线程__线程间的通信
Posted 开拖拉机的蜡笔小新
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了线程__线程间的通信相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
线程间的通信:多个线程在处理同一资源,但是任务却不同。
一、等待唤醒机制
涉及的方法:
1.wait();让线程处于冻结状态,被wait的线程会被存储到线程池中
2.notify();唤醒线程池中的一个任意线程
3.notifyAll();唤醒线程池中的所有线程
这些方法都必须定义在同步中,因为这些方法是用于操作线程状态的方法,必须要明确到底操作的是哪个锁上的线程
wait()对A锁上面的线程进行操作后只能用A锁的notify来唤醒。被wait之后的线程可认为放在线程池中。
为什么操作线程的方法wait notify notifyAll定义在Object类中?
因为这些方法是监视器的方法,监视器其实就是锁。
锁可以是任意多对象,任意的对象调用的方式一定是定义在Object中。
package com.test2;
class Resource
{
private String name;
private int count=1;
private boolean flag=false;
public synchronized void set(String name)
{
if(flag)
try{ this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){}
this.name=name+count;
count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...." + "生产者"+".........." + this.name);
flag=true;
notify();
}
public synchronized void out()
{
if(!flag)
try{ this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...."+"消费者"+"...."+this.name);
flag=false;
notify();
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable
{ private Resource r;
Producer(Resource r)
{
this.r =r;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
r.set("烤鸭");
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable
{ private Resource r;
Consumer(Resource r)
{
this.r =r;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
r.out();
}
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Resource r=new Resource();
Producer a=new Producer(r);
Consumer b=new Consumer(r);
Thread t0=new Thread(a);
Thread t1=new Thread(b);
t0.start();
t1.start();
}
}
产生的结果是:每生产一只就消费一只。
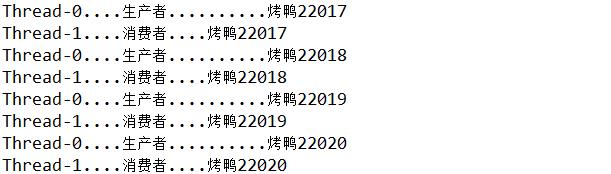
二、多生产者多消费者问题
将代码改成两个生产者两个消费者:
Thread t0=new Thread(a);
Thread t1=new Thread(a);
Thread t2=new Thread(b);
Thread t3=new Thread(b);
t0.start();
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();

可见还是产生了安全问题,关键在于这段代码中:
if(flag)
try{ this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){} //t0 t1
当t0 t1被wait()挂在那后当再次唤醒的时候不会再次去判断flag标记,而直接往下走再次去生产,导致发生错误。
只要将if改为while语句让它返回再次判断一次即可。
while(flag)
try{ this.wait();}catch(InterruptedExceptione){}
class Resource
{
private String name;
private int count=1;
private boolean flag=false;
public synchronized void set(String name)
{
while(flag)
try{ this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){}
this.name=name+count;
count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...." + "生产者"+"........" + this.name);
flag=true;
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void out()
{
while(!flag)
try{ this.wait();}catch(InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...."+"消费者"+"...."+this.name);
flag=false;
notifyAll();
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable
{ private Resource r;
Producer(Resource r)
{
this.r =r;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
r.set("烤鸭");
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable
{ private Resource r;
Consumer(Resource r)
{
this.r =r;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
r.out();
}
}
}
public class Demo3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Resource r=new Resource();
Producer a=new Producer(r);
Consumer b=new Consumer(r);
Thread t0=new Thread(a);
Thread t1=new Thread(a);
Thread t2=new Thread(b);
Thread t3=new Thread(b);
t0.start();
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
可是将代码改成这样后,却出现了死锁问题:

结果运行到这就卡死不动了。
原因:当走到t0(活),t1,t2,t3的情况时,t0走完线程代码,唤醒不是t2或者t3中间的一个而是t1,标志位也改为那么true,那么t1也被直接wait了。
现在t0,t1,t2,t3全死,不会再唤醒,出现死锁。而上面没有出现的死锁的原因在于用if语句,唤醒之后程序接着往下走,总会notify任何一个线程而不会
把所有线程都被wait,而用了while当唤醒之后首先判断标志位,会直接挂死(唤醒的是同一方的线程)。
所以究其原因是没有唤醒对方的线程。那么怎么保证每次都能至少唤醒对方的一个线程呢?
很遗憾,可是没有办法唤醒指定的线程,可以考虑将notify改为notifyAll每次唤醒所有wait的线程可以解决问题,搞定!再次会每生产一个就会消费一个。
总结:
if判断标记,只有一次,会导致不该运行的线程运行了,出现数据错误的情况。
while判断标记,解决线程获取执行权后是否要运行。
notifyAll解决了本方线程一定会唤醒对方线程,notify可能只是唤醒了本方线程,没有意义。且while标记+notify会导致死锁。
所以只要是多生产者多消费者的情况,就用while+notifyAll。
问题:在用notifyAll唤醒线程时可能唤醒了本方线程,可是唤醒本方线程是没有意义的(效率较低),本方线程已经干完活了,需要唤醒对方线程干活就行了。
在jdk1.5 java.util.concurrent.locks中提供了接口Lock
Lock实现提供了比使用synchronized方法和语句可获得的更广泛的锁定操作。
在同步代码块中,对于锁的操作是隐式的,获得和释放都是隐式。jdk1.5后将锁和同步封装成对象,按面向对象的方式显示操作锁。
Object obj=new Object();
void show ()
{ synchronized(obj)
{
}
}
变为:
Lock lock=new ReetrantLock(); //互斥锁,被一个线程获取后不能被其他线程获取。
void show ()
{ lock.lock();//获得锁
code。。。
lock.unlock();//释放锁
}
接口Conditionn将Object监视器方法(wait、notify、notifyAll)分解成截然不同的对象,以便通过这些对象与任意的lock组合使用。
其中Lock替代了synchronized方法与语句的使用,conditiont替代了Object监视器方法的使用。
Condition实例实质上被绑定在一个锁上,要为Lock实例获得Condition实例使用newCondition()方法。
对于上面问题的解决方法:生产者和消费者分别获取一个condition对象,各自拥有一组监视器方法。生产者指定唤醒消费者,消费者指定唤醒生产者。
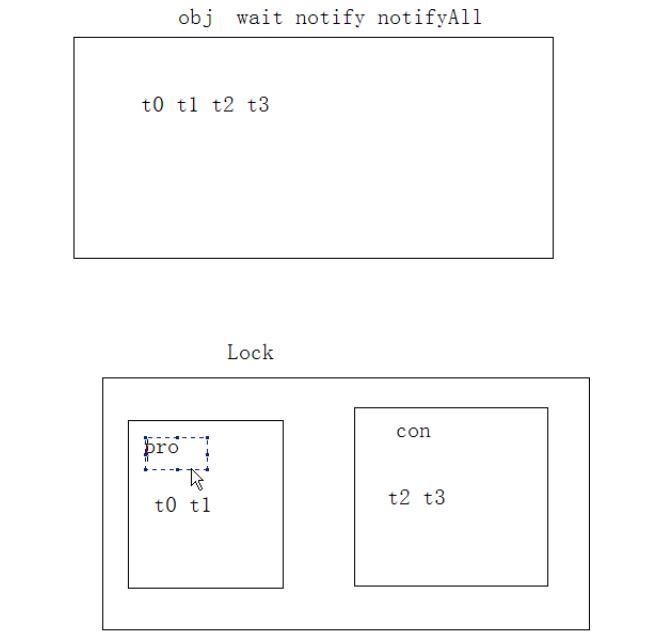
改动的代码如下:

class Resource1 {
private String name;
private int count = 1;
private boolean flag = false;
//创建一个锁对象。
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//通过已有的锁获取该锁上的监视器对象
// Condition con = lock.newCondition();
//通过已有的锁获取两组监视器,一组监视生产者,一组监视消费者
Condition producer_con=lock.newCondition();
Condition consumer_con=lock.newCondition();
public void set(String name) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag) //if()
try {
producer_con.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
this.name = name + count;
count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...." + "生产者" + "...." + this.name);
flag = true;
consumer_con.signal();//notify()
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void out() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (!flag) //if()
try {
consumer_con.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...." + "消费者" + "...." + this.name);
flag = false;
producer_con.signal();//notify()
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
class Producer1 implements Runnable
{ private Resource r;
Producer1(Resource r)
{
this.r =r;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
r.set("烤鸭");
}
}
}
class Consumer1 implements Runnable
{ private Resource r;
Consumer1(Resource r)
{
this.r =r;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
r.out();
}
}
}
public class LockDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Resource r=new Resource();
Producer a=new Producer(r);
Consumer b=new Consumer(r);
Thread t0=new Thread(a);
Thread t1=new Thread(a);
Thread t2=new Thread(b);
Thread t3=new Thread(b);
t0.start();
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
总结:
* Lock接口:出现替代了同步代码块或者同步函数。将同步隐式操作变成显示锁操作。同时更加灵活。可以一个锁上加上多组监视器。
* lock():获取锁
* unlock():释放锁,通常要要定义在finally代码块当中。
* Condition接口:出现替代了Object中wait notify notifyAll方法,这些监视器方法单独进行了封装,变成Condition监视器对象。
* 可以任意的锁进行组合。
* await()——wait()
* signal()——notify()
* signalAll()——notifyAll()
示例:假定有一个绑定的缓冲区,它支持 put 和 take 方法。如果试图在空的缓冲区上执行 take 操作,则在某一个项变得可用之前,线程将一直阻塞;
如果试图在满的缓冲区上执行 put 操作,则在有空间变得可用之前,线程将一直阻塞。
class BoundedBuffer {
final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
final Object[] items = new Object[100];
int putptr, takeptr, count;
public void put(Object x) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
items[putptr] = x;
if (++putptr == items.length) putptr = 0;
++count;
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public Object take() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
Object x = items[takeptr];
if (++takeptr == items.length) takeptr = 0;
--count;
notFull.signal();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
以上是关于线程__线程间的通信的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
