canny算法的实现
Posted Lammy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了canny算法的实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Canny边缘检测首先要对图像进行高斯去噪,前面讲到了高斯去噪处理,这里从对图像灰度进行微分运算讲起吧。微分运算常用的方法是利用模板算子,把模板中心对应到图像的每一个像素位置,然后按照模板对应的公式对中心像素和它周围的像素进行数学运算,算出图像对应像素点的值实验中模板矩阵选取了Laplacian算子[44]、Soble算子、Roberts算子。拉普拉兹算子是2阶微分算子,它的精度还算比较高,但对噪声过于敏感,有噪声的情况下效果很差。罗伯特算子在光照不均匀时候效果也很差,针对噪声影响也较为敏感。下面以较为简单的模板作为样例做出讲解:
1、计算x和y方向的梯度值从而得到灰度的梯度幅值和梯度方向
Gx=(hd[x][y+1]-hd[x][y]+hd[x+1][y+1]-hd[x+1][y])/2;
Gy=(hd[x][y]-hd[x+1][y]+hd[x][y+1]-hd[x+1][y+1])/2;
G[x][y]=(int)Math.sqrt(Gy*Gy+Gx*Gx);
angle[x][y]=Math.atan2(Gy,Gx);
2、高低阈值的选取。通常canny算子的高阈值Th和低阈值Tl的0.4,Tl=0.4*Th,而高阈值根据二值化的目的选择不同的值,先验知识通常Th选择方式:梯度幅值矩阵统计在梯度值,将所有梯度累加求和,取在q%(q%在0.75-0.85之间)的那个振幅值作为高阈值。
3、非极大值抑制,这是边缘检测的关键,是将区域内的梯度振幅值的极值当作边缘点,如下图:
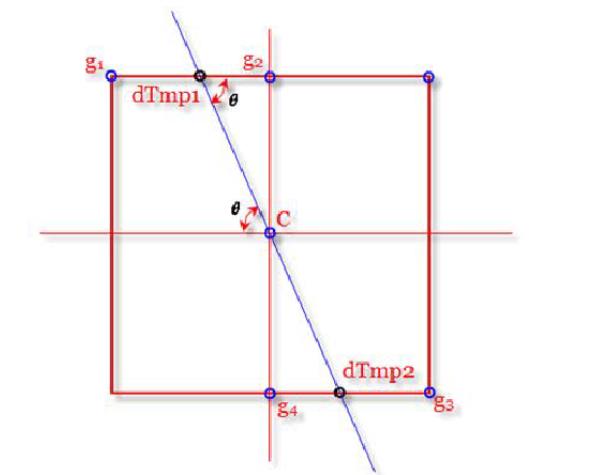
对整个梯度振幅图扫描,如图若(x,y)的点大于dTmp1点和dTmp2的振幅则将(x,y)视为预选边缘点,将起值置为255。由图可以看出dTmp1点振幅值可以G(g1) + (1-cot(sigma)) *(G(g2)-G(g1))同理可以得到dTmp2点的梯度振幅值。G这样得到一个预选边缘点矩阵:
int [][] mayEdgeMatrix = getMaxmaiLimitMatrix(Gxy,angle);
4、扫描mayEdgeMatrix里所有预选边缘点,将梯度振幅大于等于Th的则视为边缘点置为255;将低于Tl的直接置为0,视为非边缘点;介于Tl、Th之间的的置为125,视为待检测点。这样得到了一个初步的边缘图点。
5、边缘连接,对上一部得到的图像进行扫描,将255周围的8领域点进行检测,若有为125的视为边缘点,置为255,再以这些新置为255的点8领域查找待检测点,若有就将其置为255,直到没有新的边缘点产生为止。
下面给出实现的类,在下面会给出调用的方法和相应的activity

package com.example.lammy.imagetest; import android.graphics.Bitmap; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * Created by Lammy on 2016/11/12. */ public class MyCanny { private int Th; private int Tl; private float ratioOfTh; private Bitmap bitmap; private int h, w; private int[][] Gxy; private double[][] angle; private static int mayEdgePointGrayValue = 125; public MyCanny(Bitmap bitmap, float ratioOfTh) { this.bitmap = bitmap; this.ratioOfTh = ratioOfTh; init(); } private void init() { h = bitmap.getHeight(); w = bitmap.getWidth(); Gxy = new int[h][w]; angle = new double[h][w]; } //得到高斯模板矩阵 public float[][] get2DKernalData(int n, float sigma) { int size = 2 * n + 1; float sigma22 = 2 * sigma * sigma; float sigma22PI = (float) Math.PI * sigma22; float[][] kernalData = new float[size][size]; int row = 0; for (int i = -n; i <= n; i++) { int column = 0; for (int j = -n; j <= n; j++) { float xDistance = i * i; float yDistance = j * j; kernalData[row][column] = (float) Math .exp(-(xDistance + yDistance) / sigma22) / sigma22PI; column++; } row++; } return kernalData; } //获得图的灰度矩阵 public int[][] getGrayMatrix(Bitmap bitmap) { int h = bitmap.getHeight(); int w = bitmap.getWidth(); int grayMatrix[][] = new int[h][w]; for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) { int argb = bitmap.getPixel(j, i); int r = (argb >> 16) & 0xFF; int g = (argb >> 8) & 0xFF; int b = (argb >> 0) & 0xFF; int grayPixel = (int) (r + g + b) / 3; grayMatrix[i][j] = grayPixel; } return grayMatrix; } //获得高斯模糊后的灰度矩阵 public int[][] GS(int[][] hd, int size, float sigma) { float[][] gs = get2DKernalData(size, sigma); int outmax = 0; int inmax = 0; for (int x = size; x < w - size; x++) for (int y = size; y < h - size; y++) { float hc1 = 0; if (hd[y][x] > inmax) inmax = hd[y][x]; for (int k = -size; k < size + 1; k++) for (int j = -size; j < size + 1; j++) { hc1 = gs[size + k][j + size] * hd[y + j][x + k] + hc1; } hd[y][x] = (int) (hc1); if (outmax < hc1) outmax = (int) (hc1); } float rate = inmax / outmax; for (int x = size; x < w - size; x++) for (int y = size; y < h - size; y++) { hd[y][x] = (int) (hd[y][x] * rate); } return hd; } //获得Gxy 和angle即梯度振幅和梯度方向 public void getGxyAndAngle(int[][] Gs) { for (int x = 1; x < h - 1; x++) for (int y = 1; y < w - 1; y++) { int Gx = (Gs[x][y + 1] - Gs[x][y] + Gs[x + 1][y + 1] - Gs[x + 1][y]) / 2;//hd[x][y+1]-hd[x][y];// int Gy = (Gs[x][y] - Gs[x + 1][y] + Gs[x][y + 1] - Gs[x + 1][y + 1]) / 2;//hd[x+1][y]-hd[x][y];// //另外一种算子 // int Gx = (Gs[x - 1][y + 1] + 2 * Gs[x][y + 1] // + Gs[x + 1][y + 1] - Gs[x - 1][y - 1] - 2 // * Gs[x][y - 1] - Gs[x + 1][y - 1]) / 4; // int Gy=(Gs[x-1][y-1]+2*Gs[x-1][y]+Gs[x-1][y+1]-Gs[x+1][y-1]-2*Gs[x+1][y]-Gs[x+1][y+1])/4; //G[x][y]=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(Gx, 2)+Math.pow(Gy, 2)); Gxy[x][y] = (int) Math.sqrt(Gy * Gy + Gx * Gx); angle[x][y] = Math.atan2(Gy, Gx); //将梯度方向值转向(0,2*PI) if (angle[x][y] < 0) { angle[x][y] = angle[x][y] + 2 * Math.PI; } } } //非极大值抑制,将极值点存到edge边缘矩阵中,极值点是可能为边缘的点 public int[][] getMaxmaiLimitMatrix(int[][]Gxy,double[][]angle) { int[][] edge =new int[h][w]; for (int x = 0; x < h - 1; x++) for (int y = 0; y < w - 1; y++) { double angle1 = angle[x][y] / (Math.PI); if ((angle1 > 0 && angle1 <= 0.25) | (angle1 > 1 && angle1 <= 1.25)) { double dTmp1 = Gxy[x][y + 1] + Math.abs(Math.tan(angle[x][y]) * (Gxy[x - 1][y + 1] - Gxy[x][y + 1])); double dTmp2 = Gxy[x][y - 1] + Math.abs(Math.tan(angle[x][y]) * (Gxy[x + 1][y - 1] - Gxy[x][y - 1])); double dTmp = Gxy[x][y]; if (dTmp > dTmp1 && dTmp > dTmp2) edge[x][y] = 255; } if ((angle1 <= 2 && angle1 > 1.75) | (angle1 <= 1 && angle1 > 0.75)) { double dTmp1 = Gxy[x][y + 1] + Math.abs(Math.tan(angle[x][y])) * (Gxy[x + 1][y + 1] - Gxy[x][y + 1]); double dTmp2 = Gxy[x][y - 1] + Math.abs(Math.tan(angle[x][y])) * (Gxy[x - 1][y - 1] - Gxy[x][y - 1]); double dTmp = Gxy[x][y]; if (dTmp > dTmp1 && dTmp > dTmp2) edge[x][y] = 255; } if ((angle1 > 1 / 4 && angle1 <= 0.5) | (angle1 > 5 / 4 && angle1 <= 1.5)) { double dTmp1 = Gxy[x - 1][y] + Math.abs(1 / Math.tan(angle[x][y])) * (Gxy[x - 1][y + 1] - Gxy[x - 1][y]); double dTmp2 = Gxy[x + 1][y] + Math.abs(1 / Math.tan(angle[x][y])) * (Gxy[x + 1][y - 1] - Gxy[x + 1][y]); double dTmp = Gxy[x][y]; if (dTmp > dTmp1 && dTmp > dTmp2) edge[x][y] = 255; } if ((angle1 > 1.5 && angle1 <= 1.75) | (angle1 > 0.5 && angle1 <= 0.75)) { double dTmp1 = Gxy[x - 1][y] + Math.abs(1 / Math.tan(angle[x][y])) * (Gxy[x - 1][y - 1] - Gxy[x - 1][y]); double dTmp2 = Gxy[x + 1][y] + Math.abs(1 / Math.tan(angle[x][y])) * (Gxy[x + 1][y + 1] - Gxy[x + 1][y]); double dTmp = Gxy[x][y]; if (dTmp > dTmp1 && dTmp > dTmp2) edge[x][y] = 255; } } return edge; } public void ThTlLimitPoints(int [][] maxmaiLimitMatrix,int Th , int Tl) { //上面得到的为255的才可能是边缘点,下面根据高低阈值再次去掉小于Tl点,高于Th的仍然为255,定为边缘点,125的为预选点 for(int x=1;x<h-1;x++) for(int y=1;y<w-1;y++) { if(maxmaiLimitMatrix[x][y]==255) { if(Gxy[x][y]<Tl) maxmaiLimitMatrix[x][y]=0; if(Gxy[x][y]>Tl&&Gxy[x][y]<Th) maxmaiLimitMatrix[x][y]=mayEdgePointGrayValue; } } } //获得高阈值 private int getTh(int [][] Gxy) { //梯度振幅统计,因为通过计算振幅的最大值不超过500,因此用500的矩阵统计 int []amplitudeStatistics=new int[500]; for(int x=1;x<h-1;x++) for(int y=1;y<w-1;y++){ amplitudeStatistics[Gxy[x][y]]++; } int pointNumber=0; int max=0; for(int i=1;i<500;i++){ if(amplitudeStatistics[i]>0) { max=i; } pointNumber=pointNumber+amplitudeStatistics[i]; } int ThNumber=(int)(ratioOfTh*pointNumber); int ThCount=0; int Th=0; for(int i=1;i<=max;i++) { if(ThCount<ThNumber) ThCount=ThCount+amplitudeStatistics[i]; else { Th=i-1; break; } } return Th; } private int getTl(int Th) { return (int)(Th*0.4); } //canny算法的边缘连接 public void traceEdge(double maybeEdgePointGrayValue, int edge[][]){ int [][]liantongbiaoji = new int [h][w]; for(int i = 0 ; i < h ; i++) for(int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { if(edge[i][j]==255&&liantongbiaoji[i][j]==0) { if ((edge[i][j] >= maybeEdgePointGrayValue) && liantongbiaoji[i][j] == 0) { liantongbiaoji[i][j] = 1; LinkedList<Point> qu = new LinkedList<Point>(); qu.add(new Point(i, j)); while (!qu.isEmpty()) { Point cur = qu.removeFirst(); for (int a = -1; a <= 1; a++) for (int b = -1; b <= 1; b++) { if (cur.x + a >= 0 && cur.x + a < h && cur.y + b >= 0 && cur.y + b < w) { if (edge[cur.x + a][cur.y + b] >= maybeEdgePointGrayValue && liantongbiaoji[cur.x + a][cur.y + b] == 0) { qu.add(new Point(cur.x + a, cur.y + b)); liantongbiaoji[cur.x + a][cur.y + b] = 1; edge[cur.x + a][cur.y + b] = 255; } } } } } } } } //由灰度矩阵创建灰度图 public Bitmap createGrayImage(int[][]grayMatrix) { int h=grayMatrix.length; int w = grayMatrix[0].length; Bitmap bt=Bitmap.createBitmap(w, h, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888); for(int i=0;i<h;i++) for(int j=0;j<w;j++) { int grayValue=grayMatrix[i][j]; int color = ((0xFF << 24)+(grayValue << 16)+(grayValue << 8)+grayValue); bt.setPixel(j, i, color); } return bt; } public Bitmap getEdgeBitmap() { int grayMatrix[][] = getGrayMatrix(bitmap); int GS[][] = GS(grayMatrix , 1 , 0.6f); getGxyAndAngle(GS); Th = getTh(Gxy); int [][] mayEdgeMatrix = getMaxmaiLimitMatrix(Gxy,angle); Tl = getTl(Th); ThTlLimitPoints(mayEdgeMatrix , Th , Tl); traceEdge(mayEdgePointGrayValue , mayEdgeMatrix); for(int x=1;x<h-1;x++) for(int y=1;y<w-1;y++) { if(mayEdgeMatrix[x][y]!=255) mayEdgeMatrix[x][y]=0; } return createGrayImage(mayEdgeMatrix); } class Point { Point(int a, int b) { this.x = a; this.y = b; } int x; int y; } }
实现了上述算法移植到手机,发现在java平台上实现后运行效果非常好,而运行在手机端上效果很差。同样的算法为何结果相差如此之大呢?
经过一步步的排查,将每一步得到的数组打印到文件与java打印的数组比较,最终发现了原因,罪魁祸首就是安卓加载jpg、png甚至是bitmap到内存时图片的宽高都会变大,且比率不一定相同,这样导致我加载同一张图片时,android自动对图片进行了放大,导致手机的边缘更加模糊且无故增加了一些细节。为了解决这个问问题,我先获取未加载时候图片的宽高,在加载图片后再压缩回加载前图片的大小。 在acitiviy里有讲解,下面直接贴出代码:

package com.example.lammy.imagetest; import android.content.ContentResolver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.graphics.Bitmap; import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; import android.graphics.Matrix; import android.media.ThumbnailUtils; import android.net.Uri; import android.os.Environment; import android.provider.MediaStore; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.DisplayMetrics; import android.view.View; import android.widget.ImageView; import android.widget.Toast; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.Writer; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { ImageView imageView; Bitmap bt; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image); int scr =R.drawable.xl; //获取源图像的宽和高(因为android在加载图片到手机里的时候会使得图片宽高变大,且比率不一定一样,为了让其不变形必须记下加载前的图片宽高)再压缩回去 BitmapFactory.Options options=new BitmapFactory.Options(); options.inJustDecodeBounds=true;//(设为true 图片不加入内存效率高) BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),scr , options); int outWidth = options.outWidth; int outHeight = options.outHeight; System.out.println("jpg图原图"+outHeight+","+outWidth); options.inJustDecodeBounds=false; bt = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),scr ); System.out.println("加载后图:"+bt.getHeight()+","+bt.getWidth()); //将图片压缩到加载前的宽高,当然图片太大也可以宽高同比率压缩。 bt = ThumbnailUtils.extractThumbnail(bt,outWidth,outHeight); imageView.setImageBitmap(bt); // jpg图原图271,482 // 加载后图:711,1265 } public void click(View view) { MyCanny myCanny =new MyCanny(bt,0.85f); int Gs [][] =myCanny.GS(myCanny.getGrayMatrix(bt) , 1 , 0.6f); try { outPutArray(Gs ,"grayMatrix.txt"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Bitmap edge = myCanny.getEdgeBitmap(); edge = ThumbnailUtils.extractThumbnail(edge,1000,600); imageView.setImageBitmap(edge); } // 将数组写入到data目录 public void outPutArray(int[] [] a ,String filename) throws Exception { try { File file = new File("data/data/com.example.lammy.imagetest/files/"+filename); FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(file); BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fileWriter); int size = 15; for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++) { for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { String s = a[i][j] + " "; bw.write(s); bw.flush(); } bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.flush(); bw.close(); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm"); } } }
打印了一下加载图前后的大小:
jpg图原图271,482
加载后图:711,1265
发现加载到内存后放大了2.6倍左右(原因:decodeResource这个方法会根据drawable所在的资源目录适配不同的dpi,因此放大了),且为了适应手机屏幕的分辨率,宽高放大的比率不相等(相近),这导致了我们算法的效果变差的主要原因,因此我将图像压缩回加载前的大小,再使用canny算法边缘检测,效果就和java的差不多了。下面是效果:


原图的灰度图 边缘图
以上是关于canny算法的实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
