深入研究HTTP协议以及部分应用
Posted 小困
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深入研究HTTP协议以及部分应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- 引言
工作了一段时间,都是在开发网页,自然和http打交道打得最多了,投身工作之后原来理解的东西又变得模糊,所以有必要深入探讨一下http协议的细节,也借此总结一下学习的成果。
- HTTP相关认识
对HTTP的学术认识我可是总结不到位的,不过就实际应用来说,HTTP协议是对TCP协议的一个细化扩展(个人理解)。TCP是一个可靠的面向连接的传输层协议,他指出两个通信端在通信时候保证通信正常进行的步骤,比如三次握手,比如传输的报文格式,这些规定了点到点的传输形式。而HTTP是基于TCP协议在应用层方向上的扩展。
HTTP分为请求,响应。请求的格式有,请求头,请求行,请求正文,这些格式规定了通信时候服务器所作出的响应。而响应的格式也是响应头和响应主体。作为工作实际中,应用到最多的两种方法GET和POST方法。他们的区别就在于,一个是携带参数在url中,一个是把参数放在请求正文中传输。现在来探究他们的格式。
- GET请求格式
它的格式如下。首先第一行发起HTTP请求方式GET,空格,请求目标目录下的资源(可以是/index.jsp这样,在这个url上携带参数,后加?username=123&password=123),空格,请求http版本。
之后就按照格式了,每一行的key值有不同的作用,没有深究。
最后,请求结束了之后记得换行(\\r\\n),不然服务器会等待。
GET / HTTP/1.1
Accept:*/*
Accept-Language:zh-cn
User-Agent: JavaSocket/1.8.0_91
Host:www.baidu.com:80
Connection:Keep-Alive
Content-Type:text/xml;charset=GBK
- POST请求格式
格式如GET,请求正文之前换行,正文借书后要空一行。Content-Type如下是使用了表单形式,便于后端获得数据。另外还有几种类型不再介绍。
POST / HTTP/1.1 Accept:*/* Accept-Language:zh-cn User-Agent: JavaSocket/1.8.0_91 Host:www.baidu.com:80 Connection:Keep-Alive Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=GBK Content-Length:25 username=134&password=123
- Socket实现HTTP请求
一个完整的http请求由很多小步骤,但是我这里分为两步,发送请求,接受响应。而发送请求之前,必须建立连接。构建请求,就如之前说的一样,在传输上构造请求的格式,就可以实现一个http请求了。
package HttpProtocol; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.UnknownHostException; /** * 实现一个http请求 * @author ctk * */ public class HttpRequestImpl { private final static String encoding = "GBK"; public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException { Socket request = new Socket("localhost",8080); OutputStreamWriter out = new OutputStreamWriter(request.getOutputStream()); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); String content = "username=134&password=123"; //换行前不要加空格 sb.append("POST /webPractice/RecvHttpMine HTTP/1.1\\r\\n"); sb.append("Accept:*/*\\r\\n"); sb.append("Accept-Language:zh-cn\\r\\n"); sb.append("User-Agent: JavaSocket/").append(System.getProperty("java.version")).append("\\r\\n"); sb.append("Host:locahost:8080\\r\\n"); sb.append("Connection:close\\r\\n"); // sb.append("Connection:Keep-Alive\\r\\n"); // sb.append("Content-Type:text/xml;"+"charset="+encoding+"\\r\\n");//请求提交text sb.append("Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded;"+"charset="+encoding+"\\r\\n");//请求提交表单模式 sb.append("Content-Length:"+content.length()+"\\r\\n"); sb.append("\\r\\n"); sb.append(content+"\\r\\n"); //一个请求的结束应该有一个换行 sb.append("\\r\\n"); System.out.println("发送请求....."); System.out.println(sb.toString()); out.write(sb.toString()); out.flush(); //获取响应 InputStream is = request.getInputStream(); BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(is, encoding)); String str = ""; int i = 0; File f = new File("src/rev.txt"); if(!f.exists()) f.createNewFile(); FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(f); while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { fout.write((str+"\\r\\n").getBytes()); fout.flush(); System.out.println((i++)+":"+str); } is.close(); fout.close(); out.close(); request.close(); System.out.println("=============="); } }
我的servlet放在tomcat上运行,请求到来之后由tomcat进行解析。
package com.util.servlet; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * Servlet implementation class RecvHttpMine */ @WebServlet("/RecvHttpMine") public class RecvHttpMine extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet() */ public RecvHttpMine() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("get请求得到的数据: username="+request.getParameter("username")); System.out.println("get请求得到的数据: password="+request.getParameter("password")); response.getWriter().println("get success"); } /** * @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("post 接受到的参数username:"+request.getParameter("username")); System.out.println("post 接受到的参数password:"+request.getParameter("password")); response.getWriter().println("post success"); } }
socket程序执行完毕之后控制台打印如下。
servlet程序打印如下
 我这里试了很久,主要是Content-Type的问题,一定要设置成表单,不然提交之后tomcat解析为null。
我这里试了很久,主要是Content-Type的问题,一定要设置成表单,不然提交之后tomcat解析为null。
- socket实现http响应
有了如上的基础,响应也就是一堆字符串格式而已,只要做个监听的socket,访问的时候返回响应就好,解析参数就在读取响应的过程做就好了。
package HttpProtocol; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.Date; /** * http服务器 * @author ctk * */ public class HttpServer { private final static String encoding = "UTF-8"; private final static int stateCode = 200; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket server = null; String responseContent = "this is a test"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append("HTTP/1.1 ").append(stateCode).append(" OK\\r\\n"); sb.append("Server: Ctk\\r\\n"); sb.append("Content-Length: ").append(responseContent.length()).append("\\r\\n"); sb.append("Date: ").append(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString()).append("\\r\\n"); sb.append("Connection: close\\r\\n"); sb.append("\\r\\n"); sb.append(responseContent).append("\\r\\n"); sb.append("\\r\\n"); try { server = new ServerSocket(8000); System.out.println("监听开始...."); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } while(true){ Socket socket = server.accept(); System.out.println("获得连接:"+socket.getInetAddress()+":"+socket.getPort()); int len = -1; InputStream in = socket.getInputStream(); BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(in, encoding)); String str = ""; while (bufferedReader.read() != -1) { if(!((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null)) System.out.println(str); else break; } System.out.println("回送响应=============="); System.out.println(sb.toString()); OutputStreamWriter out = new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()); out.write(sb.toString()); out.flush(); out.close(); in.close(); socket.close(); } } }
运行之后控制台打印如下。
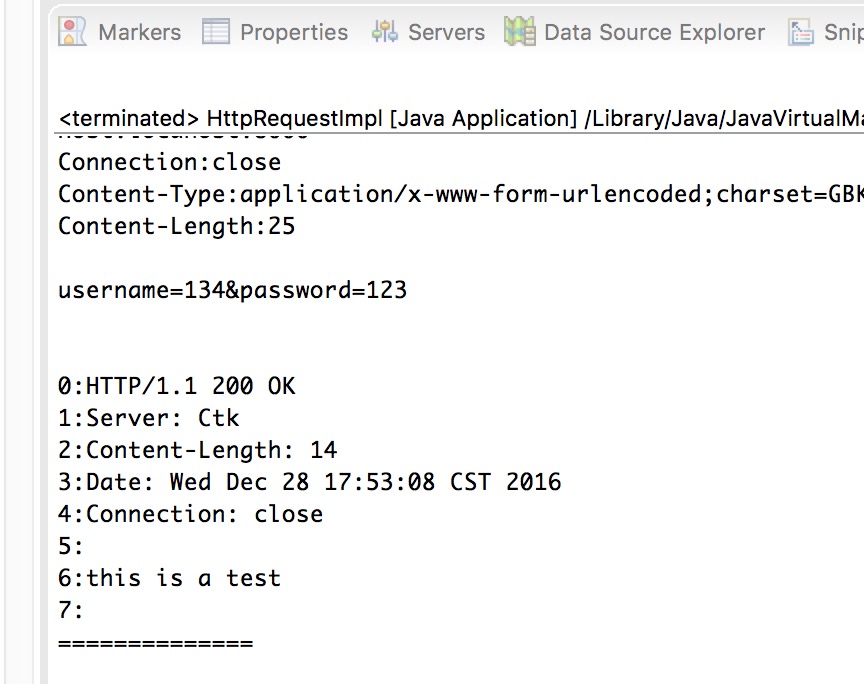
在服务器readLine的时候,要判断read是否为-1,否则无法结束。
- 另类玩法
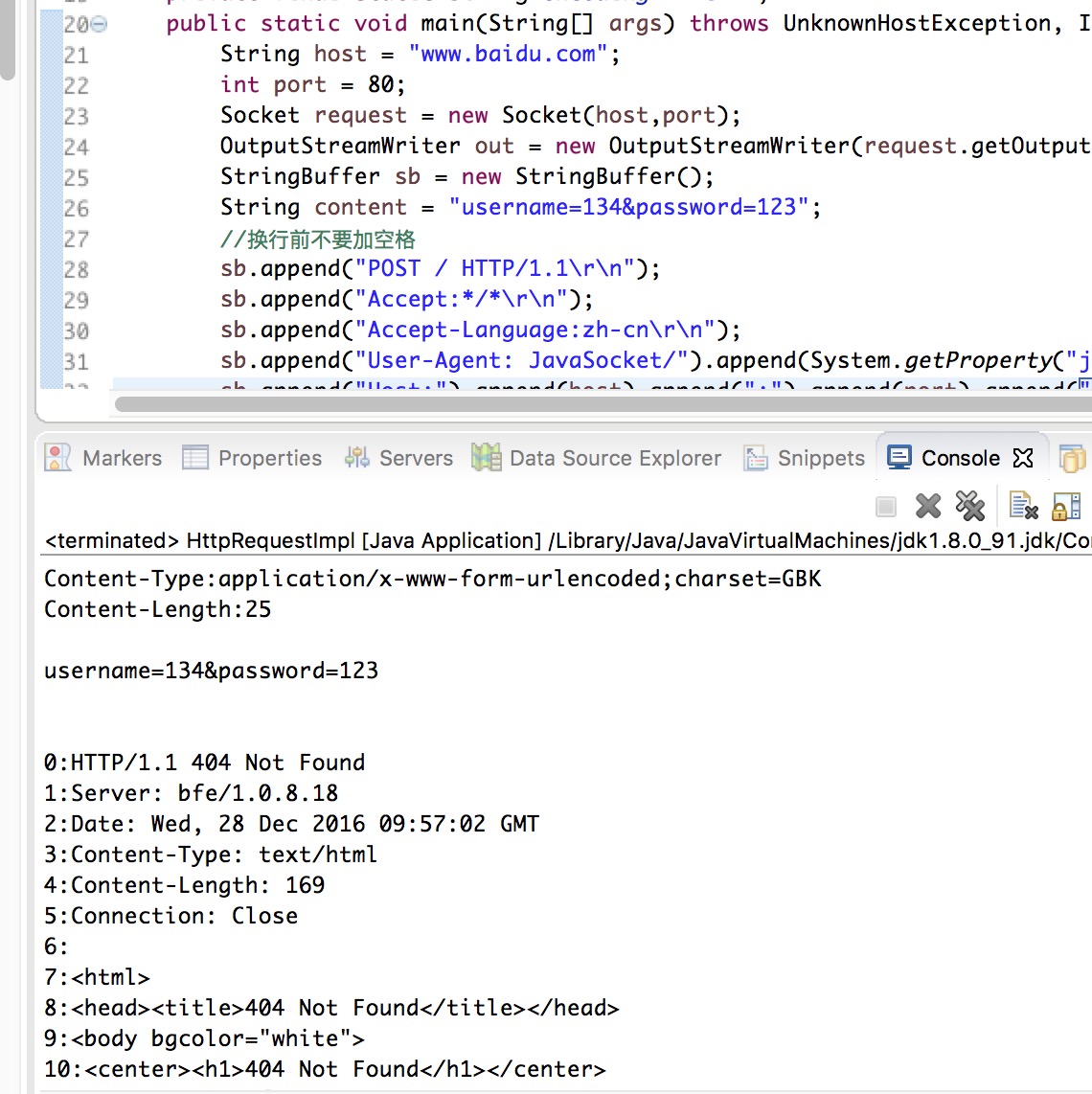
我用它来访问百度,返回了404
然后我用它来访问网易,竟然返回了8000行的代码。
如果你用post访问网易的主页,它返回一个405,method not allow。
可见,学通原理,走遍天下都不怕。
- 转发和重定向
这个是开发中最常用的概念了。
转发:客户端只产生一个请求,服务端负责转发这个请求,方老师神比喻:你找我借钱,我帮你找他借钱。
重定向:客户端再发起一个新请求,请求服务器资源,还是方老师:你找我借钱,我让你找他借钱。
转发主要的特征就是同一个请求域,在这个请求域中可以共用参数。重定向没啥好说的。
- 分步注册实例
转发实现:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript" src="jquery.min.js"></script> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>第一步</title> </head> <body> <h1>第一步</h1> <form action = "sendTest" method="post"> <input name="msg" type="text" id="msg" value="${save}"/> <input name="page" style="display:none;" value="step2.jsp"/> <br/> <button id="nextStep" type="submit">下一步</button> </form> </body> </html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript" src="jquery.min.js"></script> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>第二步</title> </head> <body> <h1>第二步</h1> <form action = "sendTest" method="post"> <input name="msg" type="text" id="msg" value="${save}"/> <input name="page" style="display:none;" id="page"/> <br/> <button id="preStep" type="submit">上一步</button> <button id="nextStep" type="submit">下一步</button> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function(){ $(\'#preStep\').click(function(){ $(\'#page\').val("step1.jsp"); }); }); $(document).ready(function(){ $(\'#nextStep\').click(function(){ $(\'#page\').val("step3.jsp"); }); }); </script> </body> </html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript" src="jquery.min.js"></script> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>第三步</title> </head> <body> <h1>第三步</h1> <form action = "sendTest" method="post"> <input name="msg" type="text" id="msg" value="${save}"/> <input name="page" style="display:none;" id="page"/> <br/> <button id="preStep" type="submit">上一步</button> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function(){ $(\'#preStep\').click(function(){ $(\'#page\').val("step2.jsp"); }); }); </script> </body> </html>
serlvet
package com.util.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * Servlet implementation class sendTest */ @WebServlet("/sendTest") public class sendTest extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String msg; private String page; /** * @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet() */ public sendTest() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub msg = request.getParameter("msg"); page = request.getParameter("page"); System.out.println("得到的msg = "+msg); System.out.println("得到的page = "+page); if(msg == null){ System.out.println("分支1"); request.setAttribute("save", ""); request.getRequestDispatcher("step1.jsp").forward(request, response); }else{ System.out.println("分支2"); request.setAttribute("save", msg); request.getRequestDispatcher(page).forward(request, response); } } /** * @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub doGet(request, response); } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } public String getPage() { return page; } public void setPage(String page) { this.page = page; } }
以上是关于深入研究HTTP协议以及部分应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章