rabbitMQ第三篇:采用不同的交换机规则
Posted lpeiNet
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了rabbitMQ第三篇:采用不同的交换机规则相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在上一篇我们都是采用发送信息到队列然后队列把信息在发送到消费者,其实实际情况并非如此,rabbitMQ其实真正的思想是生产者不发送任何信息到队列,甚至不知道信息将发送到哪个队列。相反生产者只能发送信息到交换机,交换机接收到生产者的信息,然后按照规则把它推送到对列中,交换机是如何做处理他接收到的信息,并怎么样发送到特定的队列,那么这一篇主要是讲解交换机的规则。
一:发布/订阅
在上一篇说到的队列都指定了名称,但是现在我们不需要这么做,我们需要所有的日志信息,而不只是其中的一个。如果要做这样的队列,我们需要2件事,一个就是获取一个新的空的队列,这样我就需要创建一个随机名称的队列,最好让服务器帮我们做出选择,第一个就是我们断开用户的队列,应该自动进行删除。ok下面是一副工作图。
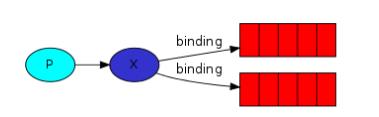
信息发送端代码
public class EmitLog { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "logs"; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException { ConnectionFactory factory=new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("localhost"); Connection connection=factory.newConnection(); Channel channel=connection.createChannel(); channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME,"fanout");//fanout表示分发,所有的消费者得到同样的队列信息 //分发信息 for (int i=0;i<5;i++){ String message="Hello World"+i; channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME,"",null,message.getBytes()); System.out.println("EmitLog Sent \'" + message + "\'"); } channel.close(); connection.close(); }
消费者代码
public class ReceiveLogs1 { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "logs"; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException { ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("localhost"); Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout"); //产生一个随机的队列名称 String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");//对队列进行绑定 System.out.println("ReceiveLogs1 Waiting for messages"); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { String message = new String(body, "UTF-8"); System.out.println("ReceiveLogs1 Received \'" + message + "\'"); } }; channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);//队列会自动删除 } }
上面就完成了一个发布/订阅模式的消息队列 看看结果

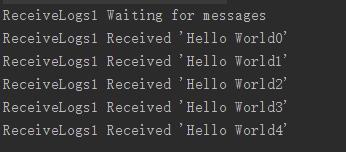
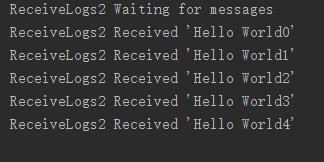
二:Routing
上面我用采用了广播的模式进行消息的发送,现在我们采用路由的方式对不同的消息进行过滤
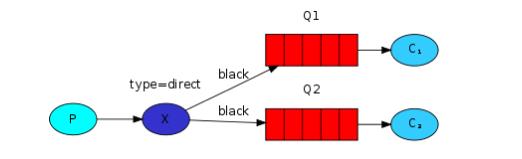
发送端代码
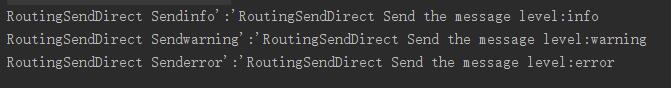
public class RoutingSendDirect { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_logs"; // 路由关键字 private static final String[] routingKeys = new String[]{"info" ,"warning", "error"}; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException { ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("localhost"); Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME,"direct");//注意是direct //发送信息 for (String routingKey:routingKeys){ String message = "RoutingSendDirect Send the message level:" + routingKey; channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME,routingKey,null,message.getBytes()); System.out.println("RoutingSendDirect Send"+routingKey +"\':\'" + message); } channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
ReceiveLogsDirect1 消费者代码
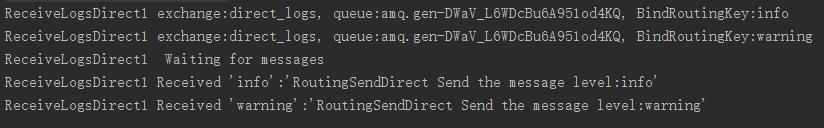
public class ReceiveLogsDirect1 { // 交换器名称 private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_logs"; // 路由关键字 private static final String[] routingKeys = new String[]{"info" ,"warning"}; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException { ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("localhost"); Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换器 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct"); //获取匿名队列名称 String queueName=channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); //根据路由关键字进行绑定 for (String routingKey:routingKeys){ channel.queueBind(queueName,EXCHANGE_NAME,routingKey); System.out.println("ReceiveLogsDirect1 exchange:"+EXCHANGE_NAME+"," + " queue:"+queueName+", BindRoutingKey:" + routingKey); } System.out.println("ReceiveLogsDirect1 Waiting for messages"); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { String message = new String(body, "UTF-8"); System.out.println("ReceiveLogsDirect1 Received \'" + envelope.getRoutingKey() + "\':\'" + message + "\'"); } }; channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer); }
ReceiveLogsDirect2消费者代码
public class ReceiveLogsDirect2 { // 交换器名称 private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_logs"; // 路由关键字 private static final String[] routingKeys = new String[]{"error"}; public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception { ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("localhost"); Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换器 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct"); //获取匿名队列名称 String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); //根据路由关键字进行多重绑定 for (String severity : routingKeys) { channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, severity); System.out.println("ReceiveLogsDirect2 exchange:"+EXCHANGE_NAME+", queue:"+queueName+", BindRoutingKey:" + severity); } System.out.println("ReceiveLogsDirect2 Waiting for messages"); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { String message = new String(body, "UTF-8"); System.out.println("ReceiveLogsDirect2 Received \'" + envelope.getRoutingKey() + "\':\'" + message + "\'"); } }; channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer); } }
上面代码可以看出这里是通过路由来找个这个对列的。我们看下结果

三:Topics
这种应该属于模糊匹配
* :可以替代一个词
#:可以替代0或者更多的词
现在我们继续看看代码来理解
发送端
public class TopicSend { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs"; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException { Connection connection = null; Channel channel = null; try{ ConnectionFactory factory=new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("localhost"); connection=factory.newConnection(); channel=connection.createChannel(); //声明一个匹配模式的交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME,"topic"); //待发送的消息 String[] routingKeys=new String[]{ "quick.orange.rabbit", "lazy.orange.elephant", "quick.orange.fox", "lazy.brown.fox", "quick.brown.fox", "quick.orange.male.rabbit", "lazy.orange.male.rabbit" }; //发送消息 for(String severity :routingKeys){ String message = "From "+severity+" routingKey\' s message!"; channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, severity, null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("TopicSend Sent \'" + severity + "\':\'" + message + "\'"); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); if (connection!=null){ channel.close(); connection.close(); } }finally { if (connection!=null){ channel.close(); connection.close(); } } } }
消费者1:
public class ReceiveLogsTopic1 { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs"; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException { ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("localhost"); Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明一个匹配模式的交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic"); String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); //路由关键字 String[] routingKeys = new String[]{"*.orange.*"}; //绑定路由 for (String routingKey : routingKeys) { channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, routingKey); System.out.println("ReceiveLogsTopic1 exchange:" + EXCHANGE_NAME + ", queue:" + queueName + ", BindRoutingKey:" + routingKey); } System.out.println("ReceiveLogsTopic1 Waiting for messages"); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { String message = new String(body, "UTF-8"); System.out.println("ReceiveLogsTopic1 Received \'" + envelope.getRoutingKey() + "\':\'" + message + "\'"); } }; channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer); } }
消费者2:
ublic class ReceiveLogsTopic2 { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs"; public static void main(String[] argv) throws IOException, TimeoutException { ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("localhost"); Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明一个匹配模式的交换器 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic"); String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 路由关键字 String[] routingKeys = new String[]{"*.*.rabbit", "lazy.#"}; // 绑定路由关键字 for (String bindingKey : routingKeys) { channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, bindingKey); System.out.println("ReceiveLogsTopic2 exchange:"+EXCHANGE_NAME+", queue:"+queueName+", BindRoutingKey:" + bindingKey); } System.out.println("ReceiveLogsTopic2 Waiting for messages"); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { String message = new String(body, "UTF-8"); System.out.println("ReceiveLogsTopic2 Received \'" + envelope.getRoutingKey() + "\':\'" + message + "\'"); } }; channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer); } }
运行后结果

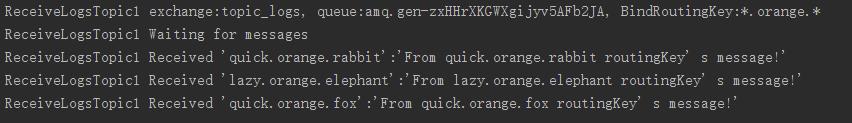

以上是关于rabbitMQ第三篇:采用不同的交换机规则的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章