排序---归并排序
Posted Pearl_zhen
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了排序---归并排序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
写在前面的话:
一枚自学Java和算法的工科妹子。
- 算法学习书目:算法(第四版) Robert Sedgewick
- 算法视频教程:Coursera Algorithms Part1&2
本文是根据《算法(第四版)》的个人总结,如有错误,请批评指正。

图1 原地归并的抽象方法的轨迹
1 private static void merge(Comparable[] a,int lo, int mid, int hi) { 2 // precondition: a[lo .. mid] and a[mid+1 .. hi] are sorted subarrays 3 assert isSorted(a, lo, mid); 4 assert isSorted(a, mid+1, hi); 5 6 // 将a[lo..hi]复制到aux[lo..hi],注意这里的aux[]是全局变量,在方法外已经声明。 7 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 8 aux[k] = a[k]; 9 } 10 11 // 归并回a[lo..hi] 12 int i = lo, j = mid+1; 13 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 14 if (i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++]; 15 else if (j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++]; 16 else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) a[k] = aux[j++]; 17 else a[k] = aux[i++]; 18 } 19 20 // postcondition: a[lo .. hi] is sorted 21 assert isSorted(a, lo, hi); 22 }
三、自顶向下的归并排序
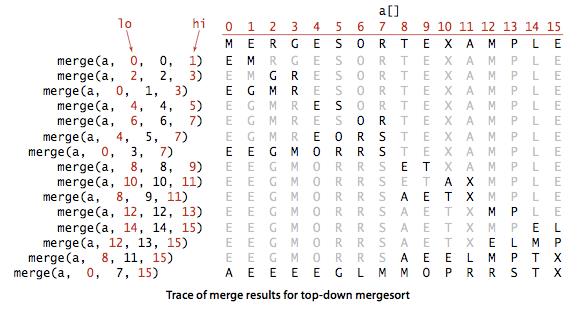

图2 自顶向下的归并排序的调用轨迹
1 public class Merge { 2 3 // This class should not be instantiated. 4 private Merge() { } 5 private static Comparable[] aux ; 6 7 // stably merge a[lo .. mid] with a[mid+1 ..hi] using aux[lo .. hi] 8 private static void merge(Comparable[] a, int lo, int mid, int hi) { 9 // precondition: a[lo .. mid] and a[mid+1 .. hi] are sorted subarrays 10 assert isSorted(a, lo, mid); 11 assert isSorted(a, mid+1, hi); 12 13 // copy to aux[] 14 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 15 aux[k] = a[k]; 16 } 17 18 // merge back to a[] 19 int i = lo, j = mid+1; 20 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 21 if (i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++]; 22 else if (j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++]; 23 else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) a[k] = aux[j++]; 24 else a[k] = aux[i++]; 25 } 26 27 // postcondition: a[lo .. hi] is sorted 28 assert isSorted(a, lo, hi); 29 } 30 31 public static void sort(Comparable[] a) { 32 aux = new Comparable[a.length]; 33 sort(a, 0, a.length-1); 34 assert isSorted(a); 35 } 36 37 // mergesort a[lo..hi] using auxiliary array aux[lo..hi] 38 private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) { 39 if (hi <= lo) return; 40 int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; 41 sort(a, lo, mid); 42 sort(a, mid + 1, hi); 43 merge(a, lo, mid, hi); 44 } 45 46 // is v < w ? 47 private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) { 48 return v.compareTo(w) < 0; 49 } 50 51 private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) { 52 return isSorted(a, 0, a.length - 1); 53 } 54 55 private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) { 56 for (int i = lo + 1; i <= hi; i++) 57 if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) return false; 58 return true; 59 } 60 61 // print array to standard output 62 private static void show(Comparable[] a) { 63 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { 64 StdOut.println(a[i]); 65 } 66 } 67 }
自顶向下归并排序的性能分析:
对于长度为N的任意数组,自顶向下的归并排序需要1/2NlgN至NlgN次比较和6NlgN次访问数组;
(1)比较次数为1/2NlgN至NlgN次的证明(三种证明方法):
- Proof 1:
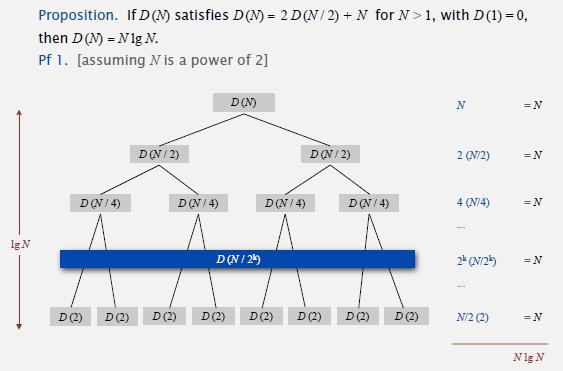
- Proof 2:

- Proof 3:

(2)访问数组为6NlgN次证明:每次归并最多需要访问数组次数为6N,其中2N次用来复制,2N次用来比较,2N次用来将比较出来的元素移动会a[].
四、自顶向下的归并排序

图3 自底向上的归并排序的归并结果
1 public class MergeBU { 2 3 // This class should not be instantiated. 4 private MergeBU() { } 5 private static Comparable[] aux; 6 7 // stably merge a[lo..mid] with a[mid+1..hi] using aux[lo..hi] 8 private static void merge(Comparable[] a, int lo, int mid, int hi) { 9 10 // copy to aux[] 11 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 12 aux[k] = a[k]; 13 } 14 15 // merge back to a[] 16 int i = lo, j = mid+1; 17 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 18 if (i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++]; // this copying is unneccessary 19 else if (j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++]; 20 else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) a[k] = aux[j++]; 21 else a[k] = aux[i++]; 22 } 23 24 } 25 26 27 public static void sort(Comparable[] a) { 28 int n = a.length; 29 aux = new Comparable[n]; 30 for (int len = 1; len < n; len *= 2) { 31 for (int lo = 0; lo < n-len; lo += len+len) { 32 merge(a, lo, lo+len-1, Math.min(lo+len+len-1, n-1)); 33 } 34 } 35 assert isSorted(a); 36 } 37 38 // is v < w ? 39 private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) { 40 return v.compareTo(w) < 0; 41 } 42 43 private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) { 44 for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) 45 if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) return false; 46 return true; 47 } 48 49 // print array to standard output 50 private static void show(Comparable[] a) { 51 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { 52 StdOut.println(a[i]); 53 } 54 } 55 }
自底向上归并排序的性能分析:
对于长度为N的任意数组,自底向上的归并排序需要1/2NlgN至NlgN次比较和6NlgN次访问数组;
五、归并排序优化
(1)节省时间(不将元素复制到辅助数组):在递归调用的每个层次交换数组和辅助数组的角色;
(2)将小数组排序改用插入排序;
(3)比较左边数组的最大值和右边数组的最小值的大小,如果小于,则不需要在归并。
优化后的代码如下:
1 public class MergeX { 2 private static final int CUTOFF = 7; // cutoff to insertion sort 3 4 // This class should not be instantiated. 5 private MergeX() { } 6 7 private static void merge(Comparable[] src, Comparable[] dst, int lo, int mid, int hi) { 8 9 // precondition: src[lo .. mid] and src[mid+1 .. hi] are sorted subarrays 10 assert isSorted(src, lo, mid); 11 assert isSorted(src, mid+1, hi); 12 13 int i = lo, j = mid+1; 14 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 15 if (i > mid) dst[k] = src[j++]; 16 else if (j > hi) dst[k] = src[i++]; 17 else if (less(src[j], src[i])) dst[k] = src[j++]; // to ensure stability 18 else dst[k] = src[i++]; 19 } 20 21 // postcondition: dst[lo .. hi] is sorted subarray 22 assert isSorted(dst, lo, hi); 23 } 24 25 private static void sort(Comparable[] src, Comparable[] dst, int lo, int hi) { 26 // if (hi <= lo) return; 27 if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) { 28 insertionSort(dst, lo, hi); 29 return; 30 } 31 int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; 32 sort(dst, src, lo, mid); 33 sort(dst, src, mid+1, hi); 34 35 // if (!less(src[mid+1], src[mid])) { 36 // for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) dst[i] = src[i]; 37 // return; 38 // } 39 40 // using System.arraycopy() is a bit faster than the above loop 41 if (!less(src[mid+1], src[mid])) { 42 System.arraycopy(src, lo, dst, lo, hi - lo + 1); 43 return; 44 } 45 46 merge(src, dst, lo, mid, hi); 47 } 48 49 50 public static void sort(Comparable[] a) { 51 Comparable[] aux = a.clone(); 52 sort(aux, a, 0, a.length-1); 53 assert isSorted(a); 54 } 55 56 // sort from a[lo] to a[hi] using insertion sort 57 private static void insertionSort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) { 58 for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) 59 for (int j = i; j > lo && less(a[j], a[j-1]); j--) 60 exch(a, j, j-1); 61 } 62 63 // exchange a[i] and a[j] 64 private static void exch(Object[] a, int i, int j) { 65 Object swap = a[i]; 66 a[i] = a[j]; 67 a[j] = swap; 68 } 69 70 // is a[i] < a[j]? 71 private static boolean less(Comparable a, Comparable b) { 72 return a.compareTo(b) < 0; 73 } 74 75 // is a[i] < a[j]? 76 private static boolean less(Object a, Object b, Comparator comparator) { 77 return comparator.compare(a, b) < 0; 78 } 79 80 public static void sort(Object[] a, Comparator comparator) { 81 Object[] aux = a.clone(); 82 sort(aux, a, 0, a.length-1, comparator); 83 assert isSorted(a, comparator); 84 } 85 86 private static void merge(Object[] src, Object[] dst, int lo, int mid, int hi, Comparator comparator) { 87 88 // precondition: src[lo .. mid] and src[mid+1 .. hi] are sorted subarrays 89 assert isSorted(src, lo, mid, comparator); 90 assert isSorted(src, mid+1, hi, comparator); 91 92 int i = lo, j = mid+1; 93 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 94 if (i > mid) dst[k] = src[j++]; 95 else if (j > hi) dst[k] = src[i++]; 96 else if (less(src[j], src[i], comparator)) dst[k] = src[j++]; 97 else dst[k] = src[i++]; 98 } 99 100 // postcondition: dst[lo .. hi] is sorted subarray 101 assert isSorted(dst, lo, hi, comparator); 102 } 103 104 105 private static void sort(Object[] src, Object[] dst, int lo, int hi, Comparator comparator) { 106 // if (hi <= lo) return; 107 if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) { 108 insertionSort(dst, lo, hi, comparator); 109 return; 110 } 111 int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; 112 sort(dst, src, lo, mid, comparator); 113 sort(dst, src, mid+1, hi, comparator); 114 115 // using System.arraycopy() is a bit faster than the above loop 116 if (!less(src[mid+1], src[mid], comparator)) { 117 System.arraycopy(src, lo, dst, lo, hi - lo + 1); 118 return; 119 } 120 121 merge(src, dst, lo, mid, hi, comparator); 122 } 123 124 // sort from a[lo] to a[hi] using insertion sort 125 private static void insertionSort(Object[] a, int lo, int hi, Comparator comparator) { 126 for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) 127 for (int j = i; j > lo && less(a[j], a[j-1], comparator); j--) 128 exch(a, j, j-1); 129 } 130 131 private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) { 132 return isSorted(a, 0, a.length - 1); 133 } 134 135 private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) { 136 for (int i = lo + 1; i <= hi; i++) 137 if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) return false; 138 return true; 139 } 140 141 private static boolean isSorted(Object[] a, Comparator comparator) { 142 return isSorted(a, 0, a.length - 1, comparator); 143 } 144 145 private static boolean isSorted(Object[] a, int lo, int hi, Comparator comparator) { 146 for (int i = lo + 1; i <= hi; i++) 147 if (less(a[i], a[i-1], comparator)) return false; 148 return true; 149 } 150 151 // print array to standard output 152 private static void show(Object[] a) { 153 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { 154 StdOut.println(a[i]); 155 } 156 } 157 }
六、归并排序总结
归并排序是一种渐进最优的基于比较的排序算法,归并排序在最坏的情况下的比较次数为~NlgN,这是其他排序算法复杂度的上限。详细证明可以见算法(第四版)pp.177-178
作者: 邹珍珍(Pearl_zhen)
出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/zouzz/
声明:本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出 原文链接 如有问题, 可邮件(zouzhenzhen@seu.edu.cn)咨询.
以上是关于排序---归并排序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章