13.ARM协处理器的知识
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了13.ARM协处理器的知识相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
13.ARM协处理器的知识
在处理器中有协处理器来辅助处理器完成部分功能的,主要是协助作用。
协处理器:
协处理器用于执行特定的处理任务,如:数学协处理器可以控制数字处理,以减轻处理器的负担。ARM可支持多达16个协处理器,其中CP15是最重要的一个。
?
在ARM9、ARM11、cortexa8等核中,CP15的功能都是一样的。
在ARM11核的文档看到图1-1:
The section gives an overall view of the system control coprocessor. For detail of the registers
in the system control coprocessor, see System control processor registers on page 3-13.
The purpose of the system control coprocessor, CP15, is to control and provide status
information for the functions implemented in the ARM1176JZF-S processor. The main
functions of the system control coprocessor are:
? overall system control and configuration
? cache configuration and management
? Tightly-Coupled Memory (TCM) configuration and management
? Memory Management Unit (MMU) configuration and management
? DMA control
? system performance monitoring.
The system control coprocessor does not exist in a distinct physical block of logic.
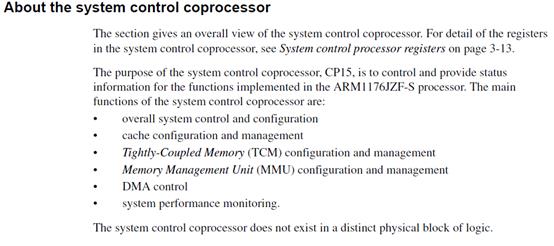
图1-1
从上面知道:
系统控制协处理器的功能是:
- 系统整体控制和配置
- 缓存配置和管理
- 紧耦合的内存(CTM)的配置和管理
- 内存管理单元(MMU)的配置和管理。
- DMA控制
- 系统性能控制。
确切的说,ARM11核中有16组协处理器,不是16个,每一组里面有很多寄存器,下面来看ARM11核的c0组里的Main ID寄存器。
System control processor registers
This section gives details of all the registers in the system control coprocessor. The section
presents a summary of the registers and detailed descriptions in register order of CRn,
Opcode_1, CRm, Opcode_2.
You can access CP15 registers with MRC and MCR instructions:
MCR{cond} P15,<Opcode_1>,<Rd>,<CRn>,<CRm>,<Opcode_2>
MRC{cond} P15,<Opcode_1>,<Rd>,<CRn>,<CRm>,<Opcode_2>

Register allocation
Table 3-2 on page 3-14 lists the allocation and reset values of the registers of the system control
coprocessor where:
? CRn is the register number within CP15
? Op1 is the Opcode_1 value for the register
? CRm is the operational register
? Op2 is the Opcode_2 value for the register.
? Type applies to the Secure, S, or the Non-secure, NS, world and is:
— B, registers banked in Secure and Non-secure worlds. If the registers are not banked
then they are common to both worlds or only accessible in one world.
— NA, no access
— RO, read-only access
— RO, read-only access in privileged modes only
— R/W, read/write access
— R/W, read/write access in privileged modes only
— WO, write-only access
— WO, write-only access in privileged modes only
— X, access depends on another register or external signal.

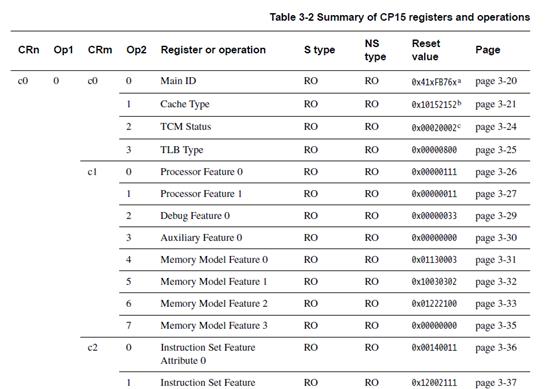
Main ID寄存器的参数:
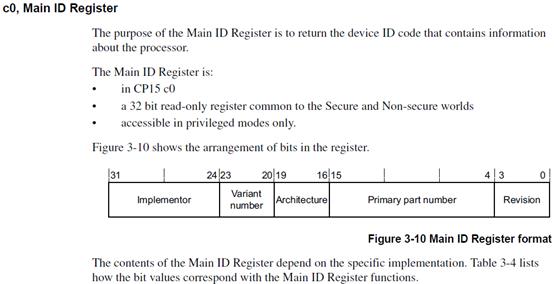
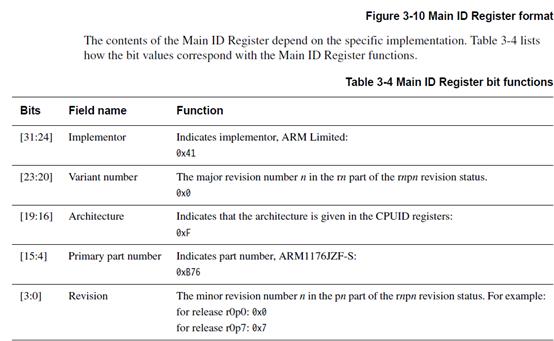

从上面c0组的Main ID寄存器,有32位,这32位被分成了5个地址段。例如[15:4]地址段是表明这是ARM11的处理器。此处的值是0xB76
?
前面的知识看到了,控制CP15协处理器,主要是设置对应的寄存器来实现控制的。接着就是来介绍如何访问协处理器的寄存器的,并且实现设置。
主要是通过两个命令来实现的mcr和mrc:r表示register普通寄存器,c表示coprocessor协处理器。
mcr命令中m表示move,c表示coprocessor,r表示register。所以mcr的意思就是把普通寄存器register的内容移到协处理器c里面。
mcr命令中m表示move,c表示coprocessor,r表示register。所以mrc的意思就是把协处理器c里面的内容移到普通寄存器register里面。
?
指令的格式:
You can access CP15 registers with MRC and MCR instructions:
MCR{cond} P15,<Opcode_1>,<Rd>,<CRn>,<CRm>,<Opcode_2>
MRC{cond} P15,<Opcode_1>,<Rd>,<CRn>,<CRm>,<Opcode_2>
上面是CP15的访问格式,CP14-CP0同理。
各个参数的值,上面的表格已经给出了:

?
上图看到在c0组的Main ID寄存器,在设置mrc,把Main ID寄存器的内容读到r1寄存器:
从上图知道:
- CRn=c0:c0组的
- Op1=0
- CRm=c0
- Op2=0
- Rd=r1:就是要把Main ID读到r0寄存器。
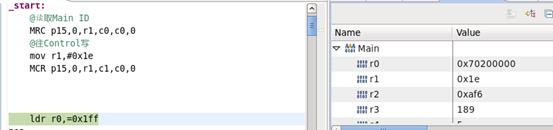
这样就设置好了。接下来实验访问Main ID:
读取Main ID指令:
MRC P15,0,r1,c0,c0,0

运行结果:

读出来的值是0x410fb766,这跟我们的核手册的说明里的值是一致的,下图。说明读取成功:
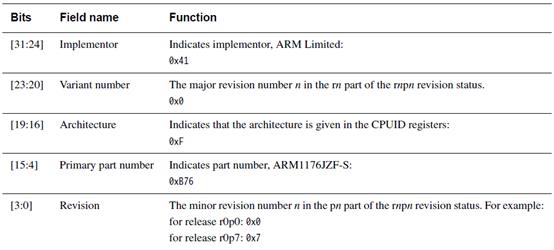
上图中[31:24]=0x41,[23:20]=0x0,[19:16]=0xF,[15:4]=0xB76,最后四位[3:0]是修订位,是在0x0到0x7之间,这里是6,也是对的。所以读出正确。
?
上面就是对CP15里的Main ID的读取操作。
?
接下来是往Control寄存器里写数据:

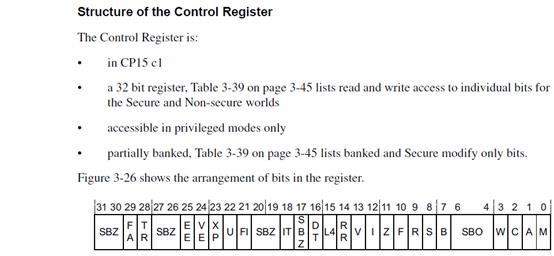
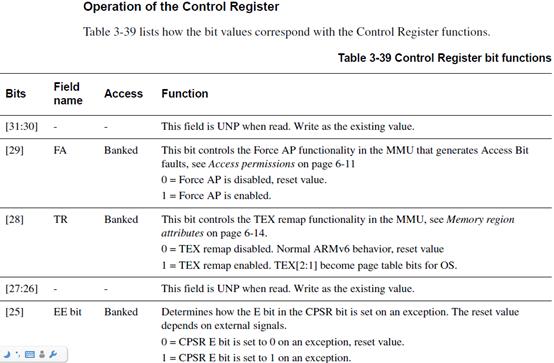
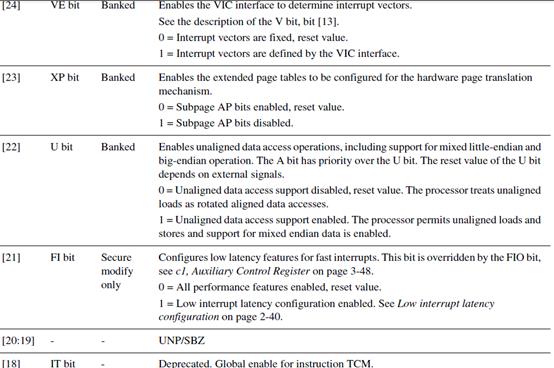

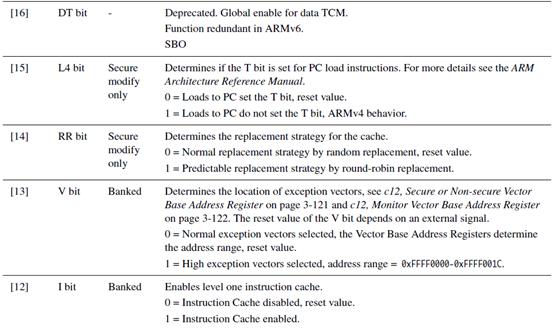


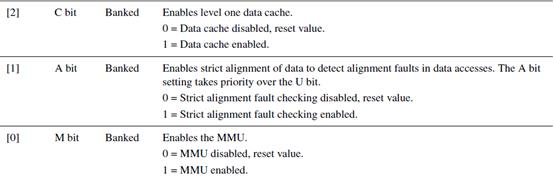
往c1组的Control寄存器写入r1寄存器的值:
MCR P15,0,r1,c1,c0,0
上面运行了,就把r1的值写进去了。
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
以上是关于13.ARM协处理器的知识的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章