多种居中方法
Posted WingedGirl
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多种居中方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、快标签自身水平居中:
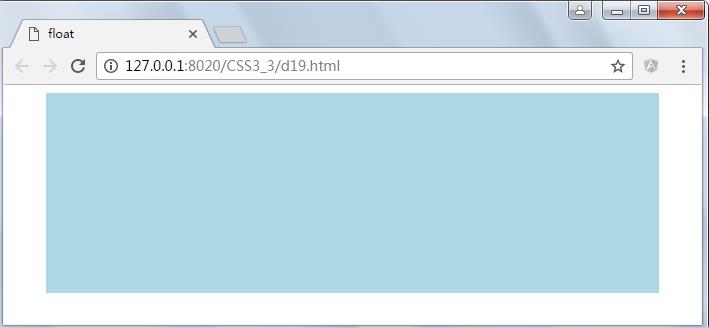
当一个有宽度的块标签设置margin:0 auto时将实现自身的水平居中,示例脚本如下

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>float</title> <style type="text/css"> #container { margin: 0 auto; width: 90%; background: lightblue; height: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="container"> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
2、快标签内对其
text-align:start | end | left | right | center | justify | match-parent | justify-all
默认值:start
适用于:块标签
left: 内容左对齐。
center: 内容居中对齐。
right: 内容右对齐。
justify: 内容两端对齐,但对于强制打断的行(被打断的这一行)及最后一行(包括仅有一行文本的情况,因为它既是第一行也是最后一行)不做处理。(CSS3)
start: 内容对齐开始边界。(CSS3)
end: 内容对齐结束边界。(CSS3)
match-parent: 这个值和 inherit 表现一致,只是该值继承的 start 或 end 关键字是针对父母的 <\' direction \'> 值并计算的,计算值可以是 left 和 right 。(CSS3)
justify-all: 效果等同于 justify,但还会让最后一行也两端对齐。(CSS3)
示例代码:

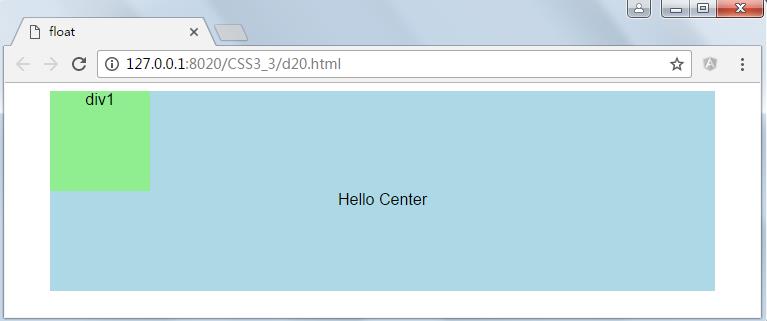
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>float</title> <style type="text/css"> #container { margin: 0 auto; width: 90%; background: lightblue; height: 200px; text-align: center; } #div1{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: lightgreen; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="container"> <div id="div1">div1</div> Hello Center </div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
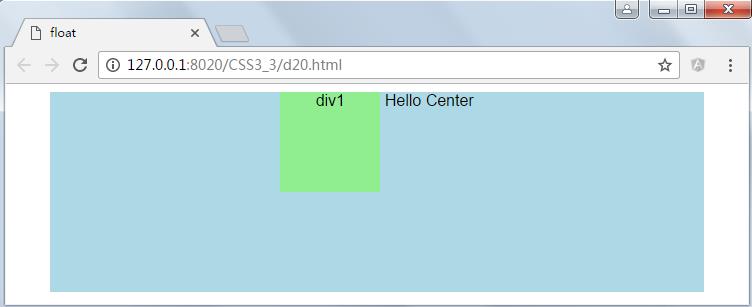
这种对齐方式只针对块标签内的行内标签(inline box)与行内块标签(inline block)有效,对块标签是无效的因为块标签默认总是占整行。如果将示例中div1的显示方式修改为行内块标签(display: inline-block;),则效果如下所示:
3、垂直居中方法一
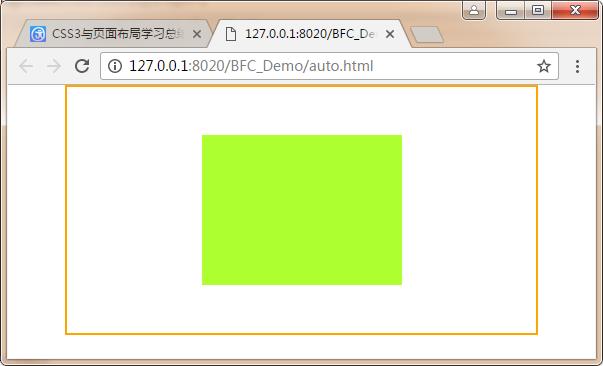
当一个设置了定位的元素所有的偏移为0且margin为auto时将水平,垂直都居中,且父元素自身的高度可动态变化。
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } html,body{ height: 100%; } #div0{ width: 80%; height: 90%; border: 2px solid orange; margin: 0 auto; position: relative;/*如果父元素不设置定位,则是相对body居中*/ } #div1{ width: 200px; height: 150px; background: greenyellow; position: absolute; top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0; margin: auto; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div0"> <div id="div1"></div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
4、垂直居中方法二
如果是单行文本,行高如块的高度一样时将居中,只一行,行高和元素一样高,居中。
line-height: 120px;
height: 120px;
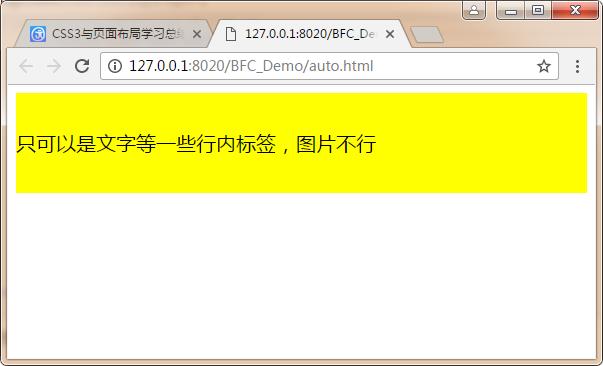
注:只可以是文字等一些行内标签,图片不行
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> #div1{ height: 100px; background: yellow; /*text-align: center;*/ line-height: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> 只可以是文字等一些行内标签,图片不行 </div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
把line-height:100px 换成是font:20px/100px "microsoft yahei" 也是一样的效果(20表示字体大小,100表示行高)
5、垂直居中方法三
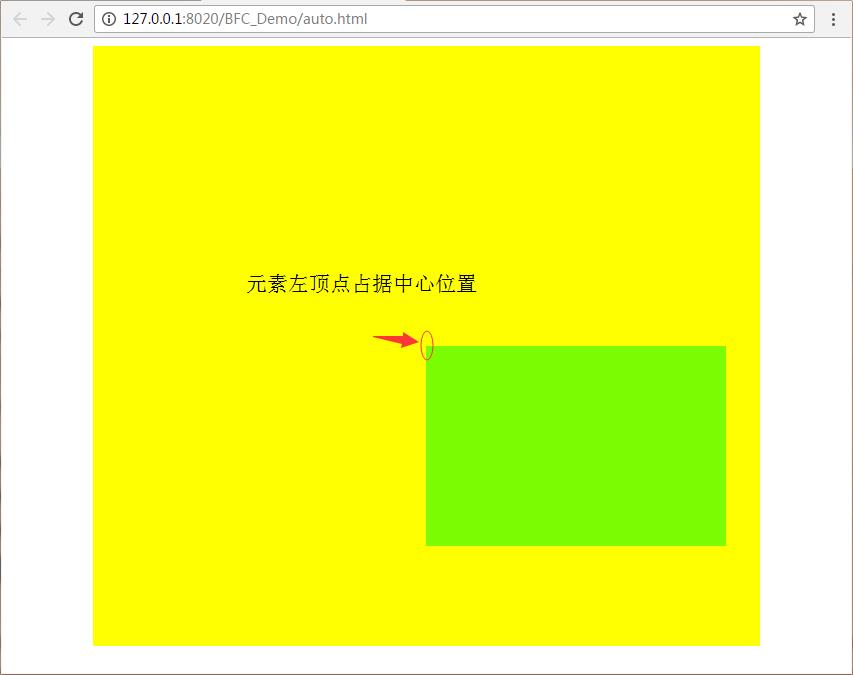
让元素相对父元素定位,偏移左50%,上50%,把自身向左移半个宽度,向上移半个高度,同时完成了水平与垂直方向的居中
(个人理解的是,让元素相对父元素定位,偏移左50%,上50%后,只是元素的左顶点居中了,把自身向左移半个宽度,向上移半个高度后,则是考虑了自身高度和宽度的影响)
示例代码:
首先只是让元素相对父元素定位,偏移左50%,上50%:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> #div1{ width: 80%; height: 600px; position: relative; background: yellow; margin: 0 auto; } #div2{ width:300px; height: 200px; position: absolute; background: lawngreen; left: 50%; top: 50%; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> <div id="div2"></div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
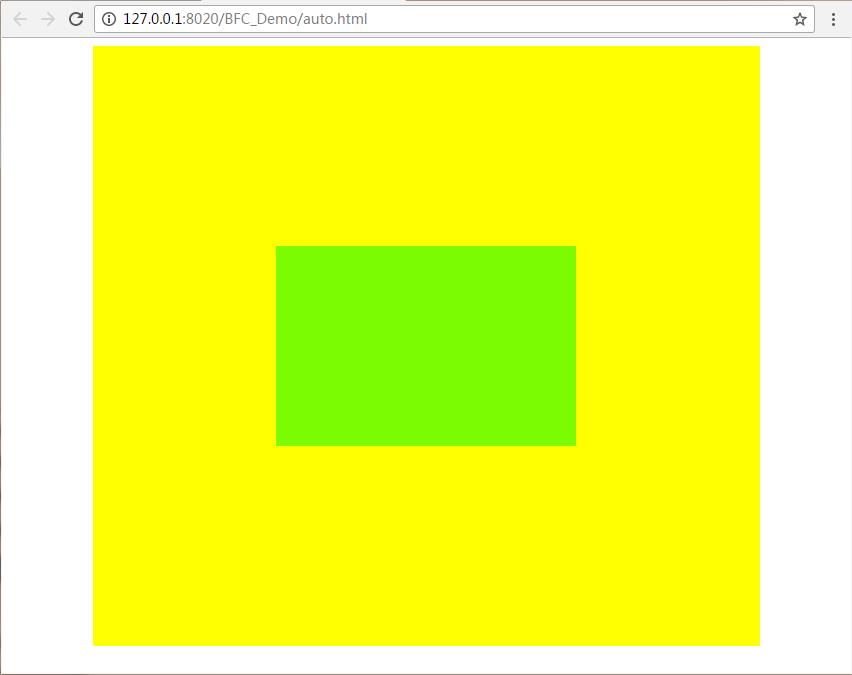
把自身向左移半个宽度,向上移半个高度后:即加上下面两句代码:
margin-left: -150px;
margin-top: -100px;
运行结果:
6、垂直居中方法四
在CSS有一个属性应该欺骗过很多开发者,一直认为使用了他就可以垂直居中了,但不行,这个属性就是:
语法:vertical-align:baseline | sub | super | top | text-top | middle | bottom | text-bottom | <percentage> | <length>
默认值:baseline
作用:设置或检索内联元素在行框内的垂直对其方式
适用于:内联级与 table-cell 元素
baseline: 把当前盒的基线与父级盒的基线对齐。如果该盒没有基线,就将底部外边距的边界和父级的基线对齐
sub: 把当前盒的基线降低到合适的位置作为父级盒的下标(该值不影响该元素文本的字体大小)
super: 把当前盒的基线提升到合适的位置作为父级盒的上标(该值不影响该元素文本的字体大小)
text-top: 把当前盒的top和父级的内容区的top对齐
text-bottom: 把当前盒的bottom和父级的内容区的bottom对齐
middle: 把当前盒的垂直中心和父级盒的基线加上父级的半x-height对齐
top: 把当前盒的top与行盒的top对齐
bottom: 把当前盒的bottom与行盒的bottom对齐
<percentage>: 把当前盒提升(正值)或者降低(负值)这个距离,百分比相对line-height计算。当值为0%时等同于baseline。
<length>: 把当前盒提升(正值)或者降低(负值)这个距离。当值为0时等同于baseline。(CSS2) 说明:
设置或检索内联元素在行框内的垂直对其方式。
对应的脚本特性为verticalAlign。
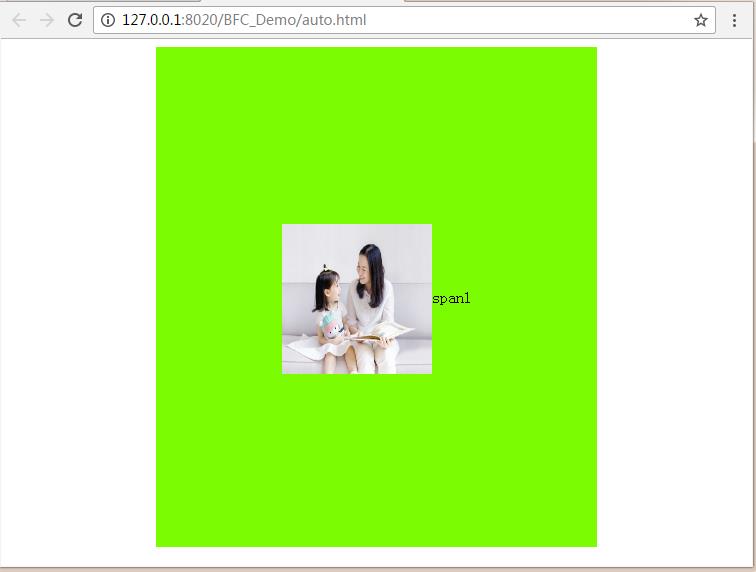
不能实现对齐的主要原因是:vertical-align这个属性的特点,它是相对兄弟级行高(line-height)来定位

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> #div1{ width: 60%; height: 500px; background: lawngreen; position: relative; margin: 0 auto; text-align: center; } #img1{ width:150px; height: 150px; vertical-align: middle; } span{ line-height: 500px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> <img src="img/bgc.jpg" id="img1" /><span>span1</span> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
7、使用表格特性居中
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> #div0{ width: 60%; height: 500px; background: lawngreen; margin: 0 auto; display: table;/*类似让div0为一个table*/ } #div1{ display: table-cell;/*类似table中的td*/ vertical-align: middle;/*垂直居中*/ text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div0"> <div id="div1"> <img src="img/bgc.jpg" id="img1" /> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果:

test:使用div构造一个表格:
示例代码:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> .dtable{ display: table; width: 50%; margin: 0 auto; } .dtr{ display: table-row; } .dtd{ display: table-cell; border: 1px solid gray; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="dtable"> <div class="dtr"> <div class="dtd">td11</div> <div class="dtd">td12</div> &以上是关于多种居中方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
