Quoit Design(最近点对+分治)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Quoit Design(最近点对+分治)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1007
Quoit Design
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 42865 Accepted Submission(s): 11128
In the field of Cyberground, the position of each toy is fixed, and the ring is carefully designed so it can only encircle one toy at a time. On the other hand, to make the game look more attractive, the ring is designed to have the largest radius. Given a configuration of the field, you are supposed to find the radius of such a ring.
Assume that all the toys are points on a plane. A point is encircled by the ring if the distance between the point and the center of the ring is strictly less than the radius of the ring. If two toys are placed at the same point, the radius of the ring is considered to be 0.
最近点对问题:
分治的思想,如果是大于3个点的时候,将所有的点按照x坐标(或者y坐标)排序,然后从中间线一份两半,分别求出左边的点的最近点距ldis,和右边点的最近点距rdis,那么问题就是要将两个部分的点合起来,令dis = min(rdis,ldis);那么中间如果想出现最近点对的时候必须要出现在中间线两侧距离为d的区域内,那么考虑区域内的左侧的点,与其产生最近点的点一定在坐标的右侧,那么为了不用枚举区域内右边所有的点,就要考虑对于每个点它如果要产生距离小于dis的对应点,肯定是在以它为圆心的dis为半径的园内,那么这个圆覆盖这个带状区域面积最大的情况就是圆心在分界线上的时候。如图
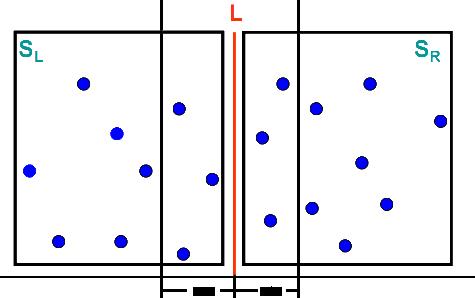
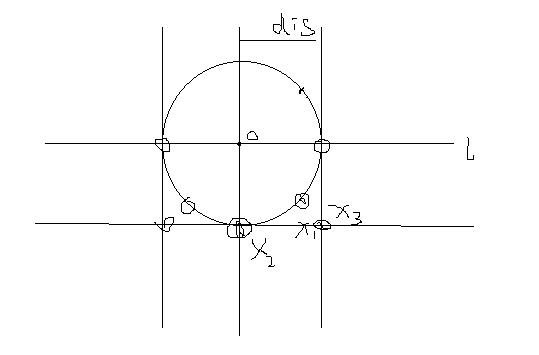
注意:在处理中间带的时候将带状区域内的点按照y坐标排序(如果之前是按照y排序的,则现在按照x坐标排序)那么因为右侧的任意两点之间的距离要大于等于dis所以要想极限情况,就是在这个圆区域内找等边三角形,因为从上到下处理的点,所以当前点的上方的点不在考虑,由于排序的时候是左右两边的点一起排序的所以要在当前点的编号向后处理7个点,如上图中划出的三个点,如果发现他们来自同一侧则不再处理
下面是模板代码:
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 #define N 100005 9 const int L = -1; 10 const int R = 1; 11 struct Node{ 12 int id; 13 double x; 14 double y; 15 }; 16 Node num[N],cp[N]; 17 18 //double Dis(Node a, Node b){ 19 // return sqrt(pow((a.x - b.x),2.0)+pow((a.y-b.y),2.0)); 20 //} 21 double Dis(Node a, Node b){ 22 double x = a.x-b.x, y = a.y-b.y; 23 return sqrt(x*x+y*y); 24 } 25 26 27 bool cmpx(Node a, Node b) 28 { 29 if(a.x==b.x) return a.y<b.y; 30 else return a.x < b.x; 31 } 32 bool cmpy(Node a, Node b) 33 { 34 if(a.y==b.y) return a.x<b.x; 35 else return a.y<b.y; 36 } 37 double solve(int low, int high) 38 { 39 double dis; 40 int sum = high - low; 41 if(sum == 0){ return 0; }//只有一个数 42 else if(sum == 1){//两个数 43 dis = Dis(num[low],num[high]); 44 } 45 else if(sum == 2){//三个数 46 double tm1,tm2,tm3; 47 tm1 = Dis(num[low],num[low+1]); 48 tm2 = Dis(num[low+1],num[high]); 49 tm3 = Dis(num[low],num[high]); 50 dis = min(tm1,min(tm2,tm3)); 51 } 52 else //大于三个数 53 { 54 double lmin,rmin,mmin; 55 int mid = (low+high)/2; 56 int p = 0; 57 int i, j; 58 lmin = solve(low,mid); 59 rmin = solve(mid+1,high); 60 dis = min(lmin,rmin); 61 /**-----------------提出来会变快-----------------*/ 62 double ldis = num[mid].x-dis; 63 double rdis = num[mid].x+dis; 64 for( i = low; i <= mid; i++) /**-----小于等于,不能是小于,因为下面标记 L R 了*/ 65 { 66 if(num[i].x >= ldis) 67 { 68 cp[p].id = L;//标记为属于左边的部分 69 cp[p].x = num[i].x; 70 cp[p].y = num[i].y; 71 p++; 72 } 73 } 74 for( ; i <= high; i++) 75 { 76 if(num[i].x <= rdis) 77 { 78 cp[p].id = R;//标记为右边的点 79 cp[p].x = num[i].x; 80 cp[p].y = num[i].y; 81 p++; 82 } 83 } 84 sort(cp,cp+p,cmpy); 85 for( i = 0; i < p; i++) 86 { 87 for( j = 1; (j <= 7)&&(i+j)<p; j++) 88 { 89 if(cp[i].id != cp[i+j].id)//最小值可能出现在分界线不同的两边 90 { 91 mmin = Dis(cp[i],cp[i+j]); 92 if(mmin<dis) 93 dis = mmin; 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 } 98 return dis; 99 } 100 int main() 101 { 102 int n; 103 while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n!=0) 104 { 105 double result = 0; 106 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 107 { 108 num[i].id = 0; 109 scanf("%lf%lf",&num[i].x,&num[i].y); 110 } 111 sort(num,num+n,cmpx); 112 result = solve(0,n-1); 113 printf("%.2f\n",result/2); 114 } 115 return 0; 116 }
下面是一开始wa的代码:
对应的错误在上面代码中用用/** -------*标识

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 #define N 100005 8 const int L = -1; 9 const int R = 1; 10 struct Node{ 11 int id; 12 double x; 13 double y; 14 }; 15 Node num[N],cp[N]; 16 17 double Dis(Node a, Node b){ 18 return sqrt(pow((a.x - b.x),2.0)+pow((a.y-b.y),2.0)); 19 } 20 21 bool cmpx(Node a, Node b) 22 { 23 if(a.x==b.x) return a.y<b.y; 24 else return a.x < b.x; 25 } 26 bool cmpy(Node a, Node b) 27 { 28 if(a.y==b.y) return a.x<b.x; 29 else return a.y<b.y; 30 } 31 32 double solve(int low, int high) 33 { 34 double dis; 35 int sum = high - low; 36 if(sum == 0){ return 0; }//只有一个数 37 else if(sum == 1){//两个数 38 dis = Dis(num[low],num[high]); 39 } 40 else if(sum == 2){//三个数 41 double tm1,tm2,tm3; 42 tm1 = Dis(num[low],num[low+1]); 43 tm2 = Dis(num[low+1],num[high]); 44 tm3 = Dis(num[low],num[high]); 45 dis = min(tm1,min(tm2,tm3)); 46 } 47 else //大于三个数 48 { 49 double lmin,rmin,mmin; 50 int mid = (low+high)/2; 51 int p = 0; 52 int i, j; 53 lmin = solve(low,mid); 54 rmin = solve(mid+1,high); 55 dis = min(lmin,rmin); 56 for( i = low; i < mid; i++) 57 { 58 double ldis = num[mid].x - dis; 59 if(num[i].x >= ldis) 60 { 61 cp[p].id = L;//标记为属于左边的部分 62 cp[p].x = num[i].x; 63 cp[p].y = num[i].y; 64 p++; 65 } 66 } 67 for( ; i < high; i++) 68 { 69 double rdis = num[mid].x+dis; 70 if(num[i].x <= rdis) 71 { 72 cp[p].id = R;//标记为右边的点 73 cp[p].x = num[i].x; 74 cp[p].y = num[i].y; 75 p++; 76 } 77 } 78 sort(cp,cp+p,cmpy); 79 for( i = 0; i < p; i++) 80 { 81 for( j = 1; (j <= 7)&&(i+j)<p; j++) 82 { 83 if(cp[i].id != cp[i+j].id)//最小值可能出现在分界线不同的两边 84 { 85 mmin = Dis(cp[i],cp[i+j]); 86 if(mmin<dis) 87 dis = mmin; 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 } 92 return dis; 93 } 94 int main() 95 { 96 int n; 97 while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n!=0) 98 { 99 double result = 0; 100 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 101 { 102 num[i].id = 0; 103 scanf("%lf%lf",&num[i].x,&num[i].y); 104 } 105 sort(num,num+n,cmpx); 106 result = solve(0,n-1); 107 printf("%.2f\n",result/2); 108 } 109 return 0; 110 }
下面给出大神的模板代码:(虽然内容差不多,感觉一下代码风格)
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cmath> 4 using namespace std; 5 #define N 100007 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 struct Point 10 { 11 double x,y; 12 }pt[N]; 13 int a[N]; 14 15 int n; 16 17 bool cmp(Point a, Point b) 18 { 19 if (a.x != b.x) return a.x < b.x; 20 else return a.y < b.y; 21 } 22 bool cmp_y(int id1, int id2){ 23 return pt[id1].y < pt[id2].y; 24 } 25 double getDis(const Point &a, const Point &b) 26 { 27 double x = a.x - b.x; 28 double y = a.y - b.y; 29 return sqrt(x*x + y*y); 30 } 31 double solve(int l, int r) 32 { 33 double ans = 0; 34 if (r - l + 1 <= 3) 35 { 36 if (r - l + 1 == 1) return ans; 37 ans = getDis(pt[l], pt[l + 1]); 38 if (r - l + 1 == 2) return ans; 39 for (int i = l; i < r; ++i) 40 { 41 for (int j = i + 1; j <= r; ++j) 42 { 43 ans = min(ans, getDis(pt[i],pt[j])); 44 } 45 } 46 return ans; 47 } 48 int m = (l + r) >> 1; 49 double s1 = solve(l, m); 50 double s2 = solve(m + 1, r); 51 ans = min(s1,s2); 52 int k = 0; 53 for (int i = m - 1; i >= l && pt[m].x - pt[i].x <= ans; --i) a[k++] = i; 54 for (int i = m + 1; i <= r && pt[i].x - pt[m].x <= ans; ++i) a[k++] = i; 55 sort(a, a + k, cmp_y); 56 for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) 57 { 58 for (int j = i + 1; j < k && j <= i + 7; ++j) 59 { 60 ans = min(ans, getDis(pt[a[i]], pt[a[j]])); 61 } 62 } 63 return ans; 64 } 65 int main() 66 { 67 while (~scanf("%d",&n)) 68 { 69 if (!n) break; 70 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) scanf("%lf%lf",&pt[i].x, &pt[i].y); 71 sort(pt, pt + n, cmp); 72 printf("%.2lf\n",solve(0, n - 1)/2.0); 73 } 74 return 0; 75 }
以上是关于Quoit Design(最近点对+分治)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
