课后作业---字符串
Posted 枫
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了课后作业---字符串相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、课后作业一
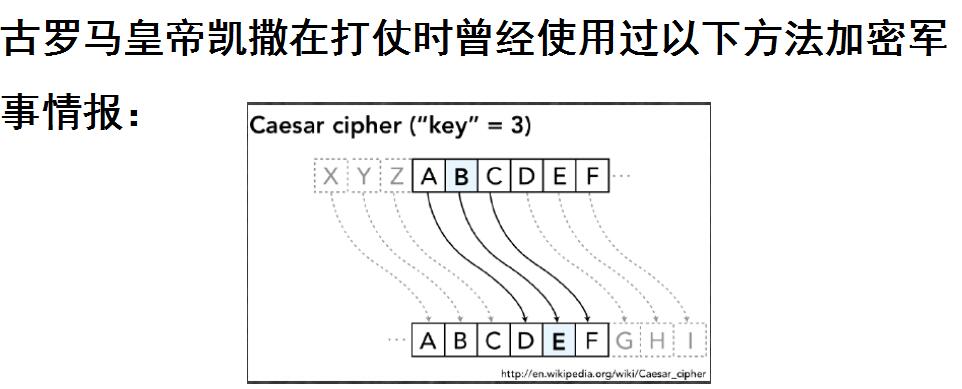
1.设计思想:根据题意,首先提示输入要进行的操作:解密或加密,然后输入一个字符串,利用charAt()方法将改变的字母连接到结果上,加密:将前23个大小写字母+3,后3个-23强制转化为char;解密:后23个大小写字母-3,前3个+23。再根据结果进行改变,添加提示。
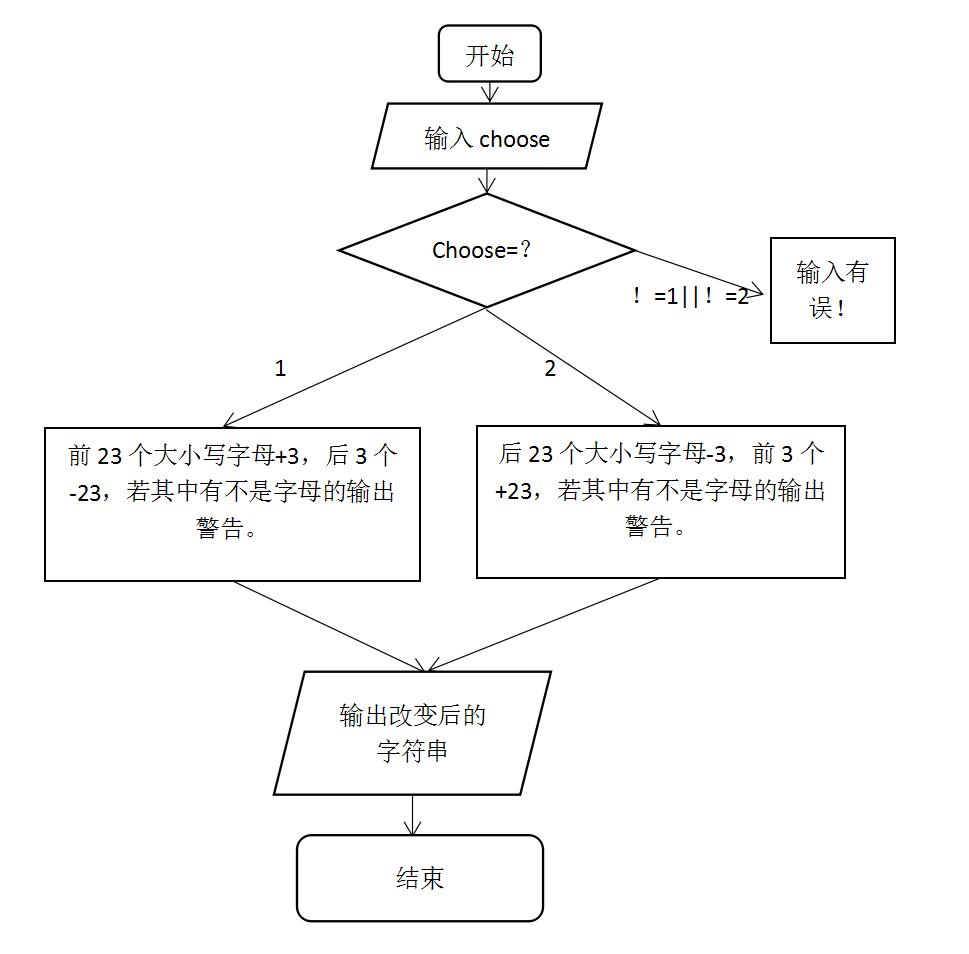
2.程序流程图:
3.源代码:
package T4;
//胡建峰,2016.10.25
//字串加密
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main( String args[] ){
Scanner N = new Scanner(System.in);//输入
System.out.print("请输入要执行操作(1.加密,2解密):");
int choose = N.nextInt();
String result="";
char temp;
if(choose == 1)//加密
{
System.out.print("请输入字符串:");
String wen = N.next();
for(int i = 0;i < wen.length();i++)
{
if((wen.charAt(i) > 64 && wen.charAt(i) < 88)||(wen.charAt(i) > 96 && wen.charAt(i) < 120))
temp=(char) (wen.charAt(i) + 3);
else if((wen.charAt(i) > 87 && wen.charAt(i) < 91)||(wen.charAt(i) > 119 && wen.charAt(i) < 123))
temp=(char) (wen.charAt(i) - 23);
else
{
System.out.println("中间输入有误!");
break;
}
result += temp;
}
System.out.println("加密后结果为:" + result);
}
else if(choose == 2)//解密
{
System.out.print("请输入字符串:");
String wen = N.next();
for(int i = 0;i < wen.length();i++)
{
if((wen.charAt(i) > 67 && wen.charAt(i) < 91)||(wen.charAt(i) > 99 && wen.charAt(i) < 123))
temp=(char) (wen.charAt(i) - 3);
else if((wen.charAt(i) > 64 && wen.charAt(i) < 68)||(wen.charAt(i) > 96 && wen.charAt(i) < 100))
temp=(char) (wen.charAt(i) + 23);
else
{
System.out.println("中间输入有误!");
break;
}
result += temp;
}
System.out.println("解密后结果为:" + result);
}
else
System.out.println("输入有误!");
N.close();
}
}
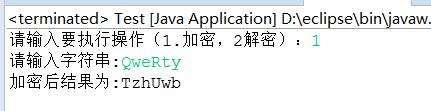
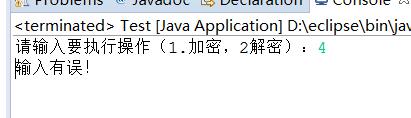
4.结果截图:


二、动手动脑:请查看String.equals()方法的实现代码,注意学习其实现方法。
equals()方法的一个重载:
public boolean equals(MyTestClass obj)
{
return obj.Value==this.Value;
}
方法实现代码:
public class StringEquals {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1=new String("Hello");
String s2=new String("Hello");
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
String s3="Hello";
String s4="Hello";
System.out.println(s3==s4);
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));
}
}
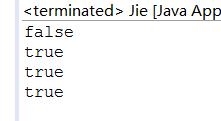
String1.equals(String2)判断的是String1和String2的值是否相同,s1、s2是新建位置不同,s3,s4建立时由于值相同所以指的是同一位置。
三、整理String类的Length()、charAt()、 getChars()、replace()、 toUpperCase()、 toLowerCase()、trim()、toCharArray()使用说明
int length() :返回当前字符串长度。
char charAt(int index):取字符串中的某一个字符,其中的参数index指的是字符串中序数。字符串的序数从0开始到length()-1 。
例如:
String s = new String("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz");
System.out.println("s.charAt(5): " + s.charAt(5) );
结果为:s.charAt(5): f
void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin):该方法将字符串拷贝到字符数组中。其中,srcBegin为拷贝的起始位置、srcEnd为拷贝的结束位置、字符串数值dst为目标字符数组、dstBegin为目标字符数组的拷贝起始位置。
例如:
char[] s1 = {\'I\',\' \',\'l\',\'o\',\'v\',\'e\',\' \',\'h\',\'e\',\'r\',\'!\'};//s1=I love her!
String s2 = new String("you!"); s2.getChars(0,3,s1,7); //s1=I love you!
System.out.println( s1 );
结果为:I love you!
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)返回一个新的字符串
String toLowerCase():将字符串转换成小写。
String toUpperCase():将字符串转换成大写。
例如:
String s = new String("java.lang.Class String");
System.out.println("s.toUpperCase(): " + s.toUpperCase() );
System.out.println("s.toLowerCase(): " + s.toLowerCase() );
结果为:
s.toUpperCase(): JAVA.LANG.CLASS STRING
s.toLowerCase(): java.lang.class string
trim():返回该字符串去掉开头和结尾空格后的字符串
char[ ] toCharArray() :将该String对象转换成char数组。
以上是关于课后作业---字符串的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章