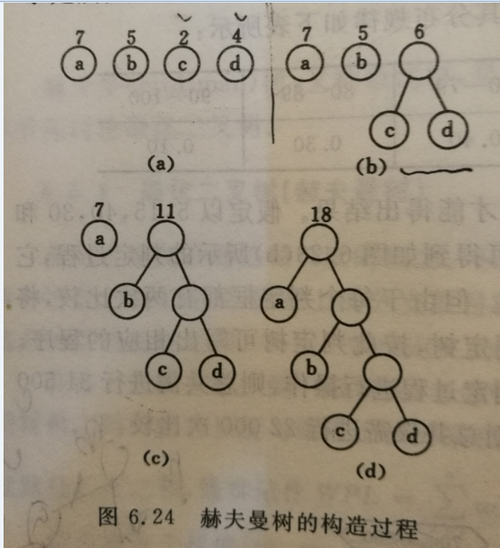
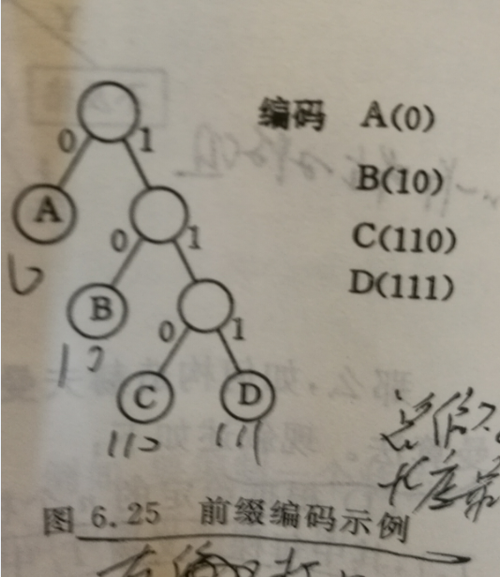
数据结构之huffman树
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构之huffman树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MAXBIT 99
#define MAXVALUE 9999
#define MAXLEAF 30
#define MAXNODE MAXLEAF*2 -1
typedef struct
{
int bit[MAXBIT];
int start;
} HCodeType; /* 编码结构体 */
typedef struct
{
int weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
int value;
} HNodeType; /* 结点结构体 */
/* 构造一颗哈夫曼树 */
void HuffmanTree (HNodeType HuffNode[MAXNODE], int n)
{
/* i、j: 循环变量,m1、m2:构造哈夫曼树不同过程中两个最小权值结点的权值,
x1、x2:构造哈夫曼树不同过程中两个最小权值结点在数组中的序号。*/
int i, j, m1, m2, x1, x2;
/* 初始化存放哈夫曼树数组 HuffNode[] 中的结点 */
for (i=0; i<2*n-1; i++)
{
HuffNode[i].weight = 0;//权值
HuffNode[i].parent =-1;
HuffNode[i].lchild =-1;
HuffNode[i].rchild =-1;
HuffNode[i].value=i; //实际值,可根据情况替换为字母
}
/* 输入 n 个叶子结点的权值 */
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf ("Please input weight of leaf node %d: \n", i);
scanf ("%d", &HuffNode[i].weight);
}
/* 循环构造 Huffman 树 */
for (i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
m1=m2=MAXVALUE; /* m1、m2中存放两个无父结点且结点权值最小的两个结点 */
x1=x2=0;
/* 找出所有结点中权值最小、无父结点的两个结点,并合并之为一颗二叉树 */
for (j=0; j<n+i; j++)
{
if (HuffNode[j].weight < m1 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1)
{
m2=m1;
x2=x1;
m1=HuffNode[j].weight;
x1=j;
}
else if (HuffNode[j].weight < m2 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1)
{
m2=HuffNode[j].weight;
x2=j;
}
} /* end for */
/* 设置找到的两个子结点 x1、x2 的父结点信息 */
HuffNode[x1].parent = n+i;
HuffNode[x2].parent = n+i;
HuffNode[n+i].weight = HuffNode[x1].weight + HuffNode[x2].weight;
HuffNode[n+i].lchild = x1;
HuffNode[n+i].rchild = x2;
printf ("x1.weight and x2.weight in round %d: %d, %d\n", i+1, HuffNode[x1].weight, HuffNode[x2].weight); /* 用于测试 */
printf ("\n");
} /* end for */
} /* end HuffmanTree */
//解码
void decodeing(char string[],HNodeType Buf[],int Num)
{
int i,tmp=0;//,code[1024];
int m=2*Num-1;
char *nump;
char num[1024];
for(i=0;i<sizeof(string)/sizeof(string[0]);i++)
{
if(string[i]==‘0‘)
num[i]=0;
else
num[i]=1;
}
i=0;
nump=&num[0];
while(nump<(&num[sizeof(string)/sizeof(string[0])]))
{
tmp=m-1;
while((Buf[tmp].lchild!=-1)&&(Buf[tmp].rchild!=-1))
{
if(*nump==0)
{
tmp=Buf[tmp].lchild ;
}
else tmp=Buf[tmp].rchild;
nump++;
}
printf("%d",Buf[tmp].value);
}
}
int main(void)
{
HNodeType HuffNode[MAXNODE]; /* 定义一个结点结构体数组 */
HCodeType HuffCode[MAXLEAF],cd; /* 定义一个编码结构体数组, 同时定义一个临时变量来存放求解编码时的信息 */
int i, j, c, p, n;
char pp[100];
printf ("Please input n:\n");
scanf ("%d", &n);
HuffmanTree (HuffNode, n);
for (i=0; i < n; i++)
{
cd.start = n-1;
c = i;
p = HuffNode[c].parent;
while (p != -1) /* 父结点存在 */
{
if (HuffNode[p].lchild == c)
cd.bit[cd.start] = 0;
else
cd.bit[cd.start] = 1;
cd.start--; /* 求编码的低一位 */
c=p;
p=HuffNode[c].parent; /* 设置下一循环条件 */
} /* end while */
/* 保存求出的每个叶结点的哈夫曼编码和编码的起始位 */
for (j=cd.start+1; j<n; j++)
{ HuffCode[i].bit[j] = cd.bit[j];}
HuffCode[i].start = cd.start;
} /* end for */
/* 输出已保存好的所有存在编码的哈夫曼编码 */
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf ("%d ‘s Huffman code is: ", i);
for (j=HuffCode[i].start+1; j < n; j++)
{
printf ("%d", HuffCode[i].bit[j]);
}
printf(" start:%d",HuffCode[i].start);
printf ("\n");
}
printf("Decoding?Please Enter code:\n");
scanf("%s",&pp);
decodeing(pp,HuffNode,n);
//getch();
return 0;
}本文出自 “11773640” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://11783640.blog.51cto.com/11773640/1877928
以上是关于数据结构之huffman树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章