最近晚上在家里看Algorithems,4th Edition,我买的英文版,觉得这本书写的比较浅显易懂,而且“图码并茂”,趁着这次机会打算好好学习做做笔记,这样也会印象深刻,这也是写这一系列文章的原因。另外普林斯顿大学在Coursera 上也有这本书同步的公开课,还有另外一门算法分析课,这门课程的作者也是这本书的作者,两门课都挺不错的。
计算机程序离不开算法和数据结构,本文简单介绍栈(Stack)和队列(Queue)的实现,.NET中与之相关的数据结构,典型应用等,希望能加深自己对这两个简单数据结构的理解。
1. 基本概念
概念很简单,栈 (Stack)是一种后进先出(last in first off,LIFO)的数据结构,而队列(Queue)则是一种先进先出 (fisrt in first out,FIFO)的结构,如下图:
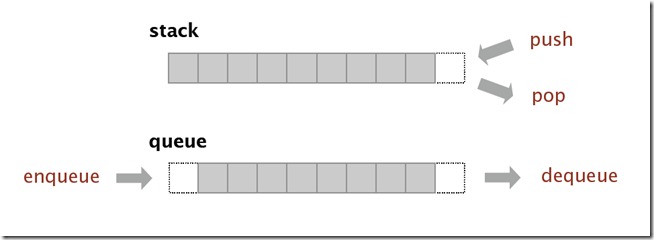
2. 实现
现在来看如何实现以上的两个数据结构。在动手之前,Framework Design Guidelines这本书告诉我们,在设计API或者实体类的时候,应当围绕场景编写API规格说明书。
1.1 Stack的实现
栈是一种后进先出的数据结构,对于Stack 我们希望至少要对外提供以下几个方法:

| Stack<T>() | 创建一个空的栈 |
| void Push(T s) | 往栈中添加一个新的元素 |
| T Pop() | 移除并返回最近添加的元素 |
| boolean IsEmpty() | 栈是否为空 |
| int Size() | 栈中元素的个数 |
要实现这些功能,我们有两中方法,数组和链表,先看链表实现:
栈的链表实现:
我们首先定义一个内部类来保存每个链表的节点,该节点包括当前的值以及指向下一个的值,然后建立一个节点保存位于栈顶的值以及记录栈的元素个数;
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
class Node{ public T Item{get;set;} public Node Next { get; set; }} |
|
1
2
|
private Node first = null;private int number = 0; |
现在来实现Push方法,即向栈顶压入一个元素,首先保存原先的位于栈顶的元素,然后新建一个新的栈顶元素,然后将该元素的下一个指向原先的栈顶元素。整个Pop过程如下:
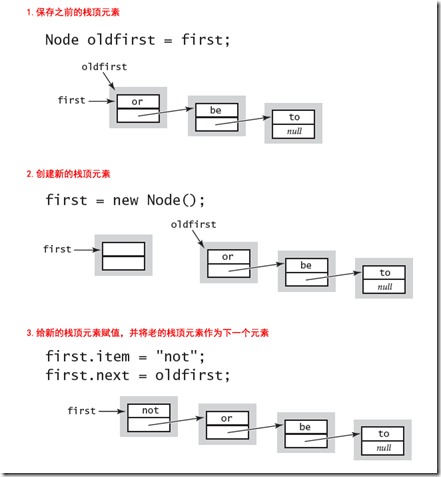
实现代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
void Push(T node){ Node oldFirst = first; first = new Node(); first.Item= node; first.Next = oldFirst; number++;} |
Pop方法也很简单,首先保存栈顶元素的值,然后将栈顶元素设置为下一个元素:
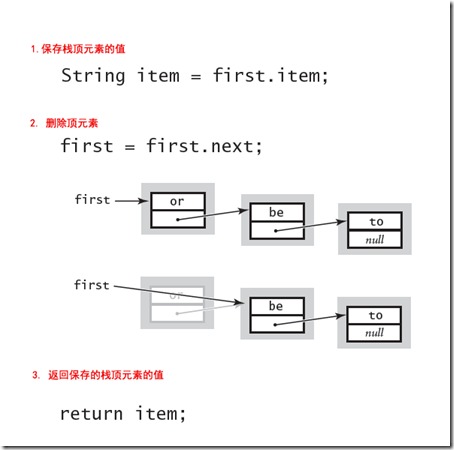
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
T Pop(){ T item = first.Item; first = first.Next; number--; return item;} |
基于链表的Stack实现,在最坏的情况下只需要常量的时间来进行Push和Pop操作。
栈的数组实现:
我们可以使用数组来存储栈中的元素Push的时候,直接添加一个元素S[N]到数组中,Pop的时候直接返回S[N-1].
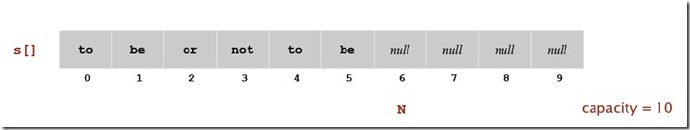
首先,我们定义一个数组,然后在构造函数中给定初始化大小,Push方法实现如下,就是集合里添加一个元素:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
T[] item;int number = 0;public StackImplementByArray(int capacity){ item = new T[capacity];} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public void Push(T _item){ if (number == item.Length) Resize(2 * item.Length); item[number++] = _item;} |
Pop方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public T Pop(){ T temp = item[--number]; item[number] = default(T); if (number > 0 && number == item.Length / 4) Resize(item.Length / 2); return temp;} |
在Push和Pop方法中,为了节省内存空间,我们会对数组进行整理。Push的时候,当元素的个数达到数组的Capacity的时候,我们开辟2倍于当前元素的新数组,然后将原数组中的元素拷贝到新数组中。Pop的时候,当元素的个数小于当前容量的1/4的时候,我们将原数组的大小容量减少1/2。
Resize方法基本就是数组复制:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private void Resize(int capacity){ T[] temp = new T[capacity]; for (int i = 0; i < item.Length; i++) { temp[i] = item[i]; } item = temp;} |
当我们缩小数组的时候,采用的是判断1/4的情况,这样效率要比1/2要高,因为可以有效避免在1/2附件插入,删除,插入,删除,从而频繁的扩大和缩小数组的情况。下图展示了在插入和删除的情况下数组中的元素以及数组大小的变化情况:
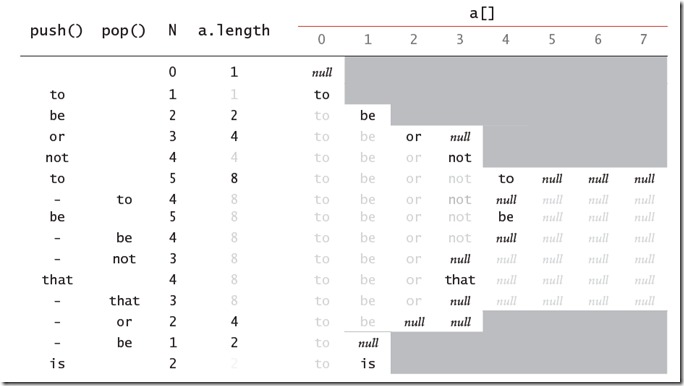
分析:1. Pop和Push操作在最坏的情况下与元素个数成比例的N的时间,时间主要花费在扩大或者缩小数组的个数时,数组拷贝上。
2. 元素在内存中分布紧凑,密度高,便于利用内存的时间和空间局部性,便于CPU进行缓存,较LinkList内存占用小,效率高。
2.2 Queue的实现
Queue是一种先进先出的数据结构,和Stack一样,他也有链表和数组两种实现,理解了Stack的实现后,Queue的实现就比较简单了。

| Stack<T>() | 创建一个空的队列 |
| void Enqueue(T s) | 往队列中添加一个新的元素 |
| T Dequeue() | 移除队列中最早添加的元素 |
| boolean IsEmpty() | 队列是否为空 |
| int Size() | 队列中元素的个数 |
首先看链表的实现:
Dequeue方法就是返回链表中的第一个元素,这个和Stack中的Pop方法相似:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public T Dequeue(){ T temp = first.Item; first = first.Next; number--; if (IsEmpety()) last = null; return temp;} |
Enqueue和Stack的Push方法不同,他是在链表的末尾增加新的元素:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public void Enqueue(T item){ Node oldLast = last; last = new Node(); last.Item = item; if (IsEmpety()) { first = last; } else { oldLast.Next = last; } number++;} |
同样地,现在再来看如何使用数组来实现Queue,首先我们使用数组来保存数据,并定义变量head和tail来记录Queue的首尾元素。
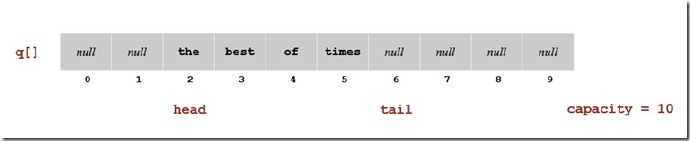
和Stack的实现方式不同,在Queue中,我们定义了head和tail来记录头元素和尾元素。当enqueue的时候,tial加1,将元素放在尾部,当dequeue的时候,head减1,并返回。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public void Enqueue(T _item){ if ((head - tail + 1) == item.Length) Resize(2 * item.Length); item[tail++] = _item;}public T Dequeue(){ T temp = item[--head]; item[head] = default(T); if (head > 0 && (tail - head + 1) == item.Length / 4) Resize(item.Length / 2); return temp;}private void Resize(int capacity){ T[] temp = new T[capacity]; int index = 0; for (int i = head; i < tail; i++) { temp[++index] = item[i]; } item = temp;} |
3. .NET中的Stack和Queue
在.NET中有Stack和Queue泛型类,使用Reflector工具可以查看其具体实现。先看Stack的实现,下面是截取的部分代码,仅列出了Push,Pop方法,其他的方法希望大家自己使用Reflector查看:
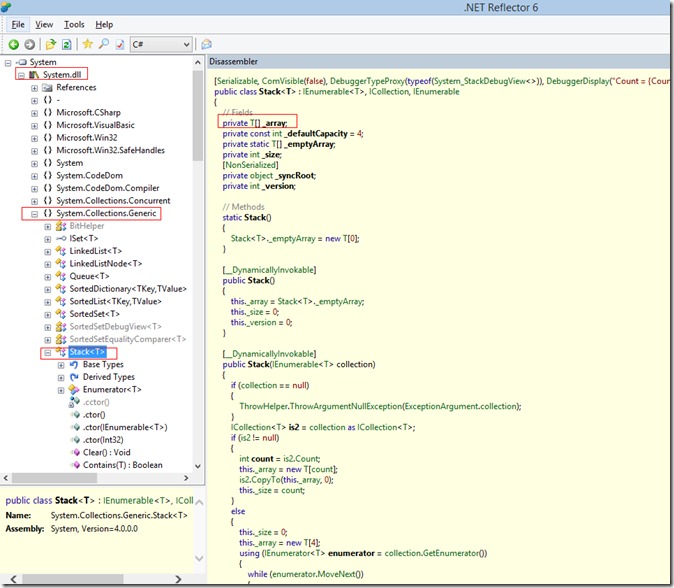
可以看到.NET中的Stack的实现和我们之前写的差不多,也是使用数组来实现的。.NET中Stack的初始容量为4,在Push方法中,可以看到当元素个数达到数组长度时,扩充2倍容量,然后将原数组拷贝到新的数组中。Pop方法和我们之前实现的基本上相同,下面是具体代码,只截取了部分:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
|
[Serializable, ComVisible(false), DebuggerTypeProxy(typeof(System_StackDebugView<>)), DebuggerDisplay("Count = {Count}"), __DynamicallyInvokable]public class Stack<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable{ // Fields private T[] _array; private const int _defaultCapacity = 4; private static T[] _emptyArray; private int _size; private int _version; // Methods static Stack() { Stack<T>._emptyArray = new T[0]; } [__DynamicallyInvokable] public Stack() { this._array = Stack<T>._emptyArray; this._size = 0; this._version = 0; } [__DynamicallyInvokable] public Stack(int capacity) { if (capacity < 0) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.capacity, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNumRequired); } this._array = new T[capacity]; this._size = 0; this._version = 0; } [__DynamicallyInvokable] public void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex) { if (array == null) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.array); } if ((arrayIndex < 0) || (arrayIndex > array.Length)) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.arrayIndex, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum); } if ((array.Length - arrayIndex) < this._size) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_InvalidOffLen); } Array.Copy(this._array, 0, array, arrayIndex, this._size); Array.Reverse(array, arrayIndex, this._size); } [__DynamicallyInvokable] public T Pop() { if (this._size == 0) { ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException(ExceptionResource.InvalidOperation_EmptyStack); } this._version++; T local = this._array[--this._size]; this._array[this._size] = default(T); return local; } [__DynamicallyInvokable] public void Push(T item) { if (this._size == this._array.Length) { T[] destinationArray = new T[(this._array.Length == 0) ? 4 : (2 * this._array.Length)]; Array.Copy(this._array, 0, destinationArray, 0, this._size); this._array = destinationArray; } this._array[this._size++] = item; this._version++; } // Properties [__DynamicallyInvokable] public int Count { [__DynamicallyInvokable, TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline this type of method across NGen image boundaries")] get { return this._size; } }} |
下面再看看Queue的实现:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
|
[Serializable, DebuggerDisplay("Count = {Count}"), ComVisible(false), DebuggerTypeProxy(typeof(System_QueueDebugView<>)), __DynamicallyInvokable] public class Queue<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable { // Fields private T[] _array; private const int _DefaultCapacity = 4; private static T[] _emptyArray; private int _head; private int _size; private int _tail; &nbs |
以上是关于浅谈算法和数据结构:栈和队列的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章