Tree Restoring
Posted mxzf0213
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Tree Restoring相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Tree Restoring
Time limit : 2sec / Memory limit : 256MB
Score : 700 points
Problem Statement
Aoki loves numerical sequences and trees.
One day, Takahashi gave him an integer sequence of length N, a1,a2,…,aN, which made him want to construct a tree.
Aoki wants to construct a tree with N vertices numbered 1 through N, such that for each i=1,2,…,N, the distance between vertex i and the farthest vertex from it is ai, assuming that the length of each edge is 1.
Determine whether such a tree exists.
Constraints
- 2≦N≦100
- 1≦ai≦N−1
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N a1 a2 … aN
Output
If there exists a tree that satisfies the condition, print Possible. Otherwise, print Impossible.
Sample Input 1
5 3 2 2 3 3
Sample Output 1
Possible
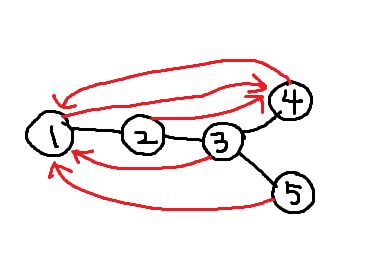
The diagram above shows an example of a tree that satisfies the conditions. The red arrows show paths from each vertex to the farthest vertex from it.
分析:对于一棵树来说,假设直径有两个端点a,b,那么任意一点到其他点最远距离必然是max(dist(p,a),dist(p,b)),
那么根据直径来构树,以树直径为奇数举例,那么这条链上必然有偶数个点,且最远距离为k,k-1,...,k/2,k/2...,k-1,k;
那么也就是不存在最远距小于k/2的点,且k/2有两个点,大于k/2的至少有2个;
树直径为偶数时同理;
代码:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <climits> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <list> #define rep(i,m,n) for(i=m;i<=n;i++) #define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++) #define mod 1000000007 #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define vi vector<int> #define pb push_back #define mp make_pair #define fi first #define se second #define ll long long #define pi acos(-1.0) #define pii pair<int,int> #define Lson L, mid, rt<<1 #define Rson mid+1, R, rt<<1|1 const int maxn=1e5+10; using namespace std; ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;} int n,m,k,t; inline ll read() { ll x=0;int f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<‘0‘||ch>‘9‘){if(ch==‘-‘)f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>=‘0‘&&ch<=‘9‘){x=x*10+ch-‘0‘;ch=getchar();} return x*f; } int a[maxn],ma,vis[maxn]; bool flag; int main() { int i,j; scanf("%d",&n); rep(i,1,n)scanf("%d",&a[i]),vis[a[i]]++,ma=max(ma,a[i]); if(ma%2==0) { rep(i,1,ma/2-1)if(vis[i])flag=true; rep(i,ma/2,ma) { if(i==ma/2) { if(vis[i]!=1)flag=true; } else if(vis[i]<2)flag=true; } } else { rep(i,1,(ma+1)/2-1)if(vis[i])flag=true; rep(i,(ma+1)/2,ma) { if(i<(ma+1)/2&&vis[i])flag=true; if(i==(ma+1)/2) { if(vis[i]!=2)flag=true; } else if(vis[i]<2)flag=true; } } if(flag)puts("Impossible"); else puts("Possible"); //system("Pause"); return 0; }
以上是关于Tree Restoring的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章