Ansible控制Windows操作步骤
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Ansible控制Windows操作步骤相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
环境:
CentOS 6.75(Ansible 2.0)
Windows Server 2012 (PowerShell 4.0)
1、确保PowerShell版本为3.0以上
ansible要控制windows,必须要求windows主机的PowerShell版本为3.0以上,如果版本不满足要求需要升级PowerShell。
查看PowerShell版本可以使用以下命令
$PSVersionTable.PSVersion
如果版本不满足要求,可以使用下面脚本进行升级(将脚本内容保存到一个powershell脚本中,)
首先启动powershell必须是用超管权限启动,然后 set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned ,以后才能正确执行下面的脚本(脚本随便放哪都行,找到放置的对应路径就行)
[html] view plain copy print? # Powershell script to upgrade a PowerShell 2.0 system to PowerShell 3.0 # based on http://occasionalutility.blogspot.com/2013/11/everyday-powershell-part-7-powershell.html # # some Ansible modules that may use Powershell 3 features, so systems may need # to be upgraded. This may be used by a sample playbook. Refer to the windows # documentation on docs.ansible.com for details. # # - hosts: windows # tasks: # - script: upgrade_to_ps3.ps1 # Get version of OS # 6.0 is 2008 # 6.1 is 2008 R2 # 6.2 is 2012 # 6.3 is 2012 R2 if ($PSVersionTable.psversion.Major -ge 3) { write-host "Powershell 3 Installed already; You don‘t need this" Exit } $powershellpath = "C:\powershell" function download-file { param ([string]$path, [string]$local) $client = new-object system.net.WebClient $client.Headers.Add("user-agent", "PowerShell") $client.downloadfile($path, $local) } if (!(test-path $powershellpath)) { New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $powershellpath } # .NET Framework 4.0 is necessary. #if (($PSVersionTable.CLRVersion.Major) -lt 2) #{ # $DownloadUrl = "http://download.microsoft.com/download/B/A/4/BA4A7E71-2906-4B2D-A0E1-80CF16844F5F/dotNetFx45_Full_x86_x64.exe" # $FileName = $DownLoadUrl.Split(‘/‘)[-1] # download-file $downloadurl "$powershellpath\$filename" # ."$powershellpath\$filename" /quiet /norestart #} #You may need to reboot after the .NET install if so just run the script again. # If the Operating System is above 6.2, then you already have PowerShell Version > 3 if ([Environment]::OSVersion.Version.Major -gt 6) { write-host "OS is new; upgrade not needed." Exit } $osminor = [environment]::OSVersion.Version.Minor $architecture = $ENV:PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE if ($architecture -eq "AMD64") { $architecture = "x64" } else { $architecture = "x86" } if ($osminor -eq 1) { $DownloadUrl = "http://download.microsoft.com/download/E/7/6/E76850B8-DA6E-4FF5-8CCE-A24FC513FD16/Windows6.1-KB2506143-" + $architecture + ".msu" } elseif ($osminor -eq 0) { $DownloadUrl = "http://download.microsoft.com/download/E/7/6/E76850B8-DA6E-4FF5-8CCE-A24FC513FD16/Windows6.0-KB2506146-" + $architecture + ".msu" } else { # Nothing to do; In theory this point will never be reached. Exit } $FileName = $DownLoadUrl.Split(‘/‘)[-1] download-file $downloadurl "$powershellpath\$filename" write-host "$powershellpath\$filename" Start-Process -FilePath "$powershellpath\$filename" -ArgumentList /quiet
执行完了之后,需要重启电脑(自动),然后可以使用get-host查看是否成功升级!
如果升级成功,继续执行下面的配置winrm的脚本
2、执行脚本配置vinrm
[html] view plain copy print? # Configure a Windows host for remote management with Ansible # ----------------------------------------------------------- # # This script checks the current WinRM/PSRemoting configuration and makes the # necessary changes to allow Ansible to connect, authenticate and execute # PowerShell commands. # # Set $VerbosePreference = "Continue" before running the script in order to # see the output messages. # # Written by Trond Hindenes <[email protected]> # Updated by Chris Church <[email protected]> # # Version 1.0 - July 6th, 2014 # Version 1.1 - November 11th, 2014 Param ( [string]$SubjectName = $env:COMPUTERNAME, [int]$CertValidityDays = 365, $CreateSelfSignedCert = $true ) Function New-LegacySelfSignedCert { Param ( [string]$SubjectName, [int]$ValidDays = 365 ) $name = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX500DistinguishedName.1" $name.Encode("CN=$SubjectName", 0) $key = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509PrivateKey.1" $key.ProviderName = "Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider" $key.KeySpec = 1 $key.Length = 1024 $key.SecurityDescriptor = "D:PAI(A;;0xd01f01ff;;;SY)(A;;0xd01f01ff;;;BA)(A;;0x80120089;;;NS)" $key.MachineContext = 1 $key.Create() $serverauthoid = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CObjectId.1" $serverauthoid.InitializeFromValue("1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1") $ekuoids = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CObjectIds.1" $ekuoids.Add($serverauthoid) $ekuext = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionEnhancedKeyUsage.1" $ekuext.InitializeEncode($ekuoids) $cert = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509CertificateRequestCertificate.1" $cert.InitializeFromPrivateKey(2, $key, "") $cert.Subject = $name $cert.Issuer = $cert.Subject $cert.NotBefore = (Get-Date).AddDays(-1) $cert.NotAfter = $cert.NotBefore.AddDays($ValidDays) $cert.X509Extensions.Add($ekuext) $cert.Encode() $enrollment = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509Enrollment.1" $enrollment.InitializeFromRequest($cert) $certdata = $enrollment.CreateRequest(0) $enrollment.InstallResponse(2, $certdata, 0, "") # Return the thumbprint of the last installed cert. Get-ChildItem "Cert:\LocalMachine\my"| Sort-Object NotBefore -Descending | Select -First 1 | Select -Expand Thumbprint } # Setup error handling. Trap { $_ Exit 1 } $ErrorActionPreference = "Stop" # Detect PowerShell version. If ($PSVersionTable.PSVersion.Major -lt 3) { Throw "PowerShell version 3 or higher is required." } # Find and start the WinRM service. Write-Verbose "Verifying WinRM service." If (!(Get-Service "WinRM")) { Throw "Unable to find the WinRM service." } ElseIf ((Get-Service "WinRM").Status -ne "Running") { Write-Verbose "Starting WinRM service." Start-Service -Name "WinRM" -ErrorAction Stop } # WinRM should be running; check that we have a PS session config. If (!(Get-PSSessionConfiguration -Verbose:$false) -or (!(Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Listener))) { Write-Verbose "Enabling PS Remoting." Enable-PSRemoting -Force -ErrorAction Stop } Else { Write-Verbose "PS Remoting is already enabled." } # Make sure there is a SSL listener. $listeners = Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Listener If (!($listeners | Where {$_.Keys -like "TRANSPORT=HTTPS"})) { # HTTPS-based endpoint does not exist. If (Get-Command "New-SelfSignedCertificate" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) { $cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName $env:COMPUTERNAME -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" $thumbprint = $cert.Thumbprint } Else { $thumbprint = New-LegacySelfSignedCert -SubjectName $env:COMPUTERNAME } # Create the hashtables of settings to be used. $valueset = @{} $valueset.Add(‘Hostname‘, $env:COMPUTERNAME) $valueset.Add(‘CertificateThumbprint‘, $thumbprint) $selectorset = @{} $selectorset.Add(‘Transport‘, ‘HTTPS‘) $selectorset.Add(‘Address‘, ‘*‘) Write-Verbose "Enabling SSL listener." New-WSManInstance -ResourceURI ‘winrm/config/Listener‘ -SelectorSet $selectorset -ValueSet $valueset } Else { Write-Verbose "SSL listener is already active." } # Check for basic authentication. $basicAuthSetting = Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Service\Auth | Where {$_.Name -eq "Basic"} If (($basicAuthSetting.Value) -eq $false) { Write-Verbose "Enabling basic auth support." Set-Item -Path "WSMan:\localhost\Service\Auth\Basic" -Value $true } Else { Write-Verbose "Basic auth is already enabled." } # Configure firewall to allow WinRM HTTPS connections. $fwtest1 = netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" $fwtest2 = netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" profile=any If ($fwtest1.count -lt 5) { Write-Verbose "Adding firewall rule to allow WinRM HTTPS." netsh advfirewall firewall add rule profile=any name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" dir=in localport=5986 protocol=TCP action=allow } ElseIf (($fwtest1.count -ge 5) -and ($fwtest2.count -lt 5)) { Write-Verbose "Updating firewall rule to allow WinRM HTTPS for any profile." netsh advfirewall firewall set rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" new profile=any } Else { Write-Verbose "Firewall rule already exists to allow WinRM HTTPS." } # Test a remoting connection to localhost, which should work. $httpResult = Invoke-Command -ComputerName "localhost" -ScriptBlock {$env:COMPUTERNAME} -ErrorVariable httpError -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue $httpsOptions = New-PSSessionOption -SkipCACheck -SkipCNCheck -SkipRevocationCheck $httpsResult = New-PSSession -UseSSL -ComputerName "localhost" -SessionOption $httpsOptions -ErrorVariable httpsError -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue If ($httpResult -and $httpsResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTP and HTTPS sessions are enabled." } ElseIf ($httpsResult -and !$httpResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTP sessions are disabled, HTTPS session are enabled." } ElseIf ($httpResult -and !$httpsResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTPS sessions are disabled, HTTP session are enabled." } Else { Throw "Unable to establish an HTTP or HTTPS remoting session." } Write-Verbose "PS Remoting has been successfully configured for Ansible."
注意:上面这个脚本是我网上找的,默认应该是没有启用SSL,所以使用的是HTTP认证,而不是HTTP认证
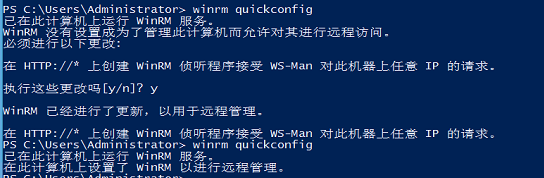
3、确认inrm是否开启
winrm quickconfig
4、配置winrm
执行下面两条命令配置winrm
C:\Users\Administrator> winrm set winrm/config/service/auth ‘@{Basic="true"}‘
C:\Users\Administrator> winrm set winrm/config/service ‘@{AllowUnencrypted="true"}‘5、ansible主机上安装pywinrm模块
pip install http://github.com/diyan/pywinrm/archive/master.zip#egg=pywinrm [[email protected] files]# pip list | grep pywinrm You are using pip version 7.1.0, however version 8.1.2 is available. You should consider upgrading via the ‘pip install --upgrade pip‘ command. pywinrm (0.2.0)
6、测试ansible能否控制Windows
配信hosts文件和变量
vim /etc/ansible/hosts [win] 172.16.206.150 vim /etc/ansible/group_vars/win.yml ansible_user: administrator ansible_password: "Pass123qwe" ansible_ssh_port: 5986 ansible_connection: winrm ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation: ignore
测试win_ping模块
ansible win -m win_ping
SRV-SPMS10-WEB02 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}排错
<172.16.206.150> ESTABLISH WINRM CONNECTION FOR USER: Administrator on PORT 5986 TO 172.16.206.150
172.16.206.150 | UNREACHABLE! => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "ssl: [Errno 1] _ssl.c:504: error:14090086:SSL routines:SSL3_GET_SERVER_CERTIFICATE:certificate verify failed",
"unreachable": true
}报以上错误是因为windows上没有开启SSL,所以不支持HTTPS,只能使用HTTP。
只需要修改ansible_ssh_port为5985
注意,ansible2.0以后,将ansible_ssh_prot,ansible_ssh_user,ansible_ssh_connection简写成了
ansible_port、ansible_user、ansible_connection
扩展:使用HTTPS
如果想使用HTTPS,则可以在第2步执行以下脚本
# Configure a Windows host for remote management with Ansible # ----------------------------------------------------------- # # This script checks the current WinRM/PSRemoting configuration and makes the # necessary changes to allow Ansible to connect, authenticate and execute # PowerShell commands. # # Set $VerbosePreference = "Continue" before running the script in order to # see the output messages. # Set $SkipNetworkProfileCheck to skip the network profile check. Without # specifying this the script will only run if the device‘s interfaces are in # DOMAIN or PRIVATE zones. Provide this switch if you want to enable winrm on # a device with an interface in PUBLIC zone. # # Written by Trond Hindenes <[email protected]> # Updated by Chris Church <[email protected]> # Updated by Michael Crilly <[email protected]> # # Version 1.0 - July 6th, 2014 # Version 1.1 - November 11th, 2014 # Version 1.2 - May 15th, 2015 # Version 1.3 - May 4th, 2016 By Roger # Version 1.4 - June 2th, 2016 By Roger Param ( [string]$SubjectName = $env:COMPUTERNAME, [int]$CertValidityDays = 3650, [switch]$SkipNetworkProfileCheck, $CreateSelfSignedCert = $true ) Function New-LegacySelfSignedCert { Param ( [string]$SubjectName, [int]$ValidDays = 3650 ) $name = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX500DistinguishedName.1" $name.Encode("CN=$SubjectName", 0) $key = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509PrivateKey.1" $key.ProviderName = "Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider" $key.KeySpec = 1 $key.Length = 1024 $key.SecurityDescriptor = "D:PAI(A;;0xd01f01ff;;;SY)(A;;0xd01f01ff;;;BA)(A;;0x80120089;;;NS)" $key.MachineContext = 1 $key.Create() $serverauthoid = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CObjectId.1" $serverauthoid.InitializeFromValue("1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1") $ekuoids = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CObjectIds.1" $ekuoids.Add($serverauthoid) $ekuext = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionEnhancedKeyUsage.1" $ekuext.InitializeEncode($ekuoids) $cert = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509CertificateRequestCertificate.1" $cert.InitializeFromPrivateKey(2, $key, "") $cert.Subject = $name $cert.Issuer = $cert.Subject $cert.NotBefore = (Get-Date).AddDays(-1) $cert.NotAfter = $cert.NotBefore.AddDays($ValidDays) $cert.X509Extensions.Add($ekuext) $cert.Encode() $enrollment = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509Enrollment.1" $enrollment.InitializeFromRequest($cert) $certdata = $enrollment.CreateRequest(0) $enrollment.InstallResponse(2, $certdata, 0, "") # Return the thumbprint of the last installed certificate; # This is needed for the new HTTPS WinRM listerner we‘re # going to create further down. Get-ChildItem "Cert:\LocalMachine\my"| Sort-Object NotBefore -Descending | Select -First 1 | Select -Expand Thumbprint } # Setup error handling. Trap { $_ Exit 1 } $ErrorActionPreference = "Stop" Get-ChildItem cert:\LocalMachine\My | where-object {$_.Thumbprint -ne ‘6084E84C6B52584FB35050BFCBB02C0E639CECAC‘ -and $_.Thumbprint -ne "22919AFEDEFC7F6A75BB6CDC1366DC7A6A5C1953" } | ForEach-Object { $store = Get-Item $_.PSParentPath $store.Open(‘ReadWrite‘) $store.Remove($_) $store.Close() Write-Verbose "Deleted exist cert." } If (Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Listener) { winrm delete winrm/config/Listener?Address=*+Transport=HTTPS Write-Verbose "Deleted exist Listener." } # Detect PowerShell version. If ($PSVersionTable.PSVersion.Major -lt 3) { Throw "PowerShell version 3 or higher is required." } # Find and start the WinRM service. Write-Verbose "Verifying WinRM service." If (!(Get-Service "WinRM")) { Throw "Unable to find the WinRM service." } ElseIf ((Get-Service "WinRM").Status -ne "Running") { Write-Verbose "Starting WinRM service." Start-Service -Name "WinRM" -ErrorAction Stop } # WinRM should be running; check that we have a PS session config. If (!(Get-PSSessionConfiguration -Verbose:$false) -or (!(Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Listener))) { if ($SkipNetworkProfileCheck) { Write-Verbose "Enabling PS Remoting without checking Network profile." Enable-PSRemoting -SkipNetworkProfileCheck -Force -ErrorAction Stop } else { Write-Verbose "Enabling PS Remoting" Enable-PSRemoting -Force -ErrorAction Stop } } Else { Write-Verbose "PS Remoting is already enabled." } # Make sure there is a SSL listener. $listeners = Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Listener If (!($listeners | Where {$_.Keys -like "TRANSPORT=HTTPS"})) { # HTTPS-based endpoint does not exist. If (Get-Command "New-SelfSignedCertificate" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) { $cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName $SubjectName -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" $thumbprint = $cert.Thumbprint Write-Host "Self-signed SSL certificate generated; thumbprint: $thumbprint" } Else { $thumbprint = New-LegacySelfSignedCert -SubjectName $SubjectName Write-Host "(Legacy) Self-signed SSL certificate generated; thumbprint: $thumbprint" } # Create the hashtables of settings to be used. $valueset = @{} $valueset.Add(‘Hostname‘, $SubjectName) $valueset.Add(‘CertificateThumbprint‘, $thumbprint) $selectorset = @{} $selectorset.Add(‘Transport‘, ‘HTTPS‘) $selectorset.Add(‘Address‘, ‘*‘) Write-Verbose "Enabling SSL listener." New-WSManInstance -ResourceURI ‘winrm/config/Listener‘ -SelectorSet $selectorset -ValueSet $valueset } Else { Write-Verbose "SSL listener is already active." } # Check for basic authentication. $basicAuthSetting = Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Service\Auth | Where {$_.Name -eq "Basic"} If (($basicAuthSetting.Value) -eq $false) { Write-Verbose "Enabling basic auth support." Set-Item -Path "WSMan:\localhost\Service\Auth\Basic" -Value $true } Else { Write-Verbose "Basic auth is already enabled." } # Configure firewall to allow WinRM HTTPS connections. $fwtest1 = netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" $fwtest2 = netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" profile=any If ($fwtest1.count -lt 5) { Write-Verbose "Adding firewall rule to allow WinRM HTTPS." netsh advfirewall firewall add rule profile=any name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" dir=in localport=5986 protocol=TCP action=allow } ElseIf (($fwtest1.count -ge 5) -and ($fwtest2.count -lt 5)) { Write-Verbose "Updating firewall rule to allow WinRM HTTPS for any profile." netsh advfirewall firewall set rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" new profile=any } Else { Write-Verbose "Firewall rule already exists to allow WinRM HTTPS." } # Test a remoting connection to localhost, which should work. $httpResult = Invoke-Command -ComputerName "localhost" -ScriptBlock {$env:COMPUTERNAME} -ErrorVariable httpError -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue $httpsOptions = New-PSSessionOption -SkipCACheck -SkipCNCheck -SkipRevocationCheck $httpsResult = New-PSSession -UseSSL -ComputerName "localhost" -SessionOption $httpsOptions -ErrorVariable httpsError -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue ## Disable HTTP Listener --Roger If ($httpResult) { winrm delete winrm/config/Listener?Address=*+Transport=HTTP } If ($httpResult -and $httpsResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTP: Enabled | HTTPS: Enabled" } ElseIf ($httpsResult -and !$httpResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTP: Disabled | HTTPS: Enabled" } ElseIf ($httpResult -and !$httpsResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTP: Enabled | HTTPS: Disabled" } Else { Throw "Unable to establish an HTTP or HTTPS remoting session." } Write-Verbose "PS Remoting has been successfully configured for Ansible."
注意:HTTPS认证需要创建证书,但是证书的有效期为一年,所以为了保证证书不过期,可以做一个计划任务的脚本,在windows主机每次重启时,执行这个脚本,这个每次重启后的证书是新的。
本文出自 “zengestudy” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://zengestudy.blog.51cto.com/1702365/1865946
以上是关于Ansible控制Windows操作步骤的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章