自定义控件——圆形圆点进度条(仿安全卫士中的一键加速)
Posted a10615
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了自定义控件——圆形圆点进度条(仿安全卫士中的一键加速)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文已授权微信公众号:鸿洋(hongyangandroid)首发。
一、源代码
源代码及demo下载(此进度条开源项目后续会持续添加、更新)
二、行动由来
在开发交流群中,一童鞋说要实现这个进度条,但在网上没有找到开源项目。

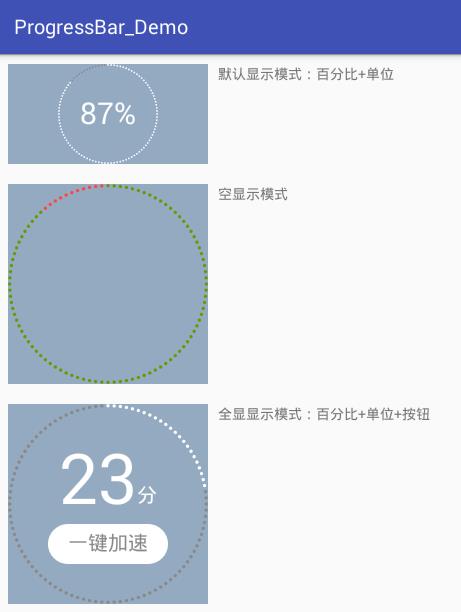
看到这个图片,很熟悉吧?有木有想点它的冲动?觉得有点意思,可以研究一下,再说也有一段时间没写自定义控件了,正好复习复习(说实话,一段时间没写,思路有,但就是不知道从哪开始)。昨天花了一天的时间才把它搞定,先看效果图:
3种显示模式:
模拟进度动画效果:
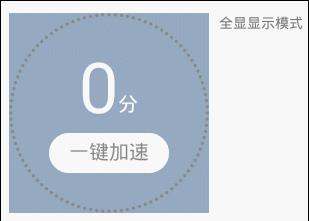
说说它的特点:
- 显示模式有三种可选。如上展示;
- 全显在控件范围内。控件宽高不一时,会以小的为边界;
- 所有颜色都可自定义;
- 百分比、单位、按钮的字体大小都可自定义;
- 单位和按钮的文字可自定义;
- 单位与百分比的对齐方式可选。详见下面的“绘制单位”;
- 按钮与百分比垂直间距可调;
- 按钮可设置点击事件(好像是废话,不然为什么叫按钮);
- 可在子线程中直接更新进度。
三、设计剖析
看到这个图,首先可以确定,它包括四个部分:
- 最外层的圆点
- 百分比
- 单位
- 按钮
当然先得知道自定义控件的步骤,参考了这位牛人的博文。
先总结下自定义控件的步骤:
- 分析控件的每个部分,设定其属性。在res/values/attrs.xml中定义好;
- 实现基本的三个构造方法,并在构造方法中获取属性值或默认值;
- 重写onDraw(Canvas canvas)方法,在此方法中绘制界面;
- 【可选】处理触摸事件;
- 在布局文件中使用。在基布局中别忘了添加命名空间(如:xmlns:zjun=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto”),这样才能使用自定义属性。
然后逐个分析。。。
1、绘制最外层的圆点
最外层的圆点,看上就很多,一圈下来感觉有100个,它当前百分比是65,数了下,确实是65个白点,灰点就不用数了,肯定就是剩下的35个。这样,一圈上点的总个数确定下来,就是100个。
点与点之间的空白距离,看上去就是一个点的空间。一圈下来,就是200个连续圆点。圆点应该内切控件边界。
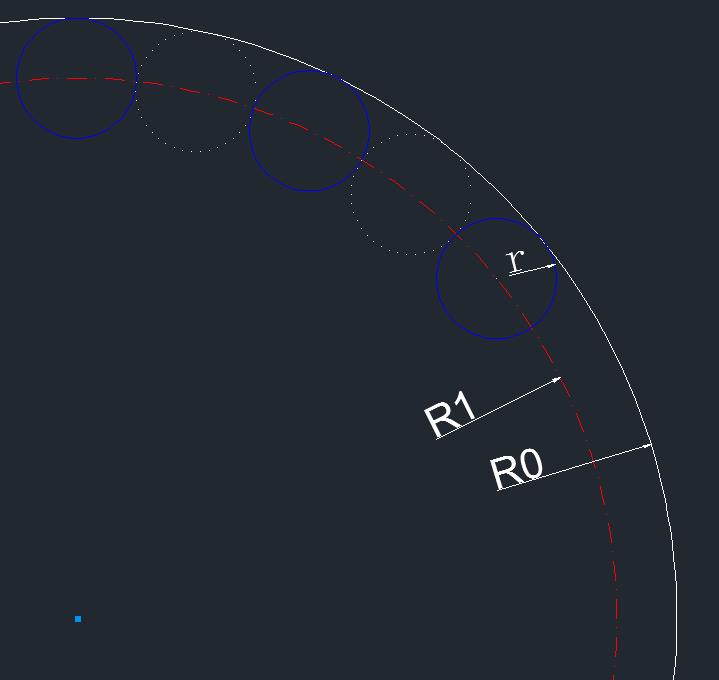
它们的关系是: R0 = R1 + r; ······ ①
其中R0控件大小(min(getWidth(), getHeight()))的一半;R1就是圆点的圆心组成的圆轨迹的半径;r是圆点半径;
另外200个连续圆点在以R1为半径的圆上,圆点与圆点都是外切关系。所以每个圆点所占的角度就是360°/200 = 1.8°
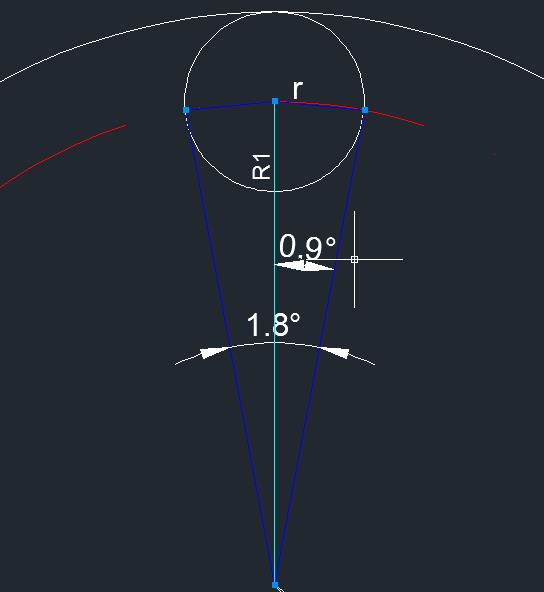
它们的关系:
sin(0.9°)=rR1
······ ②
由①和②可知,r与R0的关系:
r=sin(0.9°)sin(0.9°)+1R0
这样出来的效果,实际圆点间距离太大,最后把sin(0.9°)提高到sin(1°)。这样就比较饱满了。
mSin_1 = (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(1));
// 计算圆点半径
float outerRadius = (getWidth() < getHeight() ? getWidth() : getHeight()) / 2f;
float dotRadius = mSin_1 * outerRadius / (1 + mSin_1);求出了圆点半径,圆点圆心所在的位置也知道了。画圆点,一圈共100个,可以使用了canvas的旋转来绘制,每绘制一个圆点,就旋转3.6°(360°/100)。
至于进度,可以先画已完成进度,再画未完成进度。也可以先把未完成进度画完,把其当背景,再画已完成进度。
我这选择了第一种方法,理由:为了不重复绘制,另一个就是防止已完成进度的颜色是带透明度的,这样叠加就不是想要的颜色了。
float centerX = getWidth() / 2f;
float centerY = getHeight() / 2f;
// 1 画进度
mPaint.setColor(dotColor);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
int count = 0;
// 1.1 当前进度
while (count++ < percent) {
canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY - outerRadius + dotRadius, dotRadius, mPaint);
canvas.rotate(3.6f, centerX, centerY);
}
// 1.2 未完成进度
mPaint.setColor(dotBgColor);
count--;
while (count++ < 100) {
canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY - outerRadius + dotRadius, dotRadius, mPaint);
canvas.rotate(3.6f, centerX, centerY);
}2、绘制百分比
百分比就是文字,直接用canvas.drawText()绘制就好了。
mPaint.setTextSize(percentTextSize);
mPaint.setColor(percentTextColor);
canvas.drawText(percent + "", centerX - textWidth / 2, baseline, mPaint);绘制的时候,要找好开始绘制的位置,注意两个方向的对齐方法:
2.1 水平对齐
这个简单,先测量一下文字的宽度,左边起始位置就是centerX - textWidth/2。上面用textWidth是因为还要加上单位字体的宽度。
mPaint.setTextSize(percentTextSize);
float percentTextWidth = mPaint.measureText(percent + "");2.3 垂直对齐
baseline是y方向的起始位置,最初设置的是centerY + percentTextSize/2。在默认显示模式下,结果是酱紫:
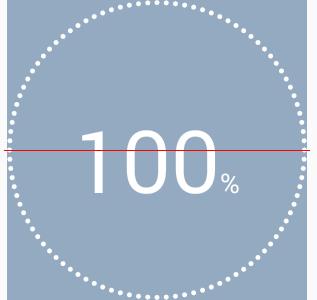
擦,这哪是垂直对齐啊。难道有万有引力?
后来找到了原因(参考)。因为它的y坐标位置是baseline,而不是我们想象中的bottom。请看下图(ascent与参考的博客有点不一样,但不用怀疑我这的准确性,因为这图是直接通过自定义控件绘制出来的)

说明:
- 这些top、bottom、ascent、descent都可以直接从FontMetrics中获取,这些值都是以baseline为基准。
- baseline就是canvas.drawText(text, x, y, paint)中的y。
- center是ascent和descent的中间线,即(ascent + descent)/2。这里可以看出,center就是文字的中间线。
而FontMetrics在设置字体大小后可以获取到:
mPaint.setTextSize(textHeight);
Paint.FontMetrics fm = mPaint.getFontMetrics();所以要居中对齐,baseline比较准确的值是:
baseline = centerY + (fm.descent - fm.ascent)/2 - fm.descent;这我理解了半天才弄明白。可以这么理解:当文字在正中间的时候,center线的y坐标值就是centerY,加上(fm.descent - fm.ascent)/2就到了descent线(要区分fm.descent的值),减去fm.descent就到了baseline线。
修正后的结果:
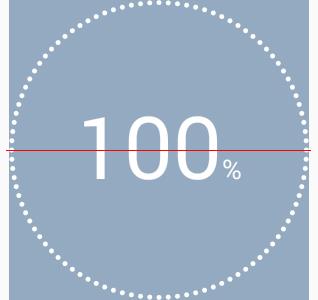
另一个比较准确的值:
baseline = centerY + (fm.bottom- fm.top)/2 - fm.bottom;3、绘制单位
绘制方式同百分比,他绘制的起始x坐标紧接着百分比的。
但,,,如果单位不是%,而是“分”,这样就不能与百分比的数字在底部对齐了。看需求吧,有的地方允许这样,但在强迫症的驱动下,又给自己整了一壶。
看看上面baseline的分析,特别是那张图。是不是发现字母、数字、汉字的底部对齐方式不太一样(里面的文字是有用途的,不是闹着玩的)。
所以添加了一个这样独特的属性:unitTextAlignMode,意为单位与百分比的对齐方式。有三种方式:
- DEFAULT:只要与baseline线底部对齐的都可以用这个,eg: %, a, b, …
- CN:中文,就用它
- EN:主要针对英文字母和字符中带尾巴的,eg: g, j, p, q, y, [, ], {, }, |, …
原理就是根据文字大小,进行了微调:
switch (unitTextAlignMode) {
case UNIT_TEXT_ALIGN_MODE_CN:
baseline -= fm_unit.descent / 4;
break;
case UNIT_TEXT_ALIGN_MODE_EN:
baseline -= fm_unit.descent * 2/3;
}效果咋样?别急,客官,我们这里又展品,看完再选也不迟:
百分比与单位字体大小一样:

百分比字体比单位字体大:
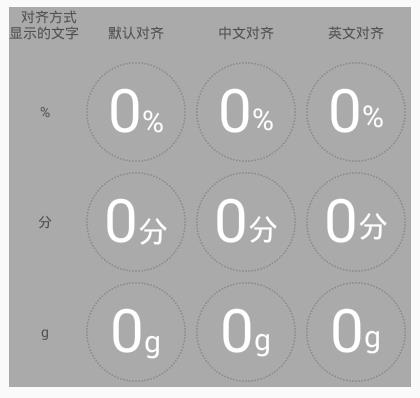
4、绘制按钮

主要是背景,仔细看,可以这么去绘制:先把背景分三部分,中间一个长方形,两边各一个半圆。长方形的长等于字体的宽度,高是字体高度的2倍。
绘制的时候,可通过Path来一次性绘制完毕:
mPath.reset();
mPath.moveTo(mButtonRect_start.x, mButtonRect_start.y);
mPath.rLineTo(buttonTextWidth, 0);
float left = centerX + buttonTextWidth/2 - mButtonRadius;
float top = centerY + buttonTopOffset;
float right = left + 2 * mButtonRadius;
float bottom = top + 2 * mButtonRadius;
mRectF.set(left, top, right, bottom);
mPath.arcTo(mRectF, 270, 180); // 参数1:内切这个方形,参数2:开始角度,参数3:画的角度范围
mPath.rLineTo(-buttonTextWidth, 0);
mRectF.offset(-buttonTextWidth, 0); // 平移位置
mPath.arcTo(mRectF, 90, 180);
mPath.close();
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);5、处理按钮的点击事件
要处理按钮的点击事件,首先要判断触摸点是否在按钮中,跟绘制一样,分别判断是否在方形、左半圆、右半圆中。
方形好判断,左半圆和右半圆的判断,我们利用解析几何的办法:判断一个点(x, y)是否在圆(
x0,y0
, r)内,先把点的坐标减去圆心的坐标,这样相当于把坐标系的原点移动到了圆心,如果在圆中,必然满足:
(x−x0)2+(y−y0)2<=r2
代码实现如下:
/**
* 判断坐标是否在按钮中
* @param x 坐标的x
* @param y 坐标的y
* @return true-在按钮中,false-不在按钮中
*/
private boolean isTouchInButton(final float x, final float y) {
// 判断是否在按钮矩形中
if (x >= mButtonRect_start.x && x <= mButtonRect_end.x
&& y >= mButtonRect_start.y && y <= mButtonRect_end.y) {
return true;
}
// 判断是否在左边半圆中:另一半圆在矩形中,也属于按钮范围,所以直接判断整个圆即可
// 把坐标系移到圆心再判断
float centerX = mButtonRect_start.x;
float centerY = (mButtonRect_start.y + mButtonRect_end.y) / 2;
float newX = x - centerX;
float newY = y - centerY;
if (newX * newX + newY * newY <= mButtonRadius * mButtonRadius) {
return true;
}
// 判断是否在右边半圆中
centerX = mButtonRect_end.x;
newX = x - centerX;
return newX * newX + newY * newY <= mButtonRadius * mButtonRadius;
}
按钮的处理事件,在onTouchEvent()中进行拦截,这样能区别按钮被点击,和控件(除按钮区域)被点击
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (showMode == SHOW_MODE_ALL) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if (isTouchInButton(event.getX(), event.getY())) {
mIsButtonTouched = true;
postInvalidate();
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
if (mIsButtonTouched) {
if (!isTouchInButton(event.getX(), event.getY())) {
mIsButtonTouched = false;
postInvalidate();
}
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
if (mIsButtonTouched && mButtonClickListener != null) {
mButtonClickListener.onClick(this);
}
mIsButtonTouched = false;
postInvalidate();
}
if (mIsButtonTouched) {
return true;
}
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}四、核心代码
除了上面按钮事件处理方法外,还有2个主要的方法:
- 构造方法中获取属性值或默认值
- onDraw()中
public CircleDotProgressBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar);
// 获取自定义属性值或默认值
progressMax = ta.getInteger(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_progressMax, 100);
dotColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_dotColor, Color.WHITE);
dotBgColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_dotBgColor, Color.GRAY);
showMode = ta.getInt(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_showMode, SHOW_MODE_PERCENT);
if (showMode != SHOW_MODE_NULL) {
percentTextSize = ta.getDimension(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_percentTextSize, dp2px(30));
percentTextColor = ta.getInt(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_percentTextColor, Color.WHITE);
unitText = ta.getString(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_unitText);
unitTextSize = ta.getDimension(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_unitTextSize, percentTextSize);
unitTextColor = ta.getInt(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_unitTextColor, Color.WHITE);
unitTextAlignMode = ta.getInt(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_unitTextAlignMode, UNIT_TEXT_ALIGN_MODE_DEFAULT);
if (unitText == null) {
unitText = "%";
}
}
if (showMode == SHOW_MODE_ALL) {
buttonText = ta.getString(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_buttonText);
buttonTextSize = ta.getDimension(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_buttonTextSize, dp2px(15));
buttonTextColor = ta.getInt(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_buttonTextColor, Color.GRAY);
buttonBgColor = ta.getInt(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_buttonBgColor, Color.WHITE);
buttonClickColor = ta.getInt(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_buttonClickColor, buttonBgColor);
buttonClickBgColor = ta.getInt(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_buttonClickBgColor, buttonTextColor);
buttonTopOffset = ta.getDimension(R.styleable.CircleDotProgressBar_buttonTopOffset, dp2px(15));
if (buttonText == null) {
buttonText = context.getString(R.string.CircleDotProgressBar_speed_up_one_key);
}
}
ta.recycle();
// 其他准备工作
mSin_1 = (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(1)); // 求sin(1°)。角度需转换成弧度
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); // 消除锯齿
mPath = new Path();
mRectF = new RectF();
mButtonRect_start = new PointF();
mButtonRect_end = new PointF();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
// 计算圆点半径
float outerRadius = (getWidth() < getHeight() ? getWidth() : getHeight()) / 2f;
float centerX = getWidth() / 2f;
float centerY = getHeight() / 2f;
// outerRadius = innerRadius + dotRadius
// sin((360°/200)/2) = sin(0.9°) = dotRadius / innerRadius;
// 为了让圆点饱满一些,把角度0.9°增加0.1°到1°
float dotRadius = mSin_1 * outerRadius / (1 + mSin_1);
// 1 画进度
mPaint.setColor(dotColor);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
int count = 0;
// 1.1 当前进度
while (count++ < percent) {
canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY - outerRadius + dotRadius, dotRadius, mPaint);
canvas.rotate(3.6f, centerX, centerY);
}
// 1.2 未完成进度
mPaint.setColor(dotBgColor);
count--;
while (count++ < 100) {
canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY - outerRadius + dotRadius, dotRadius, mPaint);
canvas.rotate(3.6f, centerX, centerY);
}
if (showMode == SHOW_MODE_NULL) {
return;
}
if (showMode == SHOW_MODE_PERCENT) {
// 2 画百分比和单位:水平和垂直居中
// 测量宽度
mPaint.setTextSize(percentTextSize);
// mPaint.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD); // 粗体
float percentTextWidth = mPaint.measureText(percent + "");
mPaint.setTextSize(unitTextSize);
float unitTextWidth = mPaint.measureText(unitText);
Paint.FontMetrics fm_unit = mPaint.getFontMetrics();
float textWidth = percentTextWidth + unitTextWidth;
float textHeight = percentTextSize > unitTextSize ? percentTextSize : unitTextSize;
// 计算Text垂直居中时的baseline
mPaint.setTextSize(textHeight);
Paint.FontMetrics fm = mPaint.getFontMetrics();
// 字体在垂直居中时,字体中间就是centerY,加上字体实际高度的一半就是descent线,减去descent就是baseline线的位置(fm中以baseline为基准)
float baseline = centerY + (fm.descent - fm.ascent)/2 - fm.descent;
// 2.1 画百分比
mPaint.setTextSize(percentTextSize);
mPaint.setColor(percentTextColor);
canvas.drawText(percent + "", centerX - textWidth / 2, baseline, mPaint);
// 2.2 画单位
mPaint.setTextSize(unitTextSize);
mPaint.setColor(unitTextColor);
// 单位对齐方式
switch (unitTextAlignMode) {
case UNIT_TEXT_ALIGN_MODE_CN:
baseline -= fm_unit.descent / 4;
break;
case UNIT_TEXT_ALIGN_MODE_EN:
baseline -= fm_unit.descent * 2/3;
}
canvas.drawText(unitText, centerX - textWidth / 2 + percentTextWidth, baseline, mPaint);
}else if (showMode == SHOW_MODE_ALL) {
// 2 画百分比和单位:水平居中,垂直方向的baseline在centerY
// 测量宽度
mPaint.setTextSize(percentTextSize);
// mPaint.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD); // 粗体
float percentTextWidth = mPaint.measureText(percent + "");
mPaint.setTextSize(unitTextSize);
float unitTextWidth = mPaint.measureText(unitText);
Paint.FontMetrics fm_unit = mPaint.getFontMetrics();
float textWidth = percentTextWidth + unitTextWidth;
// 2.1 画百分比
mPaint.setTextSize(percentTextSize);
mPaint.setColor(percentTextColor);
float baseline_per = centerY;
canvas.drawText(percent + "", centerX - textWidth / 2, baseline_per, mPaint);
// 2.2 画单位
mPaint.setTextSize(unitTextSize);
mPaint.setColor(unitTextColor);
// 单位对齐方式
switch (unitTextAlignMode) {
case UNIT_TEXT_ALIGN_MODE_CN:
baseline_per -= fm_unit.descent / 4;
break;
case UNIT_TEXT_ALIGN_MODE_EN:
baseline_per -= fm_unit.descent * 2/3;
}
canvas.drawText(unitText, centerX - textWidth / 2 + percentTextWidth, baseline_per, mPaint);
// 3 画按钮
mPaint.setTextSize(buttonTextSize);
float buttonTextWidth = mPaint.measureText(buttonText);
Paint.FontMetrics fm = mPaint.getFontMetrics();
// 3.1 画按钮背景
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPaint.setColor(mIsButtonTouched ? buttonClickBgColor : buttonBgColor);
float buttonHeight = 2 * buttonTextSize;
mButtonRadius = buttonHeight / 2;
mButtonRect_start.set(centerX - buttonTextWidth / 2, centerY + buttonTopOffset);
mButtonRect_end.set(centerX + buttonTextWidth/2, centerY + buttonTopOffset + buttonHeight);
mPath.reset();
mPath.moveTo(mButtonRect_start.x, mButtonRect_start.y);
mPath.rLineTo(buttonTextWidth, 0);
float left = centerX + buttonTextWidth/2 - mButtonRadius;
float top = centerY + buttonTopOffset;
float right = left + 2 * mButtonRadius;
float bottom = top + 2 * mButtonRadius;
mRectF.set(left, top, right, bottom);
mPath.arcTo(mRectF, 270, 180); // 参数1:内切这个方形,参数2:开始角度,参数3:画的角度范围
mPath.rLineTo(-buttonTextWidth, 0);
mRectF.offset(-buttonTextWidth, 0); // 平移位置
mPath.arcTo(mRectF, 90, 180);
mPath.close();
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
// 3.2 画按钮文本
mPaint.setColor(mIsButtonTouched ? buttonClickColor : buttonTextColor);
float baseline = centerY + buttonTopOffset + buttonTextSize + (fm.descent - fm.ascent)/2 - fm.descent;
canvas.drawText(buttonText, centerX - buttonTextWidth / 2, baseline, mPaint);
}
}
/**
* 设置进度
* 同步,允许多线程访问
* @param progress 进度
*/
public synchronized void setProgress(int progress) {
if (progress < 0 || progress > progressMax) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("progress must between 0 and max(%d)", progressMax));
}
this.progress = progress;
percent = progress * 100 / progressMax;
postInvalidate(); // 可以直接在子线程中调用,而invalidate()必须在主线程(UI线程)中调用
}
public synchronized void setProgressMax(int progressMax) {
if (progressMax < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("progressMax mustn't smaller than 0");
}
this.progressMax = progressMax;
}以上是关于自定义控件——圆形圆点进度条(仿安全卫士中的一键加速)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章