继承与接口
Posted IT瘦子
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了继承与接口相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一。运行TestInherits.java示例,观察输出,注意总结父类与子类之间构造方法的调用关系修改 Parent 构造方法的代码,显式调用 GrandParent 的另一个构造函数,注意这句调用代码是否是第一句,影响重大
1.代码:
class Grandparent{
public Grandparent(){
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string){
System.out.println("GandParean Created.string:"+string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent{
public Parent(){
//super("123456");
System.out.println("Parent Created.");
//super("123456");
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public Child(){
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Child c = new Child();
}
}
2.结果截图:
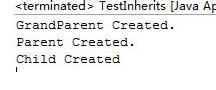

3.结果分析: 通过super调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
4.思索:为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
原因:构造函数(constructor)是一种特殊的方法 。主要用来在创建对象时初始化对象, 即为对象成员变量赋初始值,总与new运算符一起使用在创建对象的语句中 。特别的一个类可以有多个构造函数 ,可根据其参数个数的不同或参数类型的不同来区分它们 即构造函数的重载。构造函数的功能主要用于在类的对象创建时定义初始化的状态。构造一个对象,先调用其构造方法,来初始化其成员函数和成员变量.子类拥有父的成员变量和成员方法,如果不调用,则从父类继承而来的成员变量和成员方法得不到正确的初始化。不能反过来调用也是这个原因,因为父类根本不知道子类有神魔变量而且这样一来子类也得不到初始化的父类变量,导致程序运行出错!
二. 参看ExplorationJDKSource.java示例,此示例中定义了一个类A,它没有任何成员。class{}.
1.代码:
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
2.结果截图:
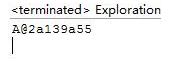
3.原因:main方法实际上调用的是: public void println(Object x),这一方法内部调用了String类的valueOf方法。
三.神奇的“+”号
1.代码:
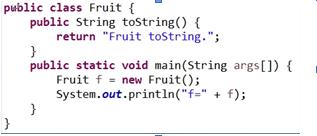
2.结果截图:
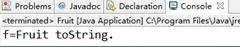
3.结论:Fruit类覆盖了Object类的toString方法。 在“+”运算中,当任何一个对象与一个String对象,连接时,会隐式地调用其toString()方法,默认情况下,此方法返回“类名 @ + hashCode”。为了返回有意义的信息,子类可以重写toString()方法。
四.方法覆盖的要点
1.代码:
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:"+string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent ()
{
super("dwjdancn");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class JC {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Child c= new Child();
}
}
2.结果截图:

3.方法覆盖的语法规则:
(1)覆盖方法的允许访问范围不能小于原方法。
(2)覆盖方法所抛出的异常不能比原方法更多。
(3)声明为final方法不允许覆盖。
例如,Object的getClass()方法不能覆盖。
4)不能覆盖静态方法。
以上是关于继承与接口的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章