MJExtension使用
Posted 小敏的博客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MJExtension使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、MJExtension第三方框架
我们在ios开发过程中,我们常常需要将字典数据(也就是JSON数据)与Model模型之间的转化,例如网络请求返回的微博数据、等等,如果我们自己全部手动去创建模型并赋值,都是一些毫无技术含量的代码,费时费力,而且还可能会赋值出错,让我们很头疼。
MJExtension框架就是为了解决这个问题而设计得第三方开源库。
提供了以下的一些方法实现:
- 简单的字典 --> 模型
- JSON字符串 --> 模型
- 复杂的字典 --> 模型 (模型里面包含了模型)
- 复杂的字典 --> 模型 (模型的数组属性里面又装着模型)
- 复杂的字典 --> 模型(模型属性名和字典的key不一样)
- 字典数组 --> 模型数组
- 模型 --> 字典
- 模型数组 --> 字典数组
- 字典 --> CoreData模型
- 归档与解档NSCoding
- 过滤字典的值
MJExtension框架是利用Obj-C的运行时机制编写的,现在iOS开发语言往Swift语言发展,我不太清楚Swift语言是否也有这种特性,该框架以后会不会在Swift语言上也发展下去不得而知,不过这个框架很轻量级,非常适合初级开发者去看它的源码,对理解Obj-C的运行时机制有非常大的帮助。
MJExtension框架是利用Obj-C的运行时机制编写的,现在iOS开发语言往Swift语言发展,我不太清楚Swift语言是否也有这种特性,该框架以后会不会在Swift语言上也发展下去不得而知,不过这个框架很轻量级,非常适合初级开发者去看它的源码,对理解Obj-C的运行时机制有非常大的帮助。
二、Runtime运行时机制简单了解
Runtime简称运行时,就是系统在运行的时候的一些机制,其中最主要的是消息机制。
OC的函数调用类似于消息发送,属于动态调用过程。在编译的时候并不能决定真正调用哪个函数。事实证明,在编译阶段,OC可以调用任何函数,即使这个函数并未实现,只要申明过就不会报错。而C语言在编译阶段就会报错。只有在真正运行的时候才会根据函数的名称找到对应的函数来调用。
例如,下面的这个代码在编译时会被转化:
/* OC方法调用 */ [obj makeTest]; /* 编译时Runtime会将上面的代码转为下面的消息发送 */ objc_msgSend(obj, @selector(makeText));
iOS的顶层基类NSObject含有一个指向objc_class结构体的isa指针:
@interface NSObject{ Class isa; }; typedef struct objc_class *Class; struct objc_class { Class isa; // 指向metaclass,也就是静态的Class Class super_class ; // 指向其父类 const char *name ; // 类名 long version ; // 类的版本信息,初始化默认为0 /* 一些标识信息,如CLS_CLASS(0x1L)表示该类为普通class; CLS_META(0x2L)表示该类为metaclass */ long info; long instance_size ; // 该类的实例变量大小(包括从父类继承下来的实例变量); struct objc_ivar_list *ivars; // 用于存储每个成员变量的地址 /* 与info的一些标志位有关,如是普通class则存储对象方法,如是metaclass则存储类方法; */ struct objc_method_list **methodLists ; struct objc_cache *cache; // 指向最近使用的方法的指针,用于提升效率; struct objc_protocol_list *protocols; // 存储该类遵守的协议 };
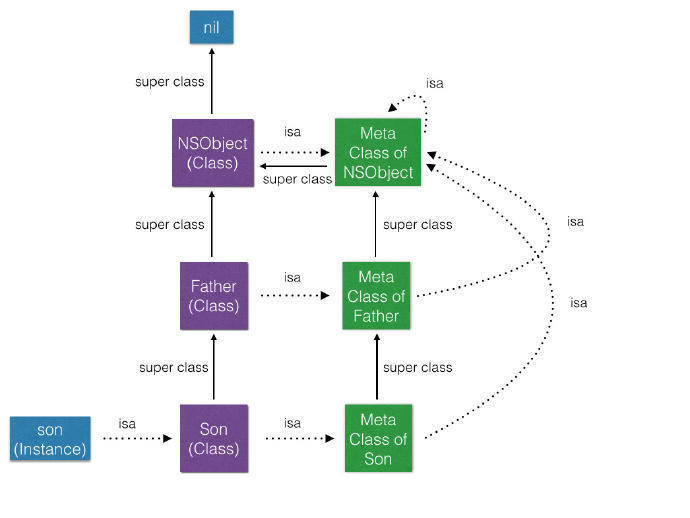
在objc_msgSend函数的调用过程:
- 首先通过obj的isa指针找到obj对应的Class。
- 在Class中先去
cache中通过SEL查找对应函数method- 若
cache中未找到,再去methodLists中查找- 若
methodLists中未找到,则进入superClass按前面的步骤进行递归查找- 若找到
method,则将method加入到cache中,以方便下次查找,并通过method中的函数指针跳转到对应的函数中去执行。- 如果一直查找到
NSObject还没查找到,则会进入消息动态处理流程。
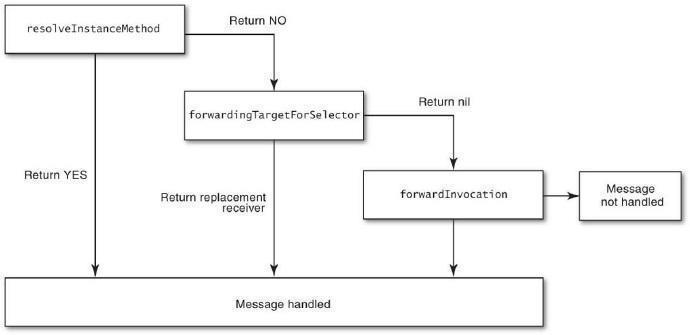
消息动态处理流程:
/* 1. 时机处理之一,在这个方法中我们可以利用runtime的特性动态添加方法来处理 */ + (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel; /* 2. 时机处理之二,在这个方法中看代理能不能处理,如果代理对象能处理,则转接给代理对象 */ - (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector; /* 3. 消息转发之一,该方法返回方法签名,如果返回nil,则转发流程终止,抛出异常 */ - (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector; /* 4. 消息转发之二,在该方法中我们可以对调用方法进行重定向 */ - (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation;
所以使用Runtime机制我们就可以动态向类添加方法或属性:
/* 动态向一个类添加属性 */ class_addIvar(kclass, "expression", size, alignment, "*"); /* 动态向一个类添加方法 */ class_addMethod(kclass, @selector(setExpressionFormula:), (IMP)setExpressionFormula, "v@:@"); class_addMethod(kclass, @selector(getExpressionFormula), (IMP)getExpressionFormula, "@@:"); static void setExpressionFormula(id self, SEL cmd, id value){ NSLog(@"call setExpressionFormula"); } static id getExpressionFormula(id self, SEL cmd) { NSLog(@"call getExpressionFormula"); return nil; }
v表示void,@表示id类型,:表示SEL类型"v@:@":表示返回值为void,接受一个id类型、一个SEL类型、一个id类型的方法"@@:":表示返回值为id类型,接受一个id类型和一个SEL类型参数的方法
具体Runtime运行时使用细节,这里就不细讲,只是简单了解下Runtime是可以做到动态向类添加属性和方法就行。
三、MJExtension使用
MJExtension的大部分方法实现都集成到了分类上,不需要使用新的类,只需要包含头文件MJExtension.h即可。MJExtension在github上的使用说明已经写得十分明白了。
1. 简单的字典 --> 模型
模型类User定义:
typedef enum { SexMale, SexFemale } Sex; @interface User : NSObject @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name;/* 姓名 */ @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *icon;/* 头像 */ @property (assign, nonatomic) unsigned int age;/* 年龄 */ @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *height;/* 身高 */ @property (strong, nonatomic) NSNumber *money;/* 资产 */ @property (assign, nonatomic) Sex sex;/* 性别 */ @property (assign, nonatomic, getter=isGay) BOOL gay;/* 是否是同性恋 */ @end
使用实例:
NSDictionary *dict = @{ @"name" : @"Jack", @"icon" : @"lufy.png", @"age" : @20, @"height" : @"1.55", @"money" : @100.9, @"sex" : @(SexFemale),/* 枚举需要使用NSNumber包装 */ @"gay" : @"NO" }; //字典转模型,使用的是mj_objectWithKeyValues:方法 User *user = [User mj_objectWithKeyValues:dict];
2. JSON字符串 --> 模型
使用实例:
// 定义一个JSON字符串 NSString *jsonString = @"{\\"name\\":\\"Jack\\", \\"icon\\":\\"lufy.png\\", \\"age\\":20}"; // JSON字符串转模型 User *user = [User mj_objectWithKeyValues:jsonString];
3. 复杂的字典 --> 模型 (模型里面包含了模型)
模型类Status定义:
@interface Status : NSObject @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *text; @property (strong, nonatomic) User *user;/* 其他模型类型 */ @property (strong, nonatomic) Status *retweetedStatus;/* 自我模型类型 */ @end
使用实例:
NSDictionary *dict = @{ @"text" : @"Agree!Nice weather!", @"user" : @{ @"name" : @"Jack", @"icon" : @"lufy.png" }, @"retweetedStatus" : @{ @"text" : @"Nice weather!", @"user" : @{ @"name" : @"Rose", @"icon" : @"nami.png" } } }; //字典转模型,模型里面含有模型 Status *status = [Status mj_objectWithKeyValues:dict]; NSString *text = status.text; NSString *name = status.user.name; NSString *icon = status.user.icon; NSLog(@"text=%@, name=%@, icon=%@", text, name, icon); // text=Agree!Nice weather!, name=Jack, icon=lufy.png NSString *text2 = status.retweetedStatus.text; NSString *name2 = status.retweetedStatus.user.name; NSString *icon2 = status.retweetedStatus.user.icon; NSLog(@"text2=%@, name2=%@, icon2=%@", text2, name2, icon2); // text2=Nice weather!, name2=Rose, icon2=nami.png
4. 复杂的字典 --> 模型 (模型的数组属性里面又装着模型)
模型类Ad和StatusResult定义:
@interface Ad : NSObject @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *image; @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *url; @end @interface StatusResult : NSObject /** 数组中存储模型Status类型数据 */ @property (strong, nonatomic) NSMutableArray *statuses; /** 数组中存储模型Ad类型数据 */ @property (strong, nonatomic) NSArray *ads; @property (strong, nonatomic) NSNumber *totalNumber; @end #import "MJExtension.h" /* 数组中存储模型数据,需要说明数组中存储的模型数据类型 */ @implementation StatusResult /* 实现该方法,说明数组中存储的模型数据类型 */ + (NSDictionary *)mj_ objectClassInArray{ return @{ @"statuses" : @"Status", @"ads" : @"Ad" }; } @end
使用实例:
NSDictionary *dict = @{ @"statuses" : @[ @{ @"text" : @"Nice weather!", @"user" : @{ @"name" : @"Rose", @"icon" : @"nami.png" } }, @{ @"text" : @"Go camping tomorrow!", @"user" : @{ @"name" : @"Jack", @"icon" : @"lufy.png" } } ], @"ads" : @[ @{ @"image" : @"ad01.png", @"url" : @"http://www.ad01.com" }, @{ @"image" : @"ad02.png", @"url" : @"http://www.ad02.com" } ], @"totalNumber" : @"2014" }; //字典转模型,支持模型的数组属性里面又装着模型 StatusResult *result = [StatusResult mj_objectWithKeyValues:dict]; //打印博主信息 for (Status *status in result.statuses) { NSString *text = status.text; NSString *name = status.user.name; NSString *icon = status.user.icon; NSLog(@"text=%@, name=%@, icon=%@", text, name, icon); } // text=Nice weather!, name=Rose, icon=nami.png // text=Go camping tomorrow!, name=Jack, icon=lufy.png //打印广告 for (Ad *ad in result.ads) { NSLog(@"image=%@, url=%@", ad.image, ad.url); } // image=ad01.png, url=http://www.ad01.com // image=ad02.png, url=http://www.ad02.com
5. 复杂的字典 --> 模型(模型属性名和字典的key不一样)
模型类Bag和Student定义:
@interface Bag : NSObject @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name; @property (assign, nonatomic) double price; @end @interface Student : NSObject @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *ID; @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *desc; @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *nowName; @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *oldName; @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *nameChangedTime; @property (strong, nonatomic) Bag *bag; @end #import "MJExtension.h" @implementation /* 设置模型属性名和字典key之间的映射关系 */ + (NSDictionary *)mj_replacedKeyFromPropertyName{ /* 返回的字典,key为模型属性名,value为转化的字典的多级key */ return @{ @"ID" : @"id", @"desc" : @"desciption", @"oldName" : @"name.oldName", @"nowName" : @"name.newName", @"nameChangedTime" : @"name.info[1].nameChangedTime", @"bag" : @"other.bag" }; } @end
使用实例:
NSDictionary *dict = @{ @"id" : @"20", @"desciption" : @"kids", @"name" : @{ @"newName" : @"lufy", @"oldName" : @"kitty", @"info" : @[ @"test-data", @{ @"nameChangedTime" : @"2013-08" } ] }, @"other" : @{ @"bag" : @{ @"name" : @"a red bag", @"price" : @100.7 } } }; //字典转模型,支持多级映射 Student *stu = [Student mj_objectWithKeyValues:dict]; //打印 NSLog(@"ID=%@, desc=%@, oldName=%@, nowName=%@, nameChangedTime=%@", stu.ID, stu.desc, stu.oldName, stu.nowName, stu.nameChangedTime); // ID=20, desc=kids, oldName=kitty, nowName=lufy, nameChangedTime=2013-08 NSLog(@"bagName=%@, bagPrice=%f", stu.bag.name, stu.bag.price); // bagName=a red bag, bagPrice=100.700000
6. 字典数组 --> 模型数组
使用实例:
NSArray *dictArray = @[ @{ @"name" : @"Jack", @"icon" : @"lufy.png" }, @{ @"name" : @"Rose", @"icon" : @"nami.png" } ]; //字典数组转模型数组,使用的是mj_objectArrayWithKeyValuesArray:方法 NSArray *userArray = [User mj_objectArrayWithKeyValuesArray:dictArray]; //打印 for (User *user in userArray) { NSLog(@"name=%@, icon=%@", user.name, user.icon); } // name=Jack, icon=lufy.png // name=Rose, icon=nami.png
7. 模型 --> 字典
使用实例:
//创建一个模型对象 User *user = [[User alloc] init]; user.name = @"Jack"; user.icon = @"lufy.png"; Status *status = [[Status alloc] init]; status.user = user; status.text = @"Nice mood!"; //模型转字典,使用的是mj_keyValues属性 NSDictionary *statusDict = status.mj_keyValues; NSLog(@"%@", statusDict); /* { text = "Nice mood!"; user = { icon = "lufy.png"; name = Jack; }; } */
8. 模型数组 --> 字典数组
使用实例:
//创建模型数组 User *user1 = [[User alloc] init]; user1.name = @"Jack"; user1.icon = @"lufy.png"; User *user2 = [[User alloc] init]; user2.name = @"Rose"; user2.icon = @"nami.png"; NSArray *userArray = @[user1, user2]; //模型数组转字典数组,使用的是mj_keyValuesArrayWithObjectArray:方法 NSArray *dictArray = [User mj_keyValuesArrayWithObjectArray:userArray]; NSLog(@"%@", dictArray); /* ( { icon = "lufy.png"; name = Jack; }, { icon = "nami.png"; name = Rose; } ) */
9. 字典 --> CoreData模型
使用实例:
NSDictionary *dict = @{ @"name" : @"Jack", @"icon" : @"lufy.png", @"age" : @20, @"height" : @1.55, @"money" : @"100.9", @"sex" : @(SexFemale), @"gay" : @"true" }; //字典转为CoreData模型 NSManagedObjectContext *context = nil; User *user = [User mj_objectWithKeyValues:dict context:context]; [context save:nil];
10. 归档与解档NSCoding
模型类Bag添加实现:
@interface Bag : NSObject <NSCoding> @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name; @property (assign, nonatomic) double price; @end #import "MJExtension.h" @implementation Bag //添加了下面的宏定义 MJExtensionCodingImplementation /* 实现下面的方法,说明哪些属性不需要归档和解档 */ + (NSArray *)mj_ignoredCodingPropertyNames{ return @[@"name"]; } @end
使用实例:
//创建模型 Bag *bag = [[Bag alloc] init]; bag.name = @"Red bag"; bag.price = 200.8; //获取归档路径 NSString *file = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Desktop/bag.data"]; //归档 [NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:bag toFile:file]; //解档 Bag *decodedBag = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:file]; NSLog(@"name=%@, price=%f", decodedBag.name, decodedBag.price); // name=(null), price=200.800000
11. 过滤字典的值
模型类Book实现:
@interface Book: NSObject @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name; @property (strong, nonatomic) NSDate *publishedTime; @end #import "MJExtension.h" @implementation Book /* 转化过程中对字典的值进行过滤和进一步转化 */ - (id)mj_newValueFromOldValue:(id)oldValue property:(MJProperty *)property { if ([property.name isEqualToString:@"publisher"]) { if (oldValue == nil) { return @""; } } else if (property.type.typeClass == [NSDate class]) { NSDateFormatter *fmt = [[NSDateFormatter alloc] init]; fmt.dateFormat = @"yyyy-MM-dd"; return [fmt dateFromString:oldValue]; } return oldValue; } @end
使用实例:
NSDictionary *dict = @{ @"name" : @"5分钟突破iOS开发", @"publishedTime" : @"2011-09-10" }; //字典转模型,过滤name为nil的情况,把NSString转为NSDate Book *book = [Book mj_objectWithKeyValues:dict]; //打印 NSLog(@"name=%@, publishedTime=%@", book.name, book.publishedTime);
MJExtension的github地址点这里:CoderMJLee/MJExtension
以上是关于MJExtension使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章