Puppet 集中配置管理系统
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Puppet 集中配置管理系统相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.什么是Puppet?
puppet 是一个配置管理工具, 典型的, puppet 是一个 C/S 结构, 当然,这里的 C 可以有很多,因此,也可以说是一个星型结构. 所有的 puppet 客户端同一个服务器端的 puppet 通讯. 每个puppet 客户端每半小时(可以设置)连接一次服务器端, 下载最新的配置文件,并且严格按照配置文件来配置服务器. 配置完成以后,puppet 客户端可以反馈给服务器端一个消息. 如果出错,也会给服务器端反馈一个消息
2.puppet 的细节和原理
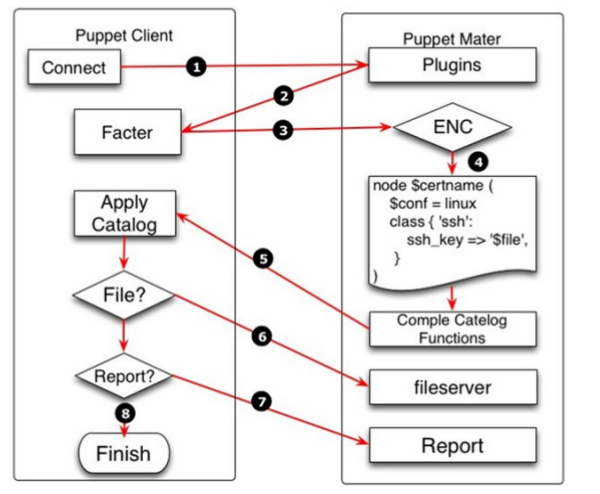
puppet 的目的是让你只集中于你要管理的目标,而忽略实现的细节,例如命令名,参数或者文件格式. puppet 把系统里面的用户,软件包,服务看作是"资源", puppet 的作用就是管理这些资源以及资源之间的相互联系.Puppet 采用了非常简单的 C/S 架构,所有数据的交互都通过 SSL 进行,以保证安全。它的工作流程如图所示
1. 客户端 Puppetd 向 Master 发起认证请求,或使用带签名的证书。
2. Master 告诉 Client 你是合法的。3. 客户端 Puppetd 调用 Facter,Facter 探测出主机的一些变量,例如主机名、内存大小、IP 地址等。Puppetd 将这些信息通过 SSL 连接发送到服务器端。
4. 服务器端的 Puppet Master 检测客户端的主机名,然后找到 manifest 对应的 node 配置,并对该部分内容进行解析。Facter 送过来的信息可以作为变量处 理,node 牵涉到的代码才解析,其他没牵涉的代码不解析。解析分为几个阶段,首先是语法检查,如果语法错误就报错;如果语法没错,就继续解析,解析的结 果生成一个中间的“伪代码”(catelog),然后把伪代码发给客户端。
5. 客户端接收到“伪代码”,并且执行。
6. 客户端在执行时判断有没有 File 文件,如果有,则向 fileserver 发起请求。
7. 客户端判断有没有配置 Report,如果已配置,则把执行结果发送给服务器。
8. 服务器端把客户端的执行结果写入日志,并发送给报告系统。
http://puppet.wikidot.com 中文 wiki
实验环境:
物理主机 redhat7.0 内核版本 3.10.0-123.el7.x86_64
虚拟机 redhat6.5 内核版本 2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64
master服务器 server1.example.com 172.25.254.1
Agent 客户端 server2.example.com172.25.254.2
Agent 客户端 server3.example.com172.25.254.3
Agent 客户端 server4.example.com172.25.254.4
1.安装puppet软件包
1)在master服务器 server1上安装puppet-server
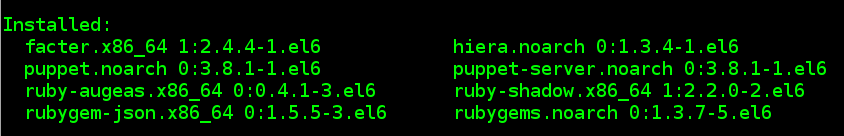
# yum install -y puppet-server-3.8.1-1.el6.noarch.rpm puppet-3.8.1-1.el6.noarch.rpm facter-2.4.4-1.el6.x86_64.rpm hiera-1.3.4-1.el6.noarch.rpm rubygem-json-1.5.5-3.el6.x86_64.rpm ruby-shadow-2.2.0-2.el6.x86_64.rpm ruby-augeas-0.4.1-3.el6.x86_64.rpm rubygems-1.3.7-5.el6.noarch.rpm
#/etc/init.d/puppetmaster start//启动puppet-server
2)在Agent 客户端 server2/server3/server4上安装puppet:
#yum install -y puppet-3.8.1-1.el6.noarch.rpm facter-2.4.4-1.el6.x86_64.rpm hiera-1.3.4-1.el6.noarch.rpm rubygem-json-1.5.5-3.el6.x86_64.rpm ruby-shadow-2.2.0-2.el6.x86_64.rpm ruby-augeas-0.4.1-3.el6.x86_64.rpm rubygems-1.3.7-5.el6.noarch.rpm
2.请求与认证(三种方式)
client 向 master 发出证书验证请求,然后等待 master 签名并返回证书。
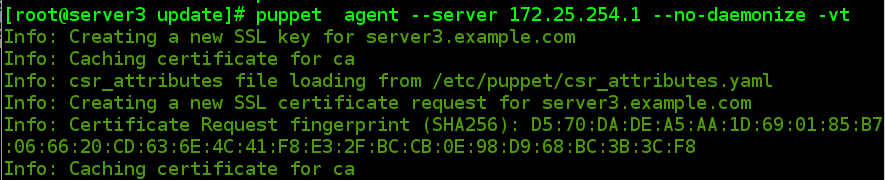
2.1 客户端(server2/server3)发送请求
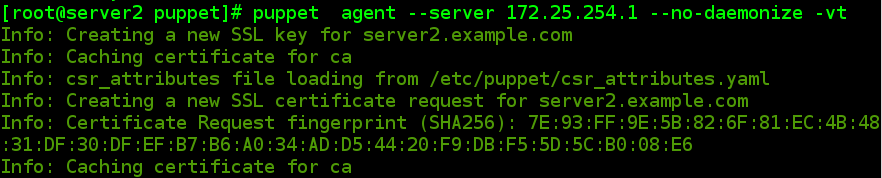
#puppet agent --server 172.25.254.1 --no-daemonize -vt
//参数--server 指定了需要连接的 puppet master 的名字或是地址,默认连接名为“puppet”的主机
如要修改默认连接主机可以修改/etc/sysconfig/puppet 文件中的 PUPPET_SERVER=puppet 选项
参数--no-daemonize 是 puppet 客户端运行在前台
参数--verbose 使客户端输出详细的日志
2.2. master服务器 server2/server3 签名认证
# cd /etc/puppet/manifests
puppet 的第一个执行的代码是在/etc/puppet/manifest/site.pp,因此这个文件必须存在,而且其他的代码也要通过该文件来调用。
# touch site.pp#没有此文件 puppet master 无法启动,配置后面再定义
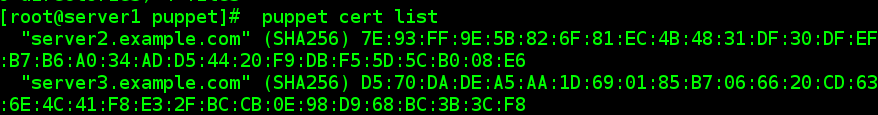
#puppet cert list//有等待,显示所有等待签名的证书
#puppet cert sign server2.example.com//签名
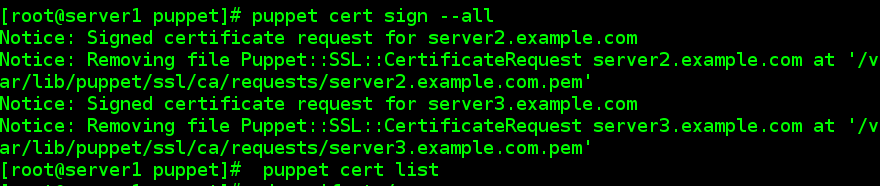
如要同时签名所有证书,执行以下命令:
# puppet cert sign --all
#puppet cert list//就没有等待了。
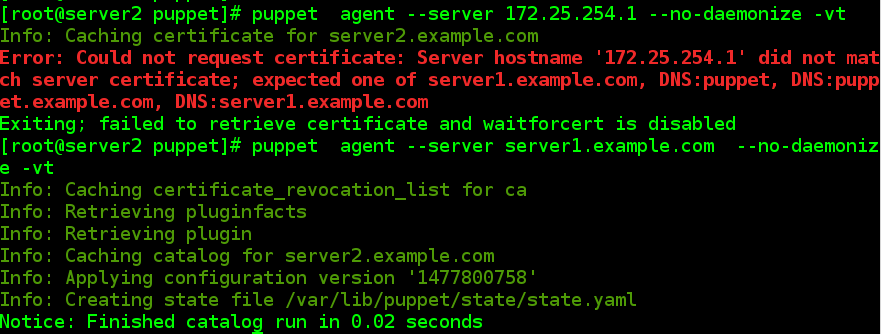
2.3 客户端(server2/server3)再次发送请求
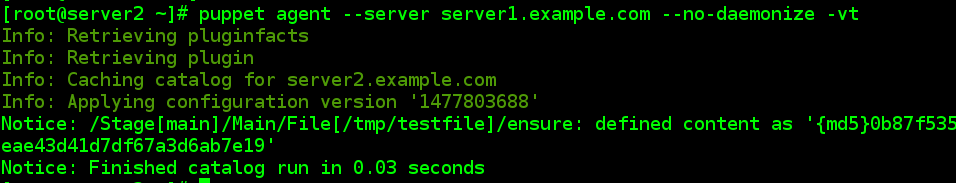
# puppet agent --server server1.example.com --no-daemonize -vt
 Notice: Finished catalog run in 0.02 seconds//出现这条信息就好了
Notice: Finished catalog run in 0.02 seconds//出现这条信息就好了
3.自动签名
3.1 master服务器 server1 修改配置文件
# cd /etc/puppet/
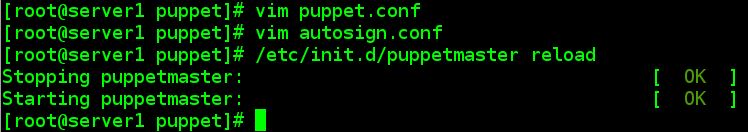
# vim puppet.conf##添加
2 autosign = true
# vim autosign.conf
1 *.example.com
# /etc/init.d/puppetmaster reload
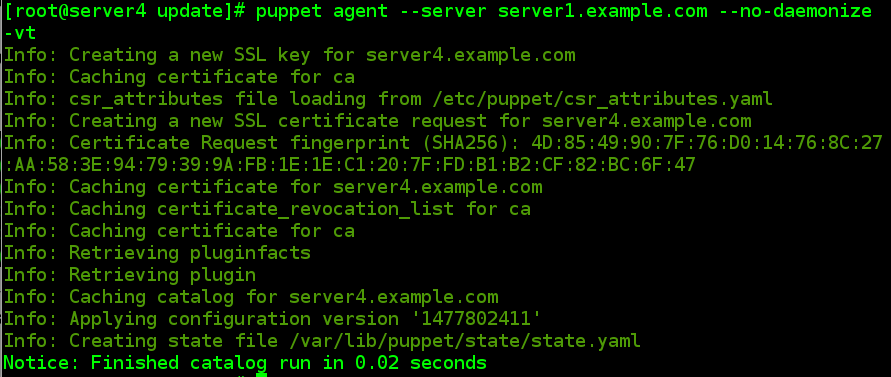
3.2 客户端(server4)发送认证请求
[[email protected] update]# puppet agent --server server1.example.com --no-daemonize -vt
3.3 重新认证测试
当客户端重新装了系统之后或者在实际中有时会修改 client 端的主机名,这样就需要重新生成证书:
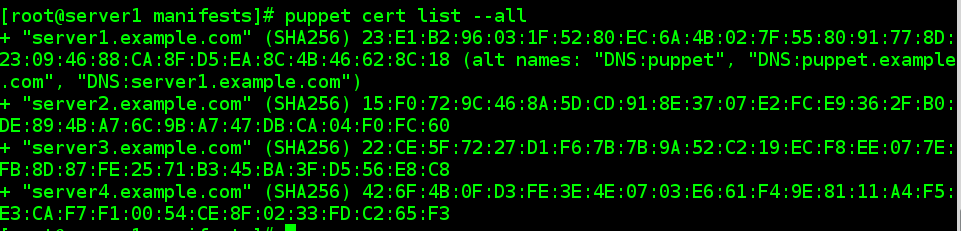
3.3.1 master服务器 server1 先删除之前认证的签名
# puppet cert list --all
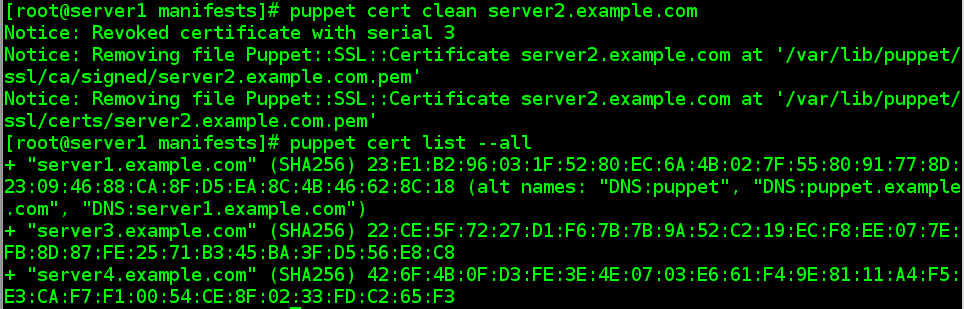
# puppet cert clean server2.example.com//要删除的原 client 端主机名
3.3.2 客户端(server2)上:
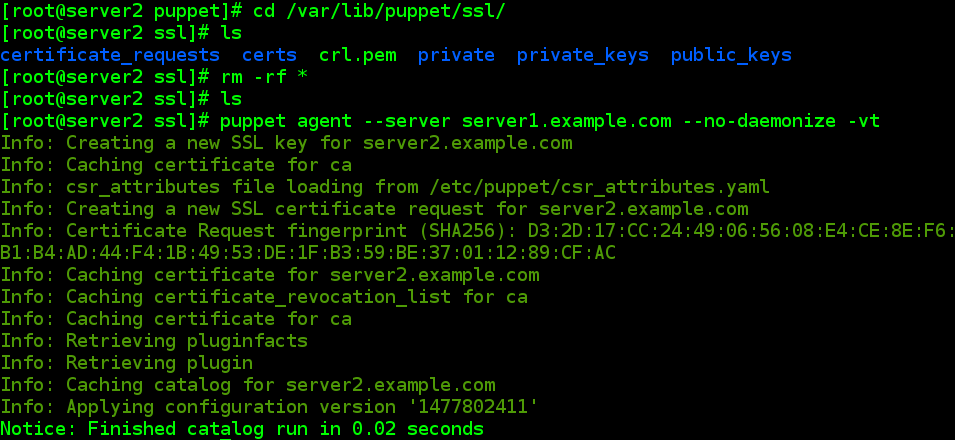
# cd /var/lib/puppet/ssl/
# rm -rf * # rpm -qf /var/lib/puppet/ssl,可以看到ssl目录是自动生成的,不依赖于任何软件包
# puppet agent --server server1.example.com --no-daemonize -vt
###再次发送请求即可
4.puppet 资源定义
以下资源均定义在/etc/puppet/manifest/site.pp 文件中,在没有指定节点的情况下,对所有已经经过验证的 client 都生效。
4.1 文件
4.1.1 master服务器 server1上:
[[email protected] manifests]# ls
site.pp
[[email protected] manifests]# vim site.pp
[[email protected] manifests]# cd /etc/puppet/
[[email protected] puppet]# mkdir files
[[email protected] puppet]# cd files
[[email protected] files]# cp /etc/passwd .
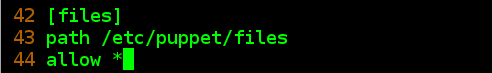
[[email protected] files]# vim /etc/puppet/fileserver.conf
[[email protected] files]# /etc/init.d/puppetmaster reload
4.1.2 在Agent 客户端 server2和客户端 server3上
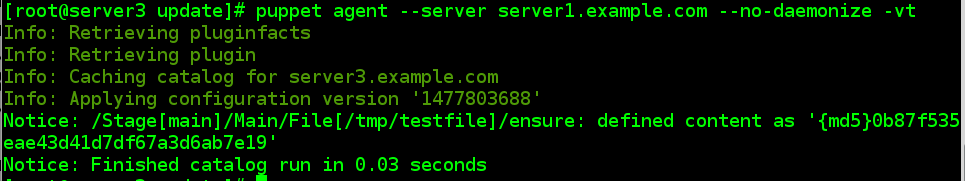
# puppet agent --server server1.example.com --no-daemonize -vt
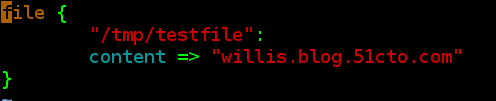
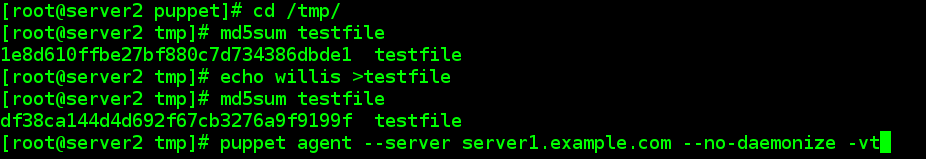
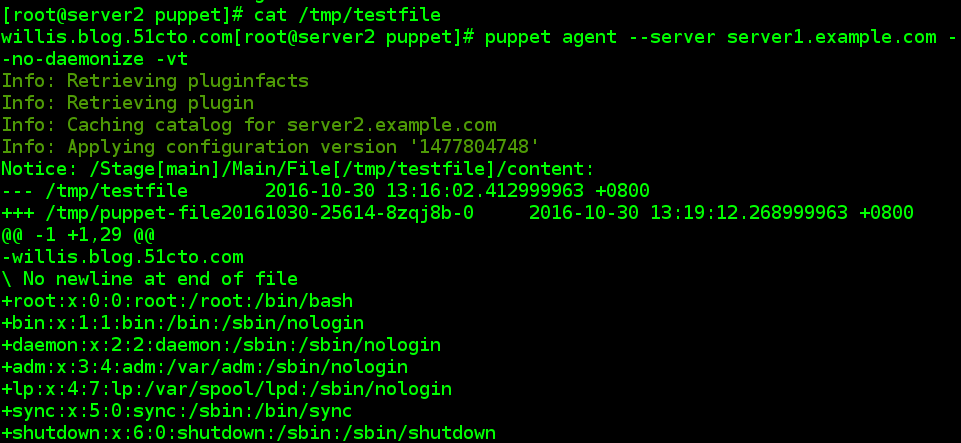
[[email protected] ~]# cat /tmp/testfile
willis.blog.51cto.com[[email protected] ~]#
[[email protected] ~]# cd /tmp/
//所创建的tmp/testfile默认设置为md5sum加密,当手动改写testfile中的内容后,它的md5会改变,当再次执行向puppt-server的请求后,md5又会再次恢复。
4.1.3 服务器server1上:
# vi /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp
1 file {
2 "/tmp/testfile":
3 source => "puppet:///files/passwd"
4 }
可再次实验认证。
server2上再次测试:
4.2软件包定义
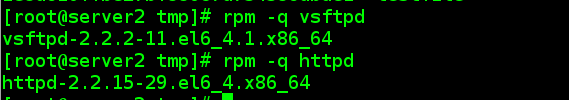
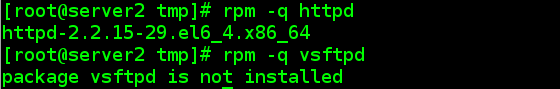
4.2.1 server2上安装httpd服务与vsftpd服务
4.2.2 服务器端server1定义软件包规则
软件包定义方法:
1)package {
"vsftpd":
ensure => absent
}
2)package {
"vsftpd":
ensure => present;
"man":
ensure => present
}
3)package {
["vsftpd","man"]:
ensure => absent;
}
[[email protected] puppet]# vim manifests/site.pp
4.2.3 客户端server2同步服务器端规则,检查软件包安装情况
[[email protected] tmp]# puppet agent --server server1.example.com --no-daemonize -vt
4.3. 服务定义
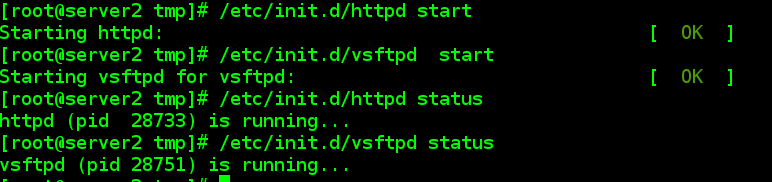
4.3.1 server2上启动httpd服务与vsftpd服务
4.3.2 服务器端server1定义服务规则
[[email protected] puppet]# vim manifests/site.pp
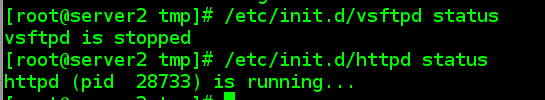
4.3.3 客户端server2同步服务器端规则,检查服务启动情况
[[email protected] tmp]# puppet agent --server server1.example.com --no-daemonize -vt
4.3.4 对httpd服务进行全面定义
服务器端server1定义服务规则如下:
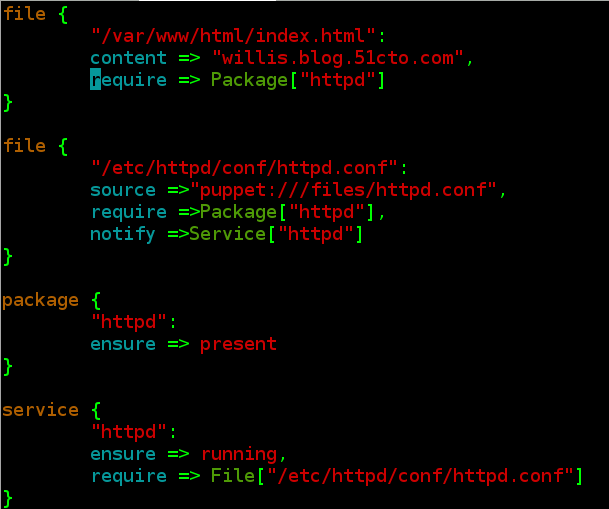
[[email protected] puppet]# vim manifests/site.pp
file {
"/var/www/html/index.html":
content => "willis.blog.51cto.com",
require => Package["httpd"]
}
file {
"/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf":
source =>"puppet:///files/httpd.conf",
require =>Package["httpd"],
notify =>Service["httpd"]
}
package {
"httpd":
ensure => present
}
service {
"httpd":
ensure => running,
require => File["/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf"]
}
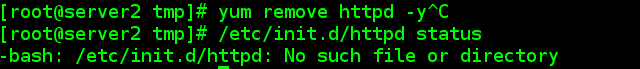
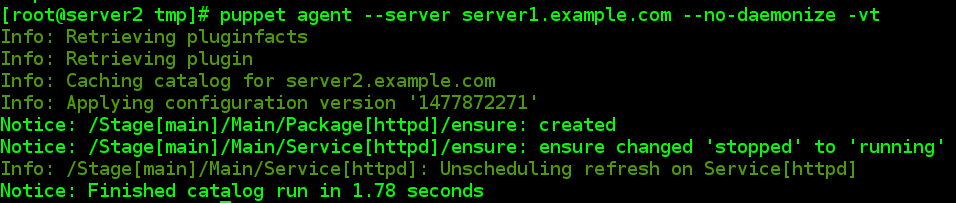
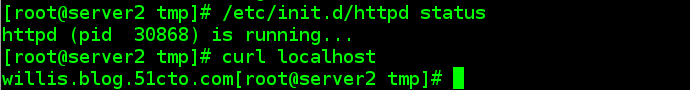
4.3.5客户端测试
首先卸载httpd服务,然后获取
[[email protected] tmp]# puppet agent --server server1.example.com --no-daemonize -vt
4.4 组定义
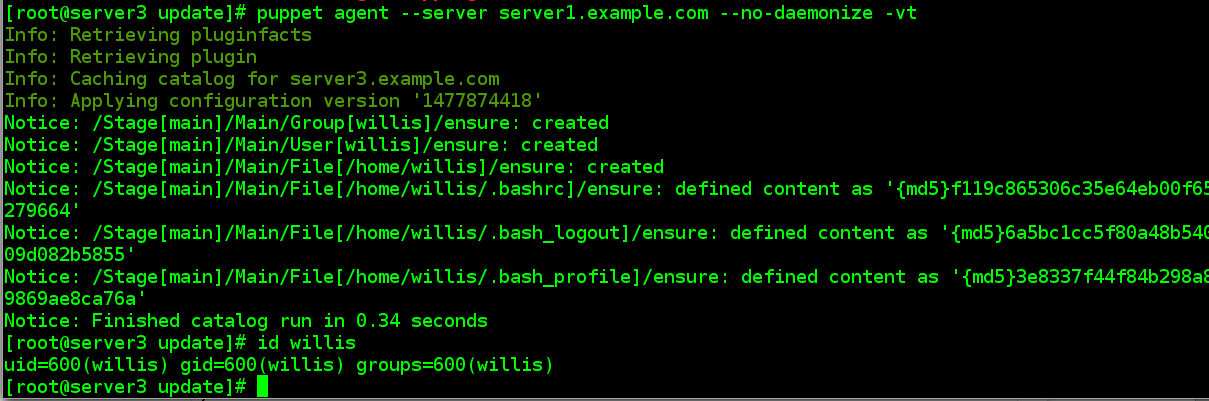
group { "willis": gid => 600 }
4.5. 用户定义
方法一:
user { "willis":
uid => 600,
gid => 600,
home => "/home/willis",
shell => "/bin/bash" ,
password => willis
}
file { "/home/willis":
owner => willis,
group => willis,
mode => 700,
ensure => directory
}
file { "/home/willis/.bash_logout":
source => "/etc/skel/.bash_logout",
owner => willis,group => willis
}
file { "/home/willis/.bash_profile":
source => "/etc/skel/.bash_profile",
owner => willis,
group => willis
}
file { "/home/willis/.bashrc":
source => "/etc/skel/.bashrc",
owner => willis,
group => willis
}
user { "test": uid => 900,
home => "/home/test",
shell => "/bin/bash",
provider => useradd,
managehome => true,
ensure => present
}
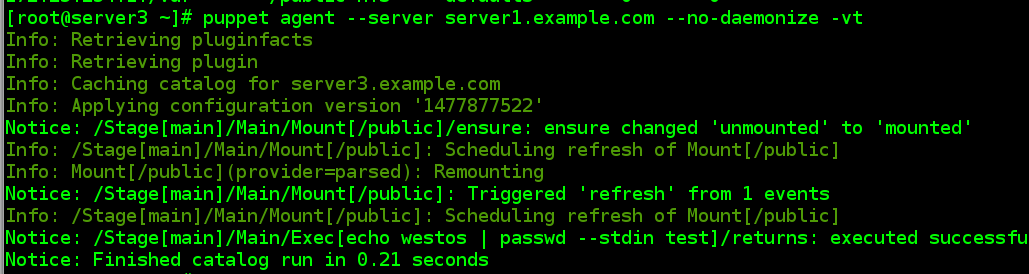
exec { "echo westos | passwd --stdin test":
path => "/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/bin",
onlyif => "id test"
}
方法二:
user {
"test": uid => 900,
home => "/home/test",
shell => "/bin/bash",
provider => useradd,
managehome => true,
ensure => present
}
exec { "echo willis | passwd --stdin test":
path => "/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/bin",
onlyif => "id test"
}
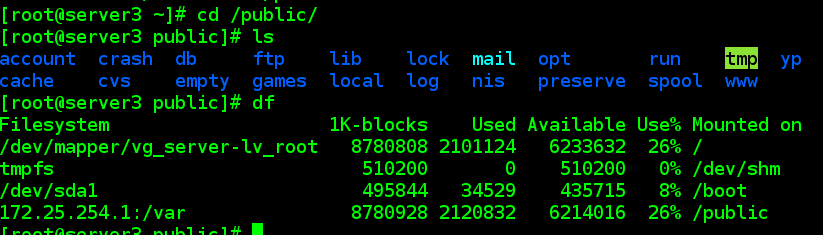
4.6文件系统挂载
4.6.1 服务端配置
[[email protected] puppet]# vim manifests/site.pp
file {
"/public":
ensure => directory
}
mount {
"/public":device => "172.25.254.1:/var",
fstype => "nfs",
options => "defaults",
ensure => mounted
}
自动挂载文件系统,并同步 fstab 文件,如果需要卸载,改为 absent
4.6.2 服务端nfs配置
[[email protected] puppet]# yum install nfs-utils -y
[[email protected] puppet]# /etc/init.d/nfs start
[[email protected] puppet]# vim /etc/exports
/var *(ro)
[[email protected] puppet]# exportfs -rv
exporting *:/var
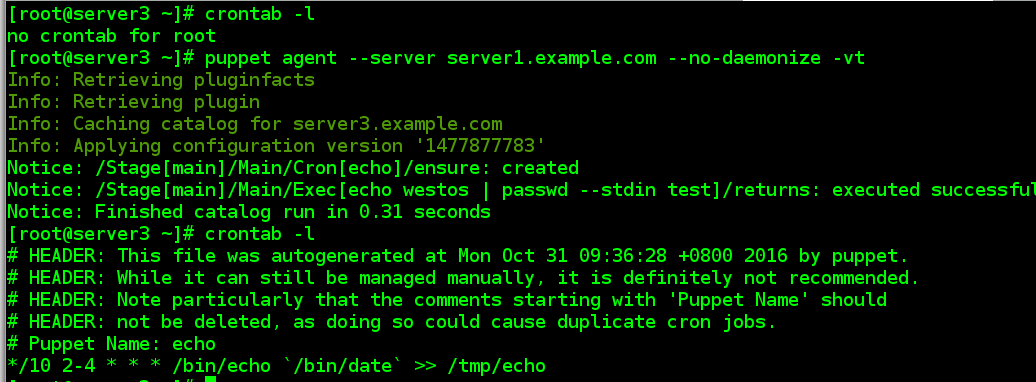
4.7 crontab 任务
[[email protected] puppet]# vim manifests/site.pp
cron { echo:
command => "/bin/echo `/bin/date` >> /tmp/echo",
user => root,
hour => [‘2-4‘],
minute => ‘*/10‘
}
# 任务会在 client 上/var/spool/cron 目录中生成。
本文出自 “技术人生,简单不简单” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://willis.blog.51cto.com/11907152/1867810
以上是关于Puppet 集中配置管理系统的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章