多线程操作实例——生产者与消费者
Posted 静若飘絮
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多线程操作实例——生产者与消费者相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
面对多线程学习生产者与消费者是最基本的实例
对于java后端开发的人员必须要掌握,还有考研考试计算机操作系统的同鞋。
下面是三个实例对于生产者与消费者的的例子,层层递进,逐步解决问题。
问题:生产者——设置信息名字name,和内容content
消费者——负责取出设置的信息。
一、基本实现
由于线程的不确定性可能出现以下问题:
(1)消费者取出的信息不匹配,即不是由同一个生产者设置的信息
(2)生产者生产了多个信息,消费者才开始取出信息,或消费者取出的重复的信息。
上面的问题下面会逐一解决,下面先看出现问题的程序:
package li.xin.hua.ch9; /*线程生产者与向消费者最基本实现,问题有: * 1、数据不匹配 * 2、数据重复取出已经取过的数据*/ class Info{ private String name; private String content; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; } }; class Producer implements Runnable{ private Info info=null; public Producer(Info info){ this.info=info; } public void run(){ boolean flag=false; for(int i=0;i<10;++i) { if(flag){ this.info.setName("胡歌"); try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } this.info.setContent("林殊"); flag=false; }else{ this.info.setName("刘涛"); try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } this.info.setContent("郡主"); flag=true; } } } }; class Consumer implements Runnable{ private Info info=null; public Consumer(Info info){ this.info=info; } public void run(){ for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(this.info.getName()+"---饰演--->"+this.info.getContent()); } } }; public class Producer_Comsumer01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Info info=new Info(); Producer pro=new Producer(info); Consumer con=new Consumer(info); new Thread(pro).start(); new Thread(con).start(); } }
运行结果如下图:
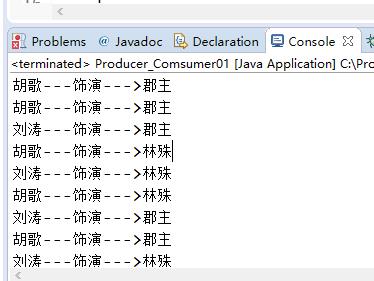
发现胡歌不仅饰演林殊,还饰演郡主,哈哈哈哈哈哈!
问题是线程生产的信息取出时是不匹配的,解决方法使用同步机制——synchronized
二、加入同步机制
将设置名称与内容定义在一个同步方法中,代码如下:
package li.xin.hua.ch9; /*线程生产者与向消费者最基本实现 * 1、数据不匹配通过同步机制已经解决 * 2、重复取数据问题还是有*/ class Info02{ private String name; private String content; public synchronized void get() { try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(this.name+"---饰演--->"+this.content); } public synchronized void set(String name,String content) { this.name=name; try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } this.content = content; } }; class Producer02 implements Runnable{ private Info02 info=null; public Producer02(Info02 info){ this.info=info; } public void run(){ boolean flag=false; for(int i=0;i<10;++i) { if(flag){ this.info.set("胡歌","林殊"); flag=false; }else{ this.info.set("刘涛","郡主"); flag=true; } } } }; class Consumer02 implements Runnable{ private Info02 info=null; public Consumer02(Info02 info){ this.info=info; } public void run(){ for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } this.info.get(); } } }; public class Producer_Comsumer02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Info02 info=new Info02(); Producer02 pro=new Producer02(info); Consumer02 con=new Consumer02(info); new Thread(pro).start(); new Thread(con).start(); } }
运行结果如下图:
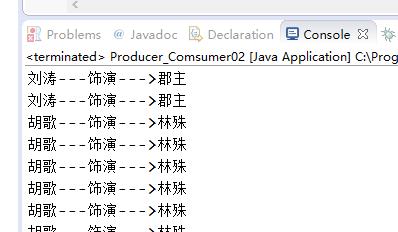
胡歌与刘涛饰演的角色没有匹配错误,但信息反复取出,需要Object类中的方法来解决。
三、加入等待唤醒机制
Object类中wait()、notify()方法,扩充点知识:wai()方法会释放线程的对象的锁,而sleep()方法不会。
设置一个标志位flag,
当flag为true时:
可以进行生产,但不能取出数据,若此时消费者线程恰巧抢到CPU资源,想要执行消费者程序,
必须将消费者线程等待wait()。生产者生产完成后要修改标示位(表示可以消费者可以取出信息了),和唤醒notify()被等待的线程。
当flag为false时:
消费者可以取出信息,但生产者不能生产信息,若此时生产者线程恰巧抢到CPU资源,想要执行生产者程序,
必须将生产者线程等待wait()。消费者完成取出信息后要修改标示位(表示可以生产者可以生产信息了),和唤醒notify()被等待的线程。
package li.xin.hua.ch9; /*线程生产者与向消费者最基本实现 * 1、数据不匹配通过同步机制已经解决 * 2、重复取数据问题通过等待唤醒机制已经解决 * 当flag为true时允许生产者生产,若此时消费者进入则要等待 * 当flag为false时允许消费者取出信息,若此时生产者进入则要等待*/ class Info03{ private String name; private String content; private boolean flag=true; /* 设置标示位:true是生产的时间,false是消费的时间。 第一次先生产*/ public synchronized void set(String name,String content) { if(!flag) /*现在不是生产的时间,线程要等待,唤醒后才能生产。*/ { try { super.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } this.name=name; try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } this.content = content; flag=false; super.notify(); } public synchronized void get() { if(flag) /*消费者*/ { try { super.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(this.name+"---饰演--->"+this.content); flag=true; super.notify(); } }; class Producer03 implements Runnable{ private Info03 info=null; public Producer03(Info03 info){ this.info=info; } public void run(){ boolean flag=false; for(int i=0;i<10;++i) { if(flag){ this.info.set("胡歌","林殊"); flag=false; }else{ this.info.set("刘涛","郡主"); flag=true; } } } }; class Consumer03 implements Runnable{ private Info03 info=null; public Consumer03(Info03 info){ this.info=info; } public void run(){ for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } this.info.get(); } } }; public class Producer_Comsumer03 { public static void main(String[] args) { Info03 info=new Info03(); Producer03 pro=new Producer03(info); Consumer03 con=new Consumer03(info); new Thread(pro).start(); new Thread(con).start(); } }
运行结果如下图:
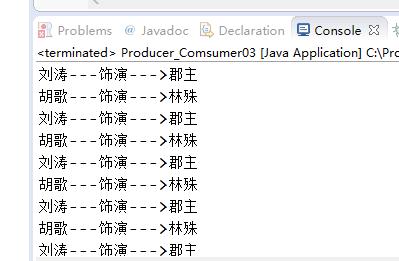
胡歌与刘涛交替出现,并且角色匹配正确。
以上是关于多线程操作实例——生产者与消费者的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章