HDU1253--胜利大逃亡--简单BFS
Posted Pic
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HDU1253--胜利大逃亡--简单BFS相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
胜利大逃亡
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 21759 Accepted Submission(s): 8538
魔王住在一个城堡里,城堡是一个A*B*C的立方体,可以被表示成A个B*C的矩阵,刚开始Ignatius被关在(0,0,0)的位置,离开城堡的门在(A-1,B-1,C-1)的位置,现在知道魔王将在T分钟后回到城堡,Ignatius每分钟能从一个坐标走到相邻的六个坐标中的其中一个.现在给你城堡的地图,请你计算出Ignatius能否在魔王回来前离开城堡(只要走到出口就算离开城堡,如果走到出口的时候魔王刚好回来也算逃亡成功),如果可以请输出需要多少分钟才能离开,如果不能则输出-1.
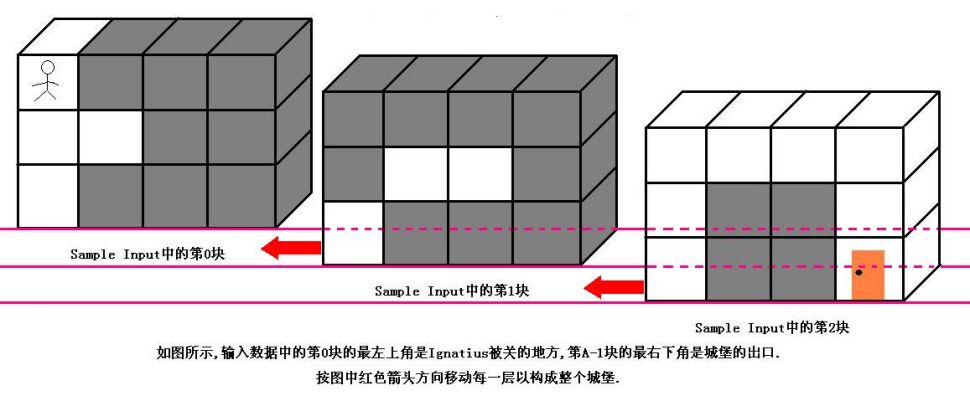
特别注意:本题的测试数据非常大,请使用scanf输入,我不能保证使用cin能不超时.在本OJ上请使用Visual C++提交.
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------
转自http://www.cnblogs.com/yuyixingkong/p/3245297.html
代码是我的..
本题是搜索题,从囚徒出发,搜索到出口的最短路线的距离值(或者反向,由出口开始,搜索到囚徒的位置的距离值),容易想到的是宽度优先搜索,首先将囚徒的点放入先进先出的一个队列,并记录走过的时间(或距离),以后不断地
(1)将队列中先进的元素推出,还原为实际储存点后,
(2)六向搜索通路点,并将搜索到的通路点放进先进先出队列。
(3)重复(1),(2),直到搜索到目标点(出口)或队列为空为止,前者只要搜索得的值低于题目给出的T值,就输出此值,其余情况输出-1;
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
本题目有几个大坑:
1,门有可能是墙壁;(墙壁不可出,但是一开始人站的地方是墙居然又可以)
2,题目给出的某些CASE的T值小于囚徒到门口的空间最短距离(A+B+C-3)。不要忘记-1的情况
3,开始可以是墙,不影响,
掉进去会使用时增多,如果你的搜索效率再不高的,就很可能超时了。
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1253
这道题没什么特别难的地方,只是有几个bug要注意一下
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<iomanip>
#include<queue>
#define INF 0x7ffffff
#define MAXN 51
using namespace std;
const double eps=1e-10;
int m[MAXN][MAXN][MAXN];
int dir[6][3]={{1,0,0},{-1,0,0},{0,1,0},{0,-1,0},{0,0,1},{0,0,-1}};
struct node
{
int a;
int b;
int c;
int n;
};
int vis[MAXN][MAXN][MAXN];
int x,y,z;
int a,b,c;
int n;
int nn;
bool ok()
{
if(x>=0&&x<a&&y>=0&&y<b&&z>=0&&z<c)
return 1;
else return 0;
}
int BFS()
{
queue<struct node> route;
struct node tem;
struct node buf;
buf.a=0;
buf.b=0;
buf.c=0;
buf.n=0;
vis[0][0][0]=1;
route.push(buf);
while(!route.empty()) {
//cout<<11111<<endl;
buf=route.front();
route.pop();
if(buf.a==a-1&&buf.b==b-1&&buf.c==c-1) {
return buf.n;
}
if(buf.n>n){
return -1;
}
//nn=buf.n+1;
for(int i=0; i<6; i++){
x=buf.a+dir[i][0];
y=buf.b+dir[i][1];
z=buf.c+dir[i][2];
if(ok()&&m[x][y][z]==0&&vis[x][y][z]==0) {
if(abs(x-a+1)+abs(y-a+1)+abs(z-c+1)+buf.n>n)//很棒的剪枝思路,见大坑2
continue;
vis[x][y][z]=1;
tem.a=x;
tem.b=y;
tem.c=z;
tem.n=buf.n+1;
route.push(tem);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("data2.in", "r", stdin);
#endif
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
int t;
int res=0;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
a=b=c=x=y=z=0;
nn=0;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
cin>>a>>b>>c>>n;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
for(int j=0;j<b;j++){
for(int k=0;k<c;k++){
cin>>m[i][j][k];
}
}
}
cout<<BFS()<<endl;
}
}
/*
5
3 3 4 20
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
0 1 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0
3 3 4 20
1 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
0 1 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0
3 3 4 20
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
0 1 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 1
3 3 4 10
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
0 1 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0
3 3 4 21
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 0
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0
*/
/*
11
11
-1
-1
-1
*/
还有一道一模一样的题目,在此也一并贴出
Asteroids!
| Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) |
| Total Submission(s): 114 Accepted Submission(s): 91 |
| |
|
Problem Description
You\'re in space.
You want to get home. There are asteroids. You don\'t want to hit them. |
|
Input
Input to this problem will consist of a (non-empty) series of up
to 100 data sets. Each data set will be formatted according to the
following description, and there will be no blank lines separating data
sets.
A single data set has 5 components: Start line - A single line, "START N", where 1 <= N <= 10. Slice list - A series of N slices. Each slice is an N x N matrix representing a horizontal slice through the asteroid field. Each position in the matrix will be one of two values: \'O\' - (the letter "oh") Empty space \'X\' - (upper-case) Asteroid present Starting Position - A single line, "A B C", denoting the <A,B,C> coordinates of your craft\'s starting position. The coordinate values will be integers separated by individual spaces. Target Position - A single line, "D E F", denoting the <D,E,F> coordinates of your target\'s position. The coordinate values will be integers separated by individual spaces. End line - A single line, "END" The origin of the coordinate system is <0,0,0>. Therefore, each component of each coordinate vector will be an integer between 0 and N-1, inclusive. The first coordinate in a set indicates the column. Left column = 0. The second coordinate in a set indicates the row. Top row = 0. The third coordinate in a set indicates the slice. First slice = 0. Both the Starting Position and the Target Position will be in empty space. |
|
Output
For each data set, there will be exactly one output set, and there will be no blank lines separating output sets.
A single output set consists of a single line. If a route exists, the line will be in the format "X Y", where X is the same as N from the corresponding input data set and Y is the least number of moves necessary to get your ship from the starting position to the target position. If there is no route from the starting position to the target position, the line will be "NO ROUTE" instead. A move can only be in one of the six basic directions: up, down, left, right, forward, back. Phrased more precisely, a move will either increment or decrement a single component of your current position vector by 1. |
|
Sample Input
START 1 O 0 0 0 0 0 0 END START 3 XXX XXX XXX OOO OOO OOO XXX XXX XXX 0 0 1 2 2 1 END START 5 OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO XXXXX XXXXX XXXXX XXXXX XXXXX OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO OOOOO 0 0 0 4 4 4 END |
|
Sample Output
1 0 3 4 NO ROUTE |
|
Source
South Central USA 2001
|
|
Recommend
zf
|
下面是AC代码
#include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <queue> using namespace std; char map[20][20][20]; int vis[20][20][20]; int n; int sx,sy,sz; int ex,ey,ez; int tx[] = {1,-1,0,0,0,0}; int ty[] = {0,0,1,-1,0,0}; int tz[] = {0,0,0,0,1,-1}; struct node { int x,y,z,step; }; int check(int x,int y,int z) { if(x<0 || y<0 || z<0 || x>=n || y>=n || z>=n || vis[x][y][z] ) return 0; return 1; } int bfs(int x,int y,int z) { int i; queue<node> Q; node a,next; a.x = x; a.y = y; a.z = z; a.step = 0; vis[x][y][z] = 1; Q.push(a); while(!Q.empty()) { a = Q.front(); Q.pop(); if(a.x == ex && a.y == ey && a.z == ez) return a.step; for(i = 0;i<6;i++) { next = a; next.x+=tx[i]; next.y+=ty[i]; next.z+=tz[i]; if(check(next.x,next.y,next.z)) { next.step++; vis[next.x][next.y][next.z] = 1; Q.push(next); } } } return -1; } int main() { char s[10]; int i,j,k; while(~scanf("%s%d",s,&n)) { for(i = 0;i<n;i++) for(j = 0;j<n;j++) scanf("%s",map[i][j]); scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d",&sx,&sy,&sz,&ex,&ey,&ez); scanf("%s",s); int ans = bfs(sx,sy,sz); if(ans>=0) printf("%d %d\\n",n,ans); else printf("NO ROUTE\\n"); } return 0; }
以上是关于HDU1253--胜利大逃亡--简单BFS的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
