mac/unix系统:C++实现一个端口扫描器
Posted 方方和圆圆
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mac/unix系统:C++实现一个端口扫描器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
简易端口扫描器
在比较早以前,我用过S扫描器, 以及大名鼎鼎的nmap扫描器, 可以快速扫描某个主机开放的端口, 今天使用C实现这样一个软件,
编译环境为Mac, 系统版本10.11.6:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <time.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> void msg() { printf("EP:scan ip startport endport\\nEP:scan ip 127.0.0.1 20 2009\\n"); } int main(int argc,char** argv) { char *ip; int startport,endport,sockfd,i; struct sockaddr_in to; float costtime; clock_t start,end; if(4!=argc) { msg(); return 0; } ip=argv[1]; startport=atoi(argv[2]); endport=atoi(argv[3]); if(startport<1 || endport>65535 || endport<startport) { printf("端口范围出错/n"); return 0; } else{ printf("IP:%s %d-%d\\n",ip,startport,endport); } to.sin_family=AF_INET; to.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(ip); start=clock(); for(i=startport;i<=endport;i++) { sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); to.sin_port=htons(i); if(connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)&to,sizeof(struct sockaddr)) == 0) { printf("%s %d\\n",ip,i); close(sockfd); }; } end=clock(); costtime=(float)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC; printf("用时:%f秒\\n",costtime); return 0; }
亲测可行:
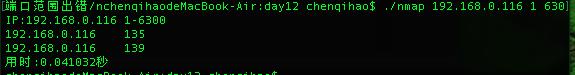
以上的代码只能检测固定的ip, 通过更改源码, 软件可以支持一段的ip端口检测, 多加一个循环:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <time.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/select.h> #include <string> void msg() { printf( "EP:scan ip startport endport\\nEP:scan ip 127.0.0.1 20 2009\\n" ); printf( "EP:scan ip endip startport endport\\nEP:scan ip 127.0.0. 250 20 2009\\n" ); } void runsock(int sockfd, struct sockaddr_in to, char *ipval, int i) { sockfd = socket( AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 ); //fcntl(sockfd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK); to.sin_port = htons( i ); //printf( "IP:%s %d\\n", ipval, i ); if ( connect( sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &to, sizeof(struct sockaddr) ) == 0 ){ printf( "%s %d\\n", ipval, i ); close( sockfd ); } } int main( int argc, char* argv[] ){ char * ip; char * endip; int startport, endport, sockfd, i; struct sockaddr_in to; float costtime; clock_t start, end; if ( 4 == argc ){ ip = argv[1]; startport = atoi( argv[2] ); endport = atoi( argv[3] ); if ( startport < 1 || endport > 65535 || endport < startport ){ printf( "端口范围出错/n" ); return(0); }else{ printf( "IP:%s %d-%d\\n", ip, startport, endport ); } to.sin_family = AF_INET; to.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr( ip ); start = clock(); for ( i = startport; i <= endport; i++ ){ runsock(sockfd, to, ip, i); } end = clock(); costtime = (float) (end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; printf( "用时:%f秒\\n", costtime ); return(0); }else if ( 5 == argc ){ ip = argv[1]; endip = argv[2]; startport = atoi( argv[3] ); endport = atoi( argv[4] ); char *tempip; if ( startport < 1 || endport > 65535 || endport < startport ){ printf( "端口范围出错/n" ); return(0); }else{ /* 循环ip地址 */ start = clock(); char ipval[20]; for ( int j = 1; j <= atoi( endip ); j++ ){ sprintf( ipval, "%s%d", ip, j ); printf( "IP:%s\\n", ipval ); to.sin_family = AF_INET; to.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr( ipval ); for ( i = startport; i <= endport; i++ ){ runsock(sockfd, to, ipval, i); } } end = clock(); costtime = (float) (end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; printf( "用时:%f秒\\n", costtime ); };/* 循环端口 */ return(0); } msg(); return(0); }
局域网网段IP端口扫描器
看起来这个扫描器是实现了, 但是还有一个天大的问题, 那就是connect是同步的, 如果有些ip是不存在的, 那么connect函数就会阻塞在那边, 导致运行非常缓慢,那就需要异步的socket连接, 涉及select.h, 通过icmp判断存活主机:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <strings.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <netinet/ip.h> #include <netinet/ip_icmp.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <setjmp.h> #include <errno.h> #include <sys/select.h> #include <fcntl.h> #define PACKET_SIZE 4096 /* 计算校验和的算法 */ unsigned short cal_chksum(unsigned short *addr,int len) { int sum=0; int nleft = len; unsigned short *w = addr; unsigned short answer = 0; /* 把ICMP报头二进制数据以2字节为单位累加起来 */ while(nleft > 1){ sum += *w++; nleft -= 2; } /* * 若ICMP报头为奇数个字节,会剩下最后一字节。 * 把最后一个字节视为一个2字节数据的高字节, * 这2字节数据的低字节为0,继续累加 */ if(nleft == 1){ *(unsigned char *)(&answer) = *(unsigned char *)w; sum += answer; /* 这里将 answer 转换成 int 整数 */ } sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff); /* 高位低位相加 */ sum += (sum >> 16); /* 上一步溢出时,将溢出位也加到sum中 */ answer = ~sum; /* 注意类型转换,现在的校验和为16位 */ return answer; } int livetest(char* ip) { char sendpacket[PACKET_SIZE]; /* 发送的数据包 */ char recvpacket[PACKET_SIZE]; /* 接收的数据包 */ pid_t pid; int datalen = 56; /* icmp数据包中数据的长度 */ struct protoent *protocol; protocol = getprotobyname("icmp"); int sockfd; int size = 50*1024; if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, protocol->p_proto)) < 0) { perror("socket error"); } setsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &size, sizeof(size) ); struct sockaddr_in dest_addr; bzero(&dest_addr, sizeof(dest_addr)); dest_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; dest_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip); //send packet; int packsize; struct icmp *icmp; struct timeval *tval; icmp = (struct icmp*)sendpacket; icmp->icmp_type = ICMP_ECHO; /* icmp的类型 */ icmp->icmp_code = 0; /* icmp的编码 */ icmp->icmp_cksum = 0; /* icmp的校验和 */ icmp->icmp_seq = 1; /* icmp的顺序号 */ icmp->icmp_id = pid; /* icmp的标志符 */ packsize = 8 + datalen; /* icmp8字节的头 加上数据的长度(datalen=56), packsize = 64 */ tval = (struct timeval *)icmp->icmp_data; /* 获得icmp结构中最后的数据部分的指针 */ gettimeofday(tval, NULL); /* 将发送的时间填入icmp结构中最后的数据部分 */ icmp->icmp_cksum = cal_chksum((unsigned short *)icmp, packsize);/*填充发送方的校验和*/ if(sendto(sockfd, sendpacket, packsize, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&dest_addr, sizeof(dest_addr)) < 0){ perror("sendto error"); } //printf("send %d, send done\\n",1 ); int n; struct sockaddr_in from; int fromlen = sizeof(from); fcntl(sockfd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK); struct timeval timeo = {1,0}; fd_set set; FD_ZERO(&set); FD_SET(sockfd, &set); //read , write; int retval = select(sockfd+1, &set, NULL, NULL, &timeo); if(retval == -1) { printf("select error\\n"); return 0; }else if(retval == 0 ) { //printf("timeout\\n"); return 0; }else{ if( FD_ISSET(sockfd, &set) ){ //printf("host is live\\n"); return 1; } return 0; } // n = recvfrom(sockfd, recvpacket,sizeof(recvpacket), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&from, (socklen_t *)&fromlen); // if(n<0) { // perror("recvfrom error"); // }else{ // printf("%d\\n",n); // } //return 0; } static void sleep_ms(unsigned int secs){ struct timeval tval; tval.tv_sec=secs/1000; tval.tv_usec=(secs*1000)%1000000; select(0,NULL,NULL,NULL,&tval); } void msg() { printf( "EP:scan ip startport endport\\nEP:scan ip 127.0.0.1 20 2009\\n" ); printf( "EP:scan ip endip startport endport\\nEP:scan ip 127.0.0. 1 250 20 2009\\n" ); } void runsock(int sockfd, struct sockaddr_in to, char *ipval, int i) { sockfd = socket( AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 ); fcntl(sockfd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK); fd_set set,writeSet; int error; //错误代码 socklen_t len = sizeof(error); //while(1){ FD_ZERO(&set); FD_ZERO(&writeSet); struct timeval timeo= {1,0}; //socklen_t len = sizeof(timeo); FD_SET(sockfd,&set); FD_SET(sockfd,&set); //setsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDTIMEO,&timeo, len); to.sin_port = htons( i ); //printf( "test %s %d , sockfd value %d\\n", ipval, i , sockfd); //printf( "IP:%s %d\\n", ipval, i ); //printf("%d\\n",i); int conn = connect( sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &to, sizeof(struct sockaddr) ); //等待 int retval = select(sockfd+ 1, &set, &writeSet, NULL, &timeo); getsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, &error, &len ); if(error == 0) printf("%s Port %d is opened\\n", ipval, i); //printf("%d\\n",sockfd); // printf("%s :%d\\n",ipval, i); // if (retval== -1) { // perror("select error\\n"); // } else if(retval == 0){ // //printf("timeout\\n"); // }else{ // //printf("find %s :%d\\n",ipval, i); // if(FD_ISSET(sockfd,&set)) { // printf("find %s :%d\\n",ipval, i); // } // } //} } int main( int argc, char* argv[] ){ char * ip; int endip, startip; int startport, endport, sockfd, i; struct sockaddr_in to; float costtime; clock_t start, end; if ( 4 == argc ){ ip = argv[1]; startport = atoi( argv[2] ); endport = atoi( argv[3] ); if ( startport < 1 || endport > 65535 || endport < startport ){ printf( "端口范围出错/n" ); return(0); }else{ printf( "IP:%s %d-%d\\n", ip, startport, endport ); } to.sin_family = AF_INET; to.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr( ip ); start = clock(); for ( i = startport; i <= endport; i++ ){ //printf("%d\\n",i); runsock(sockfd, to, ip, i); } end = clock(); costtime = (float) (end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; printf( "用时:%f秒\\n", costtime ); return(0); }else if ( 6 == argc ){ ip = argv[1]; startip = atoi(argv[2]); endip = atoi(argv[3]); startport = atoi( argv[4] ); endport = atoi( argv[5] ); char *tempip; if ( startport < 1 || endport > 65535 || endport < startport ){ printf( "端口范围出错/n" ); return(0); }else{ /* 循环ip地址 */ start = clock(); char ipval[20]; for ( int j = startip; j <= endip ; j++ ){ sprintf( ipval, "%s%d", ip, j ); printf( "IP:%s\\n", ipval ); if(livetest(ipval) == 1){ to.sin_family = AF_INET; //printf("okokok\\n"); to.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr( ipval ); for ( i = startport; i <= endport; i++ ){ runsock(sockfd, to, ipval, i); sleep_ms(1000); } } } end = clock(); costtime = (float) (end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; printf( "用时:%f秒\\n", costtime ); }; //while(1){} /* 循环端口 */ return(0); } msg(); return(0); }
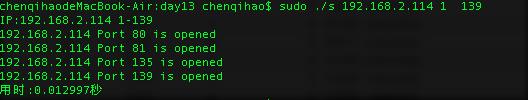
使用方式1: scan ip startport endport
sudo ./s 192.168.2.114 1 139
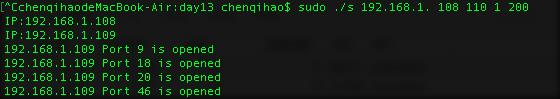
使用方式2: scan ip start endip startport endport
sudo ./s 192.168.1. 108 110 1 200
还有一个问题, 就是扫描的端口不怎么准确, 经常出现误报, 有些端口跟没开, 但是扫描器会显示目标端口有开, 应该是判断sock是否连接成功的逻辑有问题, 目前没有好的解决方案, 期待大神指点一下:
getsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, &error, &len ); if(error == 0) printf("%s Port %d is opened\\n", ipval, i);
参考链接
Linux C语言写的超级简单端口扫描器 http://blog.csdn.net/kongjiajie/article/details/4799986
Linux的SOCKET编程详解 http://blog.csdn.net/hguisu/article/details/7445768/
EOF
作者: NONO
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/diligenceday/
QQ:287101329
微信:18101055830
以上是关于mac/unix系统:C++实现一个端口扫描器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章