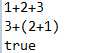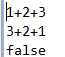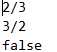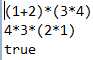小学生四则运算应用软件
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了小学生四则运算应用软件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、针对上周的程序改进:
(1)除零问题:生成题目的时候同时计算,try catch异常,若有异常则重新生成
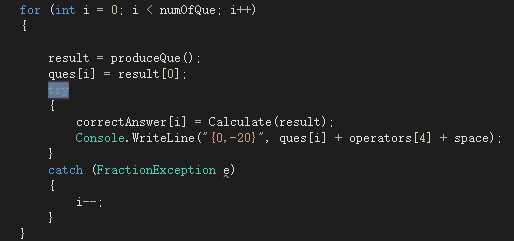
测试用例为2/(2-2),如下会产生分母不应为0的异常
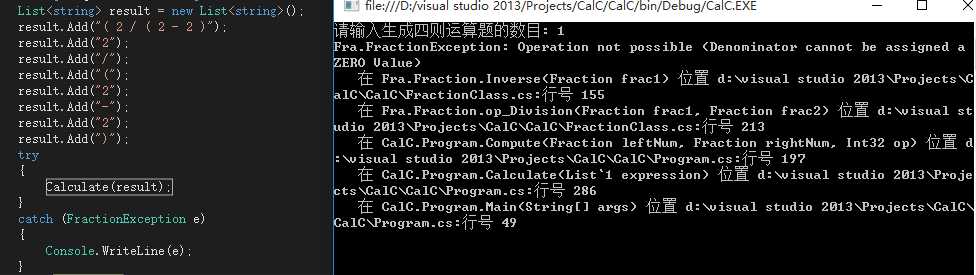
这里的FractionException有多种类型,比如分母不能为0、计算时超出数值范围、无法转化为Fraction等。
(2)参数化和用户输入异常处理:
参数化是直接使用C#主函数的String[] args,并且针对每种错误情况都要抛出相应异常,也是使用的try catch机制,其代码如下:

1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 { 3 Console.WriteLine("-n表示生成四则算式的数目"); 4 Console.WriteLine("-a表示用户是否输入答案(1输入,0不输入)"); 5 Console.WriteLine("-c表示是否显示正确答案(1显示,0不显示)"); 6 Console.WriteLine("-t表示是否生成题目文件(1生成,0不生成)"); 7 Console.WriteLine("-m表示文件生成题目的数量(若生成题目文件该参数必须输入,否则不输入)"); 8 try 9 { 10 if (args.Length != 8 && args.Length != 10) 11 throw new Exception("参数数目不正确"); 12 else if (args.Length == 8) 13 { 14 if (args[0] != "-n" || args[2] != "-a" || args[4] != "-c" || args[6] != "-t") 15 throw new Exception("参数名称不正确"); 16 if (int.Parse(args[1]) <= 0) 17 throw new Exception("题目数必须为正"); 18 if (int.Parse(args[7]) == 1) 19 throw new Exception("参数数目不正确"); 20 if ((int.Parse(args[3]) != 0 && int.Parse(args[3]) != 1) || 21 (int.Parse(args[5]) != 0 && int.Parse(args[5]) != 1)) 22 throw new Exception("参数值必须为0或1"); 23 } 24 else 25 { 26 if (args[0] != "-n" || args[2] != "-a" || args[4] != "-c" || args[6] != "-t" || args[8] != "-m") 27 throw new Exception("参数名称不正确"); 28 if (int.Parse(args[1]) <= 0 || int.Parse(args[9]) <= 0) 29 throw new Exception("题目数必须为正"); 30 if (int.Parse(args[7]) == 0) 31 throw new Exception("参数数目不正确"); 32 if ((int.Parse(args[3]) != 0 && int.Parse(args[3]) != 1) || 33 (int.Parse(args[5]) != 0 && int.Parse(args[5]) != 1)) 34 throw new Exception("参数值必须为0或1"); 35 } 36 37 int numOfQue = int.Parse(args[1]); 38 string[] inputAnswer = new string[numOfQue]; 39 string[] correctAnswer = new string[numOfQue]; 40 string[] ques = new string[numOfQue]; 41 List<string> result = new List<string>(); 42 for (int i = 0; i < numOfQue; i++) 43 { 44 45 result = produceQue(); 46 ques[i] = result[0]; 47 try 48 { 49 correctAnswer[i] = Calculate(result); 50 Console.WriteLine("{0,-20}", ques[i] + operators[4] + space); 51 } 52 catch (FractionException e) 53 { 54 i--; 55 } 56 } 57 Console.WriteLine(); 58 int input = int.Parse(args[3]); 59 if (input == 1) 60 { 61 Console.Write("输入答案: "); 62 for (int i = 0; i < numOfQue; i++) 63 { 64 Console.Write("{0,-20}", ques[i] + operators[4] + space); 65 inputAnswer[i] = Console.ReadLine(); 66 } 67 68 int numOfCorrect = 0; 69 for (int i = 0; i < numOfQue; i++) 70 { 71 if (inputAnswer[i] == correctAnswer[i]) 72 numOfCorrect++; 73 } 74 Console.WriteLine("您共答对" + numOfCorrect + "道题"); 75 } 76 input = int.Parse(args[5]); 77 if (input == 1) 78 { 79 Console.Write("正确答案: "); 80 for (int i = 0; i < numOfQue; i++) 81 Console.Write("{0,-20}", ques[i] + operators[4] + space + correctAnswer[i]); 82 Console.WriteLine(); 83 } 84 85 input = int.Parse(args[7]); 86 if (input == 1) 87 { 88 string filename = "que.txt";//这里是你的已知文件 89 FileStream fs = File.Create(filename); //创建文件 90 fs.Close(); 91 StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(filename); 92 input = int.Parse(args[9]); 93 for (int i = 0; i < input; i++) 94 { 95 string que = ""; 96 que = produceQue()[0]; 97 sw.Write("{0,-20}", que + operators[4] + space); 98 if (i % 10 == 9) 99 sw.Write("\r\n"); 100 } 101 sw.Close(); 102 } 103 } 104 catch (Exception e) 105 { 106 Console.WriteLine(e.Message); 107 Console.WriteLine("请输入正确参数"); 108 } 109 }
其中参数说明为:

测试用例及结果如图所示:
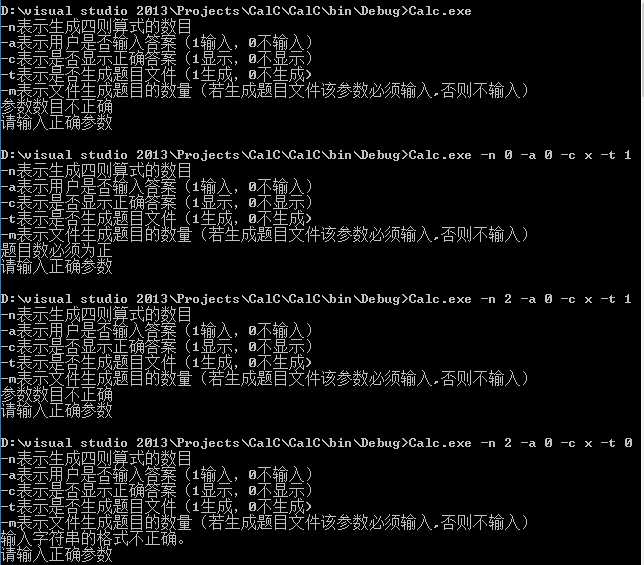
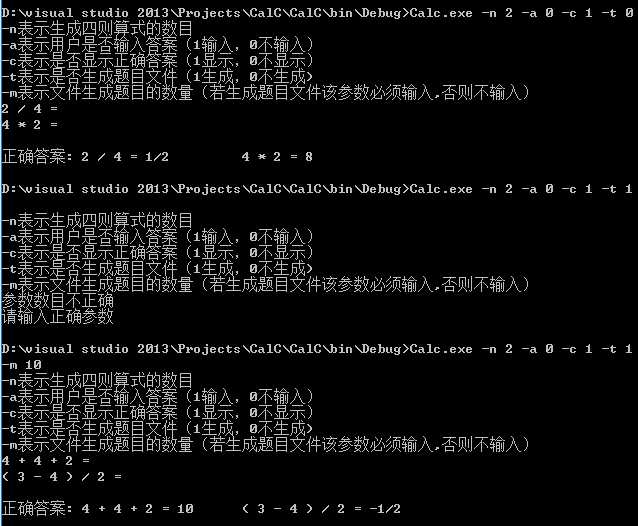

这是目前考虑的参数问题,当然我们也可以添加更多的参数,例如生成四则运算表达式运算符的数目以及操作数的范围。
(3)括号交叉重叠的问题:
目前括号的功能是通过随机生成(、)位于第几个操作数来实现,但这样可能会出现这种情况(2*(4)+3)。即第一对括号是(2*4),第二对括号是(4+3),处理的方法是如果同一个操作数前后分别有左括号和右括号,就将这两括号省略不添加。部分代码截图如下:
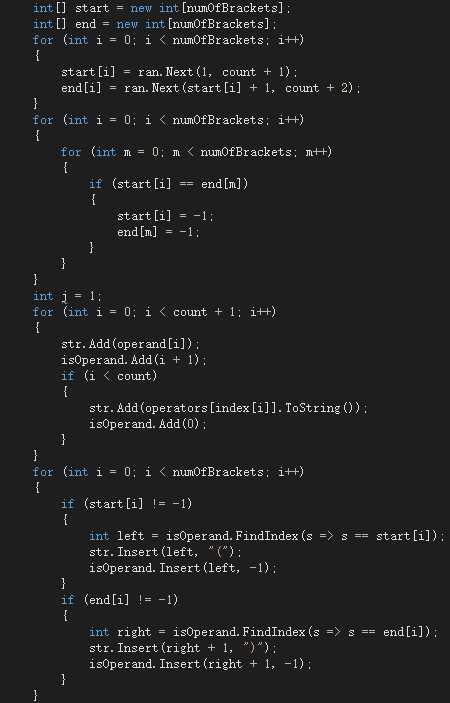
(4)代码优化及扩展:
由于最后是想将该应用以网页(Java Web)的形式显示,因此检查重复问题、优化等都是在Java程序的基础上改进。目前是已经将程序的主要功能通过Python、Java实现了,那么就浅谈下代码的转变之路。
二、C#转Python---Python功能强大之处
Python编程速度快,有很多强大的第三方库,还可以有负索引独特的语法,无数据类型的严格限制...种种优点促成了Python已然成为了当前社会下十分流行的语言。
简单举个例子,在C#辛辛苦苦写的Fraction类,Python里只需from fractions import Fraction这样一句话就可以搞定(o(╯□╰)o,独自在风中凌乱会儿)。而无数据类型的严格限制,使得我们没必要检查类型转化的错误,甚至可以在一个List里添加多种数据类型的元素。当然负索引的出现,也能让我们直接将List转化成栈和队列的这种结构。再加上Python代码的严格缩进,又会让代码风格整齐美观,这些怎能不令程序猿为之欣喜若狂?废话不多说,直接上代码:

1 from fractions import Fraction 2 import random 3 input0 = 1 4 operators = "+-*/=" 5 space = " " 6 priorities = {"#": -1, "+": 0, "-": 0,"*":1,"/":1} 7 def produceQue(): 8 strque = [] 9 isOperand = [] 10 count = random.randint(1, 2) 11 num = [] 12 den = [] 13 operand = [] 14 index = [] 15 numOfBrackets = 0 16 for i in range(count + 1): 17 num.append(random.randint(2, 4)) 18 if random.randint(1, 10) < 8: 19 den.append(1) 20 else: 21 den.append(random.randint(1, 4)) 22 numOfBrackets = random.randint(1, count) 23 operand.append(Fraction(num[i], den[i])) 24 if i < count: 25 index.append(random.randint(0, 3)) 26 start = [] 27 end = [] 28 for i in range(numOfBrackets): 29 start.append(random.randint(1, count)) 30 end.append(random.randint(start[i]+1, count + 1)) 31 for i in range(len(start)): 32 for j in range(len(end)): 33 if start[i] == end[j]: 34 start.pop(i) 35 end.pop(j) 36 start.append(-1) 37 end.append(-1) 38 j = 1 39 for i in range(count + 1): 40 strque.append(str(operand[i])) 41 isOperand.append(i + 1) 42 if i < count: 43 strque.append(operators[index[i]]) 44 isOperand.append(0) 45 for i in range(numOfBrackets): 46 if start[i] != -1: 47 left = isOperand.index(start[i]) 48 strque.insert(left, "(") 49 isOperand.insert(left, -1) 50 if end[i] != -1: 51 right = isOperand.index(end[i]) 52 strque.insert(right+1, ")") 53 isOperand.insert(right+1, -1) 54 strque.insert(0, "") 55 j = 1 56 while j < len(strque): 57 strque[0] += strque[j] + space 58 j = j + 1 59 return strque 60 61 def Compute(leftNum,rightNum,op): 62 if op == 0: 63 return Fraction(leftNum)+Fraction(rightNum) 64 if op == 1: 65 return Fraction(leftNum)-Fraction(rightNum) 66 if op == 2: 67 return Fraction(leftNum)*Fraction(rightNum) 68 if op == 3: 69 return Fraction(leftNum)/Fraction(rightNum) 70 71 def IsOperator(op): 72 try: 73 i = operators.index(str(op)) 74 bo = True 75 except: 76 bo = False 77 finally: 78 return bo 79 80 def IsLeftAssoc(op): 81 if op == "+" or op == "-" or op == "*" or op == "/": 82 return True 83 else: 84 return False 85 86 87 def PreOrderToPostOrder(expression): 88 result = [] 89 operatorStack = [] 90 operatorStack.append("#") 91 top = "" 92 cur = "" 93 tempChar = "" 94 tempNum = "" 95 i = 1 96 while i < len(expression): 97 cur = expression[i] 98 top = operatorStack[-1] 99 if cur == "(": 100 operatorStack.append(cur) 101 else: 102 if(IsOperator(cur)): 103 while IsOperator(top) and (IsLeftAssoc(cur) and priorities[cur] <= priorities[top]) or (not IsLeftAssoc(cur) and priorities[cur] < priorities[top]): 104 result.append(operatorStack.pop()) 105 top = operatorStack[-1] 106 operatorStack.append(cur) 107 elif cur == ")": 108 tempChar = operatorStack.pop() 109 while len(operatorStack) > 0 and tempChar != "(": 110 result.append(tempChar) 111 tempChar = operatorStack.pop() 112 else: 113 tempNum = cur 114 result.append(tempNum) 115 i = i + 1 116 117 while len(operatorStack) > 0: 118 cur = operatorStack.pop() 119 if cur == "#": 120 continue; 121 if len(operatorStack) > 0: 122 top = operatorStack[-1] 123 result.append(cur) 124 return result 125 126 def Calculate(expression): 127 rpn = PreOrderToPostOrder(expression) 128 operandStack = [] 129 left = "" 130 right = "" 131 while len(rpn) > 0: 132 cur = rpn.pop(0) 133 if IsOperator(cur): 134 right = operandStack.pop() 135 left = operandStack.pop() 136 index = operators.index(cur) 137 operandStack.append(Compute(left,right,index)) 138 else: 139 operandStack.append(cur) 140 return operandStack.pop() 141 142 while input0 == 1: 143 print("请输入生成四则运算题的数目:") 144 numOfQue = int(input()) 145 inputAnswer = [] 146 correctAnswer = [] 147 ques = [] 148 result =[] 149 for i in range(numOfQue): 150 result = produceQue() 151 ques.append(result[0]) print(result[0]+space+operators[4]+space+str(Calculate(result)))
测试用例如下:
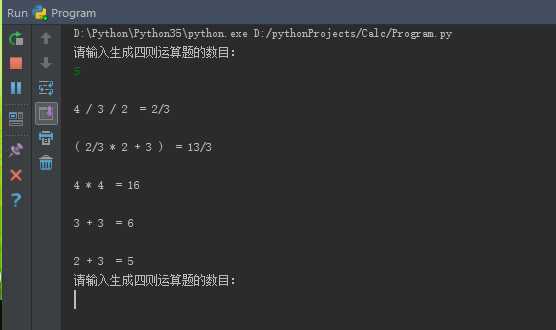
三、C#转Java---一切只为了网页显示
很不幸Java也没有Fraction类,那就自己写呗,主要功能实现如下:

1 public class Fraction { 2 long m_iNumerator; 3 long m_iDenominator; 4 5 6 public Fraction() throws Exception 7 { 8 Initialize(0,1); 9 } 10 11 public Fraction(long iWholeNumber) throws Exception 12 { 13 Initialize(iWholeNumber, 1); 14 } 15 16 public Fraction(String strValue) throws Exception 17 { 18 Fraction temp=ToFraction(strValue); 19 Initialize(temp.getNumerator(), temp.getDenominator()); 20 } 21 22 public Fraction(long iNumerator, long iDenominator) throws Exception 23 { 24 Initialize(iNumerator, iDenominator); 25 } 26 private void Initialize(long iNumerator, long iDenominator) throws Exception 27 { 28 this.setNumerator(iNumerator); 29 this.setDenominator(iDenominator); 30 ReduceFraction(this); 31 } 32 33 34 35 public long getNumerator() 36 { 37 return m_iNumerator; 38 } 39 public void setNumerator(long Numerator) 40 { 41 m_iNumerator = Numerator; 42 } 43 public long getDenominator() throws Exception 44 { 45 if(m_iDenominator != 0) 46 return m_iDenominator; 47 else 48 throw new Exception("Denominator cannot be assigned a ZERO Value"); 49 } 50 public void setDenominator(long Denominator) throws Exception 51 { 52 if(Denominator != 0) 53 m_iDenominator = Denominator; 54 else 55 throw new Exception("Denominator cannot be assigned a ZERO Value"); 56 } 57 58 59 60 61 public String ToString() throws Exception 62 { 63 String str; 64 if ( this.getDenominator()==1 ) 65 str=Long.toString(this.getNumerator()); 66 else 67 str=this.getNumerator() + "/" + this.getDenominator(); 68 return str; 69 } 70 71 public static Fraction ToFraction(String strValue) throws Exception 72 { 73 int i; 74 for (i=0;i<strValue.length();i++) 75 if (strValue.charAt(i)==‘/‘) 76 break; 77 78 if (i==strValue.length()) 79 return new Fraction(Long.parseLong(strValue),1); 80 81 long iNumerator=Long.parseLong(strValue.substring(0,i)); 82 long iDenominator=Long.parseLong(strValue.substring(i+1)); 83 return new Fraction(iNumerator, iDenominator); 84 } 85 86 public static void ReduceFraction(Fraction frac) throws Exception 87 { 88 try 89 { 90 if (frac.getNumerator()==0) 91 { 92 frac.setDenominator(1); 93 return; 94 } 95 96 long iGCD=GCD(frac.getNumerator(), frac.getDenominator()); 97 frac.setNumerator(frac.getNumerator()/iGCD); 98 frac.setDenominator(frac.getDenominator()/iGCD); 99 100 if ( frac.getDenominator()<0 ) 101 { 102 frac.setNumerator(frac.getNumerator()*(-1)); 103 frac.setDenominator(frac.getDenominator()*(-1)); 104 } 105 } 106 catch(Exception exp) 107 { 108 throw new Exception("Cannot reduce Fraction: " + exp.getMessage()); 109 } 110 } 111 private static long GCD(long iNo1, long iNo2) 112 { 113 114 if (iNo1 < 0) iNo1 = -iNo1; 115 if (iNo2 < 0) iNo2 = -iNo2; 116 117 do 118 { 119 if (iNo1 < iNo2) 120 { 121 long tmp = iNo1; 122 iNo1 = iNo2; 123 iNo2 = tmp; 124 } 125 iNo1 = iNo1 % iNo2; 126 } while (iNo1 != 0); 127 return iNo2; 128 } 129 130 public static Fraction Inverse(Fraction frac1) throws Exception 131 { 132 if (frac1.getNumerator()==0) 133 throw new Exception("Operation not possible (Denominator cannot be assigned a ZERO Value)"); 134 long iNumerator=frac1.getDenominator(); 135 long iDenominator=frac1.getNumerator(); 136 return ( new Fraction(iNumerator, iDenominator)); 137 } 138 139 public String Add(String str1, String str2) 140 { 141 142 try{ 143 Fraction frac1 = new Fraction(str1); 144 Fraction frac2 = new Fraction(str2); 145 long iNumerator=frac1.getNumerator()*frac2.getDenominator() + frac2.getNumerator()*frac1.getDenominator(); 146 long iDenominator=frac1.getDenominator()*frac2.getDenominator(); 147 return ( new Fraction(iNumerator, iDenominator).ToString() ); 148 }catch(Exception e){ 149 return e.getMessage(); 150 } 151 } 152 153 public String Multiply(String str1, String str2) 154 { 155 try{ 156 Fraction frac1 = new Fraction(str1); 157 Fraction frac2 = new Fraction(str2); 158 long iNumerator=frac1.getNumerator()*frac2.getNumerator(); 159 long iDenominator=frac1.getDenominator()*frac2.getDenominator(); 160 return ( new Fraction(iNumerator, iDenominator).ToString() ); 161 }catch(Exception e){ 162 return e.getMessage(); 163 } 164 } 165 }
主函数代码为:

1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.HashMap; 3 import java.util.LinkedList; 4 import java.util.Queue; 5 import java.util.Random; 6 import java.util.Scanner; 7 import java.util.Stack; 8 9 public class Program{ 10 11 static Random ran = new Random(); 12 static HashMap<String, String> priorities = new HashMap<String, String>() { 13 { 14 put("#", "-1"); 15 put("+", "0"); 16 put("-", "0"); 17 put("*", "1"); 18 put("/", "1"); 19 } 20 }; 21 final static String operators = "+-*/="; 22 final static String space = " "; 23 24 public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ 25 int input = 1; 26 while (input == 1) 27 { 28 System.out.println("请输入生成四则运算题的数目: "); 29 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 30 int numOfQue = sc.nextInt(); 31 String[] ques = new String[numOfQue]; 32 ArrayList que = new ArrayList(); 33 34 for(int i = 0;i < numOfQue;i++){ 35 que = produceQue(); 36 ques[i] = (String) que.get(0); 37 TreeNode s = suffixExpressionToTree(PreOrderToPostOrder(que)); 38 System.out.println(); 39 System.out.println(ques[i] + operators.charAt(4) + space + Calculate(que)); 40 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 static ArrayList produceQue() throws Exception{ 45 ArrayList str = new ArrayList(); 46 ArrayList isOperand = new ArrayList(); 47 int count = ran.nextInt(2) + 1; 48 int[] num = new int[count+1]; 49 int[] den = new int[count+1]; 50 String[] operand = new String[count+1]; 51 int[] index = new int[count]; 52 int numOfBrackets = 0; 53 if(count > 1) 54 numOfBrackets = ran.nextInt(count); 55 for(int i = 0;i < count + 1;i++){ 56 num[i] = ran.nextInt(3) + 2; 57 if(ran.nextInt(10) < 8) 58 den[i] = 1; 59 else{ 60 den[i] = ran.nextInt(4)+1; 61 } 62 operand[i] = new Fraction(num[i],den[i]).ToString(); 63 if(i < count) 64 index[i] = ran.nextInt(4); 65 } 66 ArrayList start = new ArrayList(numOfBrackets); 67 ArrayList end = new ArrayList(numOfBrackets); 68 for(int i = 0;i < numOfBrackets;i++){ 69 start.add(ran.nextInt(count-1) + 1); 70 end.add(ran.nextInt(count-(int)start.get(i)) + (int)start.get(i) + 1); 71 } 72 for(int i = 0;i < numOfBrackets;i++) 73 for(int j = 0;j < numOfBrackets;j++){ 74 if(start.get(i).equals(end.get(j))){ 75 start.set(i, -1); 76 end.set(j, -1); 77 } 78 } 79 for(int i = 0;i < count + 1;i++){ 80 str.add(operand[i]); 81 isOperand.add(i + 1); 82 if(i < count){ 83 str.add(operators.charAt(index[i])); 84 isOperand.add(0); 85 } 86 } 87 for(int i = 0;i < numOfBrackets;i++){ 88 if((int)start.get(i) != -1){ 89 int left = isOperand.indexOf(start.get(i)); 90 str.add(left, "("); 91 isOperand.add(left,0); 92 } 93 if((int)end.get(i) != -1){ 94 int right = isOperand.indexOf(end.get(i))+1; 95 str.add(right,")"); 96 isOperand.add(right,0); 97 } 98 } 99 str.add(0,""); 100 int j = 1; 101 while(j < str.size()){ 102 str.set(0, str.get(0).toString()+str.get(j).toString()+space); 103 j = j + 1; 104 } 105 return str; 106 } 107 static boolean IsOperator(String op){ 108 return operators.contains(op); 109 } 110 static boolean IsLeftAssoc(String op){ 111 if(op.equals("+") || op.equals("-") || op.equals("*") || op.equals("/")) 112 return true; 113 else 114 return false; 115 } 116 static String Compute(String leftNum,String rightNum,int op) throws Exception{ 117 Fraction result = new Fraction(); 118 switch(op){ 119 case 0: 120 return result.Add(leftNum,rightNum); 121 case 1: 122 rightNum = "-"+rightNum; 123 return result.Add(leftNum,rightNum); 124 case 2: 125 return result.Multiply(leftNum, rightNum); 126 case 3: 127 rightNum = result.Inverse(new Fraction(rightNum)).ToString(); 128 return result.Multiply(leftNum, rightNum); 129 } 130 return null; 131 } 132 static Queue PreOrderToPostOrder(ArrayList expression){ 133 Queue<String> result=new LinkedList<String>(); 134 Stack<String> operatorStack=new Stack<String>(); 135 operatorStack.push("#"); 136 String top,cur,tempChar,tempNum; 137 for(int i = 1;i < expression.size();i++){ 138 cur = expression.get(i).toString(); 139 top = operatorStack.peek(); 140 if(cur == "(") 141 operatorStack.push(cur); 142 else{ 143 if(IsOperator(cur)){ 144 while(IsOperator(top) && ((IsLeftAssoc(cur) && priorities.get(cur).compareTo(priorities.get(top))<=0) 145 ||(!IsLeftAssoc(cur) && priorities.get(cur).compareTo(priorities.get(top)) < 0))){ 146 result.add(operatorStack.pop()); 147 top = operatorStack.peek(); 148 } 149 operatorStack.push(cur); 150 } 151 else if(cur == ")"){ 152 while(operatorStack.size() > 0 && (tempChar = operatorStack.pop()) != "("){ 153 result.add(tempChar); 154 } 155 } 156 else{ 157 tempNum = cur; 158 result.add(tempNum); 159 } 160 } 161 } 162 while(operatorStack.size()>0){ 163 cur = operatorStack.pop(); 164 if(cur == "#") continue; 165 if(operatorStack.size() > 0) 166 top = operatorStack.peek(); 167 result.add(cur); 168 } 169 return result; 170 } 171 172 static String Calculate(ArrayList expression) throws Exception 173 { 174 Queue rpn = PreOrderToPostOrder(expression); 175 Stack operandStack = new Stack<String>(); 176 String left, right,cur; 177 while (rpn.size() > 0) 178 { 179 cur = (String) rpn.poll(); 180 int index = operators.indexOf(cur); 181 if (index >= 0) 182 { 183 right = (String) operandStack.pop(); 184 left = (String) operandStack.pop(); 185 operandStack.push(Compute(left, right, index)); 186 } 187 else 188 { 189 operandStack.push(cur); 190 } 191 } 192 return (String) operandStack.pop(); 193 } 194 static TreeNode suffixExpressionToTree(Queue suffixStr) 195 { 196 if (suffixStr.isEmpty()) return null; 197 // 用于临时存储节点的栈 198 Object[] chs = suffixStr.toArray(); 199 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); 200 // 遍历所有字符,不是运算符的入栈,是运算符的,将栈中两个节点取出,合成一颗树然后入栈 201 for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) 202 { 203 if (IsOperator(chs[i].toString())) 204 { 205 if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.size() < 2) 206 { 207 System.err.println("输入的后缀表达式不正确"); 208 return null; 209 } 210 TreeNode root = new TreeNode(chs[i]); 211 root.right = stack.pop(); 212 root.left = stack.pop(); 213 stack.push(root); 214 } 215 else 216 { 217 stack.push(new TreeNode(chs[i])); 218 } 219 } 220 if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.size() > 1) 221 { 222 System.err.println("输入的后缀表达式不正确"); 223 return null; 224 } 225 //stack.pop().printAll(); 226 return stack.pop(); 227 228 } 229 static boolean CompTree(TreeNode tree1,TreeNode tree2) 230 { 231 if(tree1 == null && tree2 == null) 232 return true; 233 234 if(tree1 != null && tree2 != null) 235 { 236 if(tree1.val.equals(tree2.val)) 237 { 238 if(tree1.val.equals("+") || tree1.val.equals("*")) 239 { 240 if(CompTree(tree1.left, tree2.left) && 241 CompTree(tree1.right, tree2.right) || 242 CompTree(tree1.right, tree2.left) && 243 CompTree(tree1.left, tree2.right)) 244 { 245 return true; 246 } 247 } 248 else{ 249 if(CompTree(tree1.left, tree2.left) && CompTree(tree1.right, tree2.right)) 250 { 251 return true; 252 } 253 } 254 } 255 } 256 return false; 257 } 258 }
测试用例如下:
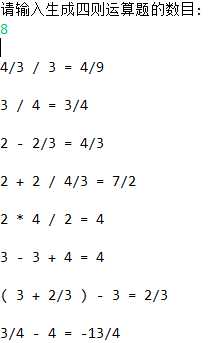
这里着重讲下关于生成题目的重复检测问题,刚开始我想着是把四则运算表达式转化成一棵二叉树,那么这就归结成二叉树同构的问题了。函数suffixExpressionToTree便是通过算式后缀式生成一棵二叉树。网上根据http://blog.csdn.net/smartxxyx/article/details/23992487,也请教了一个算法大神,说是要用到哈希。具体策略为:先随机产生一系列随机数作为存到数组,接着从根节点出发,递归计算每个子树的哈希值,将子树的哈希值相加然后和父节点自己对应的数组上的随机数相加得到父节点的哈希值。这个计算结果和子树的顺序是没有关系的,所以同构的树一哈希值一定是一样的。对于异构的树,必然在某些节点计算的哈希值不同,由于都是随机产生的一些数字,因而他们相加值和另外一棵树哈希值相同的概率也会非常低。在"国家集训队2007论文集1.杨弋《Hash在信息学竞赛中的一类应用》.doc"一文中,是使用一种类似树状递推的方法计算二叉树的Hash值,
对于一个节点v,先求出它所有儿子节点的Hash值,并从小到大排序,记作H1,H2,…,HD。那么v的Hash值就可以计算为:
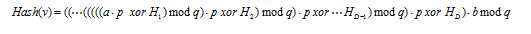
换句话说,就是从某个常数开始,每次乘以p,和一个元素异或,再除以q取余,再乘以p,和下一个元素异或,除以q取余……一直进行到最后一个元素为止。最后把所得到的结果乘以b,再对q取余。
+_+那么这样构造的算式二叉树,叶子节点肯定都是操作数,那么Hash值直接取操作数,而后随机a、p、b计算二叉树根的Hash值进行比较。代码实现起来我还是一脸懵逼,如果有谁有这方面的见解,欢迎指教!
现在我只是使用简单粗暴的方式来比较两棵二叉树,就是递归比较他们的左右孩子是否相同,如果节点为"+"或"*",还要互换左右孩子进行比较。
部分测试用例如下:
四、总结
整个代码转化比较痛苦,毕竟疏通路是个艰难的过程。而在转化的时候不得不考虑各种语言的特性,可能一种简单的数据结构在另一种语言并没有实现,而复杂的却已封装好,不过这也许就是程序语言的魅力之处了。接下来的工作就是网页显示和细节优化了,敬请期待!
以上是关于小学生四则运算应用软件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章