115, dy+70), Size(15,15), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+185, dy+70), Size(15,15), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+115, dy+70), Size(5,5), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+185, dy+70), Size(5,5), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+150, dy+100), Size(10,5), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+150, dy+150), Size(40,10), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+27, dy+100), Size(20,35), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); ellipse( img, Point(dx+273, dy+100), Size(20,35), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); }
2.3.创建显示源图像的窗口
namedWindow( "image", 1 );
2.4.显示源图像
imshow( "image", img );
2.5.查找轮廓
vector<vector<Point> > contours0;
findContours( img, contours0, hierarchy, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
2.6.对轮廓进行逼近
contours.resize(contours0.size());
for( size_t k = 0; k < contours0.size(); k++ )
approxPolyDP(Mat(contours0[k]), contours[k], 3, true);
2.7.创建显示目标图像(绘制轮廓图像)的窗口
namedWindow( "contours", 1 );
2.8.为目标图像预览窗口创建滑动条
createTrackbar( "levels+3", "contours", &levels, 7, on_trackbar );
注意:
为窗口添加滑动条,在OpenCV研发中非常普遍和实用,其大致步骤如下:
step1: 参数全局变量的声明与初始化;
step2:声明存储图像的全局变量;
step3:定义响应滑动条的回调函数,根据参数全局变量,和图像全局变量,以及图像算法进行处理,并显示;
step4:创建显示图像的窗口;
step5:在函数中使用createTrackbar创建滑动条;
step6:在函数中手动调用回调函数on_trackbar 一次,用于初始化。
2.9.手动调用
on_trackbar(0,0);
2.10等待键盘事件
waitKey();
注意:
在OpenCV中常常使用waitKey函数,因为显示图像后,需要驻留代码。以便于观察和操作。
3.on_trackbar函数分析
3.1创建目标图像
Mat cnt_img = Mat::zeros(w, w, CV_8UC3);
3.2处理参数
int _levels = levels - 3;
3.3绘制轮廓
drawContours( cnt_img, contours, _levels <= 0 ? 3 : -1, Scalar(128,255,255),
3, LINE_AA, hierarchy, std::abs(_levels) );
3.4显示目标图像
imshow("contours", cnt_img);
Example代码

1 #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" 2 #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" 3 #include <math.h> 4 #include <iostream> 5 6 using namespace cv; 7 using namespace std; 8 9 static void help() 10 { 11 cout 12 << "\\nThis program illustrates the use of findContours and drawContours\\n" 13 << "The original image is put up along with the image of drawn contours\\n" 14 << "Usage:\\n" 15 << "./contours2\\n" 16 << "\\nA trackbar is put up which controls the contour level from -3 to 3\\n" 17 << endl; 18 } 19 20 const int w = 500; 21 int levels = 3; 22 23 vector<vector<Point> > contours; 24 vector<Vec4i> hierarchy; 25 26 static void on_trackbar(int, void*) 27 { 28 Mat cnt_img = Mat::zeros(w, w, CV_8UC3); 29 int _levels = levels - 3; 30 drawContours( cnt_img, contours, _levels <= 0 ? 3 : -1, Scalar(128,255,255), 31 3, LINE_AA, hierarchy, std::abs(_levels) ); 32 33 imshow("contours", cnt_img); 34 } 35 36 int main( int argc, char**) 37 { 38 Mat img = Mat::zeros(w, w, CV_8UC1); 39 if(argc > 1) 40 { 41 help(); 42 return -1; 43 } 44 //Draw 6 faces 45 for( int i = 0; i < 6; i++ ) 46 { 47 int dx = (i%2)*250 - 30; 48 int dy = (i/2)*150; 49 const Scalar white = Scalar(255); 50 const Scalar black = Scalar(0); 51 52 if( i == 0 ) 53 { 54 for( int j = 0; j <= 10; j++ ) 55 { 56 double angle = (j+5)*CV_PI/21; 57 line(img, Point(cvRound(dx+100+j*10-80*cos(angle)), 58 cvRound(dy+100-90*sin(angle))), 59 Point(cvRound(dx+100+j*10-30*cos(angle)), 60 cvRound(dy+100-30*sin(angle))), white, 1, 8, 0); 61 } 62 } 63 64 ellipse( img, Point(dx+150, dy+100), Size(100,70), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); 65 ellipse( img, Point(dx+115, dy+70), Size(30,20), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); 66 ellipse( img, Point(dx+185, dy+70), Size(30,20), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); 67 ellipse( img, Point(dx+115, dy+70), Size(15,15), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); 68 ellipse( img, Point(dx+185, dy+70), Size(15,15), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); 69 ellipse( img, Point(dx+115, dy+70), Size(5,5), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); 70 ellipse( img, Point(dx+185, dy+70), Size(5,5), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); 71 ellipse( img, Point(dx+150, dy+100), Size(10,5), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); 72 ellipse( img, Point(dx+150, dy+150), Size(40,10), 0, 0, 360, black, -1, 8, 0 ); 73 ellipse( img, Point(dx+27, dy+100), Size(20,35), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); 74 ellipse( img, Point(dx+273, dy+100), Size(20,35), 0, 0, 360, white, -1, 8, 0 ); 75 } 76 //show the faces 77 namedWindow( "image", 1 ); 78 imshow( "image", img ); 79 //Extract the contours so that 80 vector<vector<Point> > contours0; 81 findContours( img, contours0, hierarchy, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE); 82 83 contours.resize(contours0.size()); 84 for( size_t k = 0; k < contours0.size(); k++ ) 85 approxPolyDP(Mat(contours0[k]), contours[k], 3, true); 86 87 namedWindow( "contours", 1 ); 88 createTrackbar( "levels+3", "contours", &levels, 7, on_trackbar ); 89 90 on_trackbar(0,0); 91 waitKey(); 92 93 return 0; 94 }
参考资料:
1.《opencv 例程四 寻找轮廓》http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_662c78590100z0rg.html
2.《实用OpenCV》(六) 图像中的形状(1)》http://www.2cto.com/kf/201401/270283.html
3.《findContours函数参数说明及相关函数》http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7155fb1a0101a90h.html
以上是关于OpenCV示例学习笔记-contours2.cpp-通过findContours 函数实现轮廓提取的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
