netfilter-在内核态操作网络数据包
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了netfilter-在内核态操作网络数据包相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.概述
netfilter是自2.4内核的一个数据包过滤框架。可以过滤数据包,网络地址和端口转换(nat和napt技术),以及其他操作数据包的功能。主要工作原理是在内核模块注册回调函数(hook函数)到内核,内核执行到相关点时会触发这个回调函数,然后根据回调函数里的逻辑,对包含网络协议栈的sk_buff结构进行操作!!!iptables的内核模块就是使用的netfilter。netfilter官方网站:http://www.netfilter.org/
二.基本函数接口
1.把hook函数注册到内核需要使用结构体nf_hook_ops来关联,该结构体定义在内核头文件目录的linux/netfilter.h里面,这里以2.6.39内核为例:
1 struct nf_hook_ops { 2 struct list_head list; 3 4 /* User fills in from here down. */ 5 nf_hookfn *hook; 6 struct module *owner; 7 u_int8_t pf; 8 unsigned int hooknum; 9 /* Hooks are ordered in ascending priority. */ 10 int priority; 11 };
nf_hookfn就是要填充的hook函数。pf时8位协议族,如ipv4就是PF_INET。hooknum是指定hook函数注册的数据包的路径地点。priority是该hook的优先级,当有多个hook在同一个点注册的时候,会按照优先级来执行hook。
2.nf_hookfn函数声明也是在linux/netfilter.h里面:
1 typedef unsigned int nf_hookfn(unsigned int hooknum, 2 struct sk_buff *skb, 3 const struct net_device *in, 4 const struct net_device *out, 5 int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *));
sk_buff是内核维护的网络协议栈结构,里面可以取出各协议栈信息。该函数的返回值:
1 /* Responses from hook functions. */ 2 #define NF_DROP 0 3 #define NF_ACCEPT 1 4 #define NF_STOLEN 2 5 #define NF_QUEUE 3 6 #define NF_REPEAT 4 7 #define NF_STOP 5
NF_ACCEPT:接收数据包,由内核继续正常的报文传送
NF_DROP:丢弃数据包
NF_STOLEN:数据包的操作全部由hook函数处理
NF_QUEUE:将报文入队,通常交由用户程序处理
NF_REPEAT:再次调用该hook函数。
3.hooknum的5个通用注册点也是定义在linux/netfilter.h
1 enum nf_inet_hooks { 2 NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING, 3 NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, 4 NF_INET_FORWARD, 5 NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT, 6 NF_INET_POST_ROUTING, 7 NF_INET_NUMHOOKS 8 };
NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING:系统收到数据后,且没有经过路由
NF_INET_LOCAL_IN:系统收到数据,经过路由后,如果数据的目标地址是本机就经过该点
NF_INET_FORWARD:系统收到数据,经过路由后,如果数据的目标地址是其他地方就经过该点
NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT:系统发送数据时,未经过路由
NF_INET_POST_ROUTING:系统发送数据时,经过了路由阶段,马上就发出去了
对于ipv4的注册点值跟上面一样,只是用的宏定义:
1 /* IP Hooks */ 2 /* After promisc drops, checksum checks. */ 3 #define NF_IP_PRE_ROUTING 0 4 /* If the packet is destined for this box. */ 5 #define NF_IP_LOCAL_IN 1 6 /* If the packet is destined for another interface. */ 7 #define NF_IP_FORWARD 2 8 /* Packets coming from a local process. */ 9 #define NF_IP_LOCAL_OUT 3 10 /* Packets about to hit the wire. */ 11 #define NF_IP_POST_ROUTING 4 12 #define NF_IP_NUMHOOKS 5 13 #endif /* ! __KERNEL__ */
4.注册和撤销注册函数:
1 /* Function to register/unregister hook points. */ 2 int nf_register_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg); 3 void nf_unregister_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg);
参数都是nf_hook_ops结构指针。
三.简单例子
我们用一个简单例子观察vxlan的数据包在各hook点的ip情况,vxlan环境可以参考Docker+OpenvSwitch搭建VxLAN实验环境
本例子是内核模块编程,可以参考初探linux内核编程,参数传递以及模块间函数调用
1 /** 2 * @file netfilter_hook.c 3 */ 4 5 #include <linux/module.h> 6 #include <linux/kernel.h> 7 8 #include <linux/ip.h> 9 #include <linux/netfilter_ipv4.h> 10 11 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); 12 MODULE_AUTHOR("yuuyuu"); 13 MODULE_DESCRIPTION("netfilter"); 14 MODULE_VERSION("1.0"); 15 16 /* 打印点分制ip地址 */ 17 #define printk_ip(info, be32_addr) 18 printk("%s %d.%d.%d.%d\\n", 19 info, 20 ((unsigned char *)&(be32_addr))[0], 21 ((unsigned char *)&(be32_addr))[1], 22 ((unsigned char *)&(be32_addr))[2], 23 ((unsigned char *)&(be32_addr))[3]) 24 25 int filter_ip(__be32 addr) 26 { 27 unsigned char net_num = ((unsigned char *)&addr)[0]; 28 unsigned char host_num = ((unsigned char *)&addr)[3]; 29 if (net_num == 10 || host_num == 1 || host_num == 2) 30 return 1; 31 return 0; 32 } 33 34 int filter_src_dst_ip(__be32 s_addr, __be32 d_addr) 35 { 36 int i = filter_ip(s_addr) && filter_ip(d_addr); 37 return i; 38 } 39 40 /* NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING */ 41 unsigned int pre_routing_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb, 42 const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out, 43 int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *)) 44 { 45 struct iphdr *ip_header; 46 47 ip_header = ip_hdr(skb); 48 if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr)) 49 { 50 printk("pre_routing_hook()==================================\\n"); 51 printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr); 52 printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr); 53 } 54 55 return NF_ACCEPT; 56 } 57 58 struct nf_hook_ops pre_routing_ops = 59 { 60 .hook = pre_routing_hook, 61 .pf = PF_INET, 62 .hooknum = NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING, 63 .priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST 64 }; 65 66 /* NF_INET_LOCAL_IN */ 67 unsigned int local_in_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb, 68 const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out, 69 int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *)) 70 { 71 struct iphdr *ip_header; 72 73 ip_header = ip_hdr(skb); 74 if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr)) 75 { 76 printk("local_in_hook()========================================\\n"); 77 printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr); 78 printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr); 79 } 80 81 return NF_ACCEPT; 82 } 83 84 struct nf_hook_ops local_in_ops = 85 { 86 .hook = local_in_hook, 87 .pf = PF_INET, 88 .hooknum = NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, 89 .priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST 90 }; 91 92 /* NF_INET_FORWARD */ 93 unsigned int forward_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb, 94 const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out, 95 int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *)) 96 { 97 struct iphdr *ip_header; 98 99 ip_header = ip_hdr(skb); 100 if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr)) 101 { 102 printk("forward_hook=========================================\\n"); 103 printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr); 104 printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr); 105 } 106 107 return NF_ACCEPT; 108 } 109 110 struct nf_hook_ops forward_ops = 111 { 112 .hook = forward_hook, 113 .pf = PF_INET, 114 .hooknum = NF_INET_FORWARD, 115 .priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST 116 }; 117 118 /* NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT */ 119 unsigned int local_out_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb, 120 const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out, 121 int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *)) 122 { 123 struct iphdr *ip_header; 124 125 ip_header = ip_hdr(skb); 126 if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr)) 127 { 128 printk("local_out_hook===========================================\\n"); 129 printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr); 130 printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr); 131 } 132 133 return NF_ACCEPT; 134 } 135 136 struct nf_hook_ops local_out_ops = 137 { 138 .hook = local_out_hook, 139 .pf = PF_INET, 140 .hooknum = NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT, 141 .priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST 142 }; 143 144 /* NF_INET_POST_ROUTING */ 145 unsigned int post_routing_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb, 146 const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out, 147 int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *)) 148 { 149 struct iphdr *ip_header; 150 151 ip_header = ip_hdr(skb); 152 if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr)) 153 { 154 printk("post_routing_hook====================================\\n"); 155 printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr); 156 printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr); 157 } 158 159 return NF_ACCEPT; 160 } 161 162 struct nf_hook_ops post_routing_ops = 163 { 164 .hook = post_routing_hook, 165 .pf = PF_INET, 166 .hooknum = NF_INET_POST_ROUTING, 167 .priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST 168 }; 169 170 /* 注册 */ 171 static int hook_init(void) 172 { 173 printk("hook_init()======================\\n"); 174 nf_register_hook(&pre_routing_ops); 175 nf_register_hook(&local_in_ops); 176 nf_register_hook(&forward_ops); 177 nf_register_hook(&local_out_ops); 178 nf_register_hook(&post_routing_ops); 179 180 return 0; 181 } 182 183 static void hook_exit(void) 184 { 185 printk("hook_exit()=====================\\n"); 186 nf_unregister_hook(&pre_routing_ops); 187 nf_unregister_hook(&local_in_ops); 188 nf_unregister_hook(&forward_ops); 189 nf_unregister_hook(&local_out_ops); 190 nf_unregister_hook(&post_routing_ops); 191 } 192 193 module_init(hook_init); 194 module_exit(hook_exit);
第27,34行简单过滤下本环境的IP,方便查看结果。
Makefile文件
1 KERNEL_DIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build 2 PWD := $(shell pwd) 3 4 obj-m := netfilter_hook.o 5 6 default: 7 $(MAKE) -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(PWD) modules
四.验证
vxlan环境:
host1:eth0:192.168.2.1,虚拟网桥10.1.2.10
host2:eth0:192.168.2.2,虚拟网桥10.1.2.11
编译后插入模块,在host1里面ping一次host2的虚拟网桥10.1.2.11
1 ping 10.2.1.11 -c 1
然后参看内核输出信息:
1 sudo dmesg
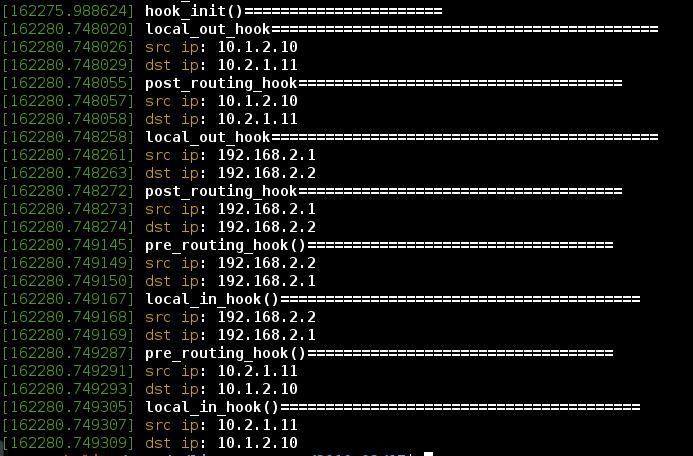
可以看到vxlan的icmp请求有2个IP在工作,分别经过local_out_hook和post_routing_hook。
同理host2的icmp应答进入本机也是2个IP都经过了pre_routing_hook和local_in_hook。
以上是关于netfilter-在内核态操作网络数据包的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章