信号量解决哲学家就餐问题(GUI动态演示)
Posted littleschemer
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了信号量解决哲学家就餐问题(GUI动态演示)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
问题描述:餐桌前坐着5位哲学家,两个人中间有一只筷子,桌子中央有面条。哲学家思考问
题,当饿了的时候拿起左右两只筷子吃饭,必须同时拿到两只筷子才能吃饭。当5个哲学家都
拿起自己右手边的筷子,准备拿左手边的筷子时可能产生死锁现象。
为了解决互斥问题,必须将筷子资源作为同步资源。在同一时刻,对于一个筷子对象,只能由
一个哲学家(线程)对其进行访问。由于Java程序语言提供了同步机制,可以轻松解决线程互
斥问题。
算法设计思路:将哲学家、筷子、房间分别定义为三个独立的类。其中,哲学家继承自线程,
拥有think()和eat()两个同步方法。筷子属于共享资源,定义takeup()和putdown()为PV操作。
算法的伪代码如下:
var chopstick:array[0..4] of semaphore(:=1); i:integer; room:semaphore(:=4); procedure philosopher(i:integer, chopstick left, chopstick right) begin repeat think(); room.enter(); left.takeup(); right.takeup(); eat(); right.putdown(); left.putdown(); room.exit(); forever; end; begin(*main) parbegin philosopher(1).start(); philosopher(2).start(); philosopher(3).start(); philosopher(4).start(); philosopher(5).start(); parend end.1. 定义筷子类。筷子属于同步资源,被持有者持有,同时被索取者竞争。因此,取筷子和放筷子的操作必须作好同步。
public class Chopstick
{
private boolean avilable; //筷子是否可用标记
private Philosopher taker; //索取者
private Philosopher owner;//占有者
private Dinner.DinnerTable table;
public Chopstick(int id, Dinner.DinnerTable table) {
this.table = table;
avilable = true;
}
//取筷子,相当于P操作
public synchronized void takeup(Philosopher taker) {
this.setTaker(taker);
while (!avilable) {
try {
//System.out.println("哲学家等待另一根筷子");
taker.setFace(2);
wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
avilable = false;
this.setOwner(taker);
table.repaint();
}
//放下筷子,相当于V操作
public synchronized void putdown() {
avilable = true;
this.setOwner(null);
notify(); //唤醒其他等待的线程
table.repaint();
}
public int getOwnerId(){
return this.getOwner().getPersonId();
}
public Philosopher getTaker() {
return taker;
}
public void setTaker(Philosopher taker) {
this.taker = taker;
}
public Philosopher getOwner() {
return owner;
}
public void setOwner(Philosopher owner) {
this.owner = owner;
}
}
2.定义哲学家类。哲学家参与资源的竞争,申明为一个线程,其run()方法为一个死循环操作,
不断切换思考和吃饭两个动作(思考和吃饭设置一个随机时间)。
import java.util.Random;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class Philosopher extends Thread
{
public static final byte STATUS_OF_NORMAL = 0; //初始表情
public static final byte STATUS_OF_THINK =1; //思考表情
public static final byte STATUS_OF_HUNGRY = 2; //饥饿表情
public static final byte STATUS_OF_EAT = 3; //就餐表情
private Room room;
private Chopstick left, right;
private int personId;
private ImageIcon init, eat, think, hungry;
private ImageIcon currentFace;
private Random rand = new Random(); //随机休眠时间
public Philosopher(Room room, int id, Chopstick left, Chopstick right) {
this.room = room;
this.personId = id;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
eat = new ImageIcon("eat.png");
think = new ImageIcon("think.png");
hungry = new ImageIcon("hungry.png");
init = new ImageIcon("init.png");
currentFace = init;
setFace(Philosopher.STATUS_OF_NORMAL);
}
public void eat() {
left.takeup(Philosopher.this);
right.takeup(Philosopher.this);
setFace(Philosopher.STATUS_OF_EAT);
// System.out.println("哲学家" + this.philoId + "正在用餐");
}
public void think() {
left.putdown();
right.putdown();
setFace(Philosopher.STATUS_OF_THINK);
// System.out.println("哲学家" + this.philoId + "正在思考");
}
/**
* 设置表情图片
*/
public void setFace(int faceId) {
switch (faceId) {
case Philosopher.STATUS_OF_NORMAL:
currentFace = init;
break;
case Philosopher.STATUS_OF_THINK:
currentFace = think;
break;
case Philosopher.STATUS_OF_HUNGRY:
currentFace = hungry;
break;
case Philosopher.STATUS_OF_EAT:
currentFace = eat;
break;
}
}
public ImageIcon getFace() {
return currentFace;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
think();//哲学家思考
try {
sleep((int) ((rand.nextFloat() + 0.5) * 3000));
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// room.enter();//进入房间
eat();//哲学家就餐
try {
sleep((int) ((rand.nextFloat() + 0.5) * 4000));
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// room.exit();//离开房间
}
}
public int getPersonId() {
return personId;
}
public void setPersonId(int personId) {
this.personId = personId;
}
}3. 用Swing实现图形界面,将界面和业务逻辑代码分开。
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.BoxLayout;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class Dinner extends JFrame
{
private static final int personCount = 20; //哲学家数量
private static Room room = new Room(personCount - 1);//房间锁变量,用于控制同时就餐的人数dd
private JButton startBtn = new JButton("开始");
private JButton stopBtn = new JButton("暂停");
private JButton continueBtn = new JButton("继续");
private JButton endBtn = new JButton("结束");
private boolean started = false;
private boolean stopped = false;
final static Chopstick[] chopstick = new Chopstick[personCount];
final static Philosopher[] philos = new Philosopher[personCount];
ImageIcon normalFace, eatFace, thinkFace, hungryFace; //表情图片
// 因Table(餐桌)类与Dinner类联系较为紧密,故将其作为内部类,方便消息的传递
class DinnerTable extends JPanel
{
private int counts;
private int r1 = 20;
private int CHOPS_LENGTH = 35; //筷子的长度
private int DISTANCE = 100; //筷子与人的距离
private int VERTICAL_DIS = -20; //表情与名字的距离
private int r2 = r1 + CHOPS_LENGTH;
private int r3 = r2 + DISTANCE;
private int delta;
private int delta0 = -18;
public DinnerTable(int counts) {
setOpaque(false);
this.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(550, 400));
this.counts = counts;
this.delta = 360 / counts;
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics page) {
super.paintComponent(page);
int x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3;
page.fillOval(200, 150, 150, 150);
//画餐桌上的筷子
for (int i = 0; i < counts; i++) {
page.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
//根据坐标系 x = r*cos(delta) , y = r*sin(delta) 计算点
x1 = 275 + (int) (r1 * Math.cos(((delta * i)+ delta0*(-5) ) * Math.PI / 180));
y1 = 225 + (int) (r1 * Math.sin(((delta * i) + delta0*(-5) ) * Math.PI / 180));
x2 = 275 + (int) (r2 * Math.cos(((delta * i) + delta0 *(-5) ) * Math.PI / 180));
y2 = 225 + (int) (r2 * Math.sin(((delta * i) + delta0 *(-5) ) * Math.PI / 180));
x3 = 275 + (int) (r3 * Math.cos(((delta * i) + delta0 ) * Math.PI / 180));
y3 = 225 + (int) (r3 * Math.sin(((delta * i) + delta0 ) * Math.PI / 180));
if (chopstick[i].getOwner() != null && philos[i].getPersonId() == chopstick[i].getOwnerId()) {
//检查哲学家是否拿到左边筷子
page.drawLine(x3 - 20, y3, x3 - 20, y3 + CHOPS_LENGTH);
}
if (chopstick[(i + 1) % personCount].getOwner() != null && philos[i].getPersonId() == chopstick[(i + 1) % personCount].getOwnerId() ) {
//检查哲学家是否拿到右边筷子
page.drawLine(x3 + 45, y3, x3 + 45, y3 + CHOPS_LENGTH);
}
if (chopstick[i].getOwner() == null) {
//筷子在餐桌上
page.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
philos[i].getFace().paintIcon(this, page, x3, y3); //画表情
page.setColor(Color.BLUE);
page.drawString("哲学家" + (i + 1), x3 - 5, y3 + VERTICAL_DIS);//画名字
}
}
}
/**
* 设置窗口居中
*/
private void putUIInCenter(){
int windowWidth = this.getWidth(); //获得窗口宽
int windowHeight = this.getHeight(); //获得窗口高
Toolkit kit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); //定义工具包
Dimension screenSize = kit.getScreenSize(); //获取屏幕的尺寸
int screenWidth = screenSize.width; //获取屏幕的宽
int screenHeight = screenSize.height; //获取屏幕的高
this.setLocation(screenWidth / 2 - windowWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2 - windowHeight / 2);
}
public Dinner() {
setTitle("哲学家就餐");
setPreferredSize(new Dimension(600, 650));
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.pack();
setVisible(true);
setResizable(false);
putUIInCenter();
normalFace = new ImageIcon("init.png");
eatFace = new ImageIcon("eat.png");
thinkFace= new ImageIcon("think.png");
hungryFace = new ImageIcon("hungry.png");
JPanel btnPanel = new JPanel();
btnPanel.setBounds(160, 20, 300, 200);
btnPanel.setOpaque(false);
btnPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
btnPanel.add(startBtn);
btnPanel.add(stopBtn);
btnPanel.add(continueBtn);
btnPanel.add(endBtn);
//各种按钮增加点击事件
startBtn.addActionListener(new startListener());
continueBtn.addActionListener(new continueListener());
stopBtn.addActionListener(new stopListener());
endBtn.addActionListener(new endListener());
JPanel mainPanel = new JPanel();
mainPanel.setLayout(null);
mainPanel.setBackground(Color.black);
mainPanel.add(btnPanel);
DinnerTable table = new DinnerTable(personCount);
table.setBounds(20, 50, 500, 420);
for (int i = 0; i < chopstick.length; i++) {
chopstick[i] = new Chopstick(i, table);
}
for (int i = 0; i < philos.length; i++) {
philos[i] = new Philosopher(room, i,
chopstick[i], chopstick[(i + 1) % personCount]);
}
mainPanel.add(table);
JPanel descipPanel = new JPanel();
descipPanel.setBounds(20, 480, 200, 200);
descipPanel.setOpaque(false);
descipPanel.setForeground(Color.red);
descipPanel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(descipPanel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
JLabel label0 = new JLabel("哲学家就餐问题(信号量解决)");
label0.setForeground(Color.red);
JLabel label1 = new JLabel("初始状态的哲学家", normalFace, JLabel.RIGHT);
label1.setForeground(Color.red);
JLabel label2 = new JLabel("思考状态的哲学家", thinkFace, JLabel.RIGHT);
label2.setForeground(Color.red);
JLabel label3 = new JLabel("饥饿状态的哲学家", hungryFace, JLabel.RIGHT);
label3.setForeground(Color.red);
JLabel label4 = new JLabel("正在吃饭的哲学家", eatFace, JLabel.RIGHT);
label4.setForeground(Color.red);
descipPanel.add(label0);
descipPanel.add(label1);
descipPanel.add(label2);
descipPanel.add(label3);
descipPanel.add(label4);
mainPanel.add(descipPanel);
getContentPane().add(mainPanel);
}
private class startListener implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
if (!started) {
started=true;
for (int i = 0; i < personCount; i++) {
philos[i].start();
}
}
}
}
private class stopListener implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
for (int i = 0; i < personCount; i++) {
philos[i].suspend();
}
stopped = true;
}
}
private class continueListener implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
if (stopped) {
for (int i = 0; i < personCount; i++) {
philos[i].resume();
}
stopped = false;
}
}
}
private class endListener implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
System.exit(1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Dinner();
}
}4.程序运行结果如下:
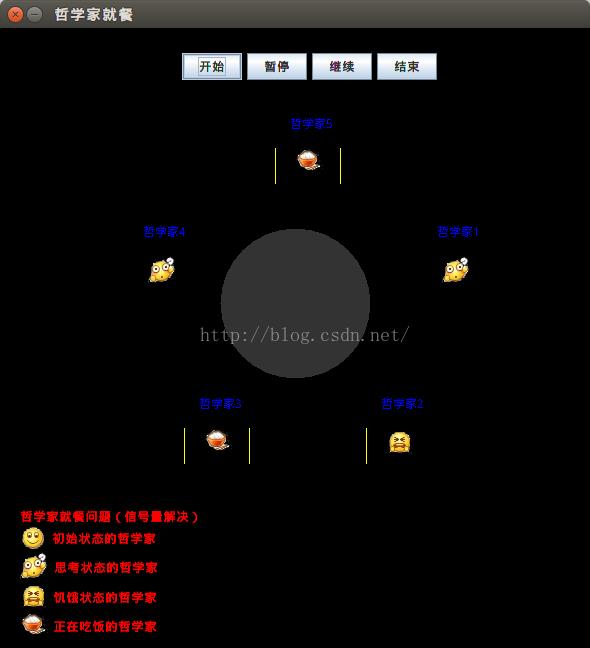
5.若修改Dinner类设置的常量 personCount为10,重新运行程序,如下:
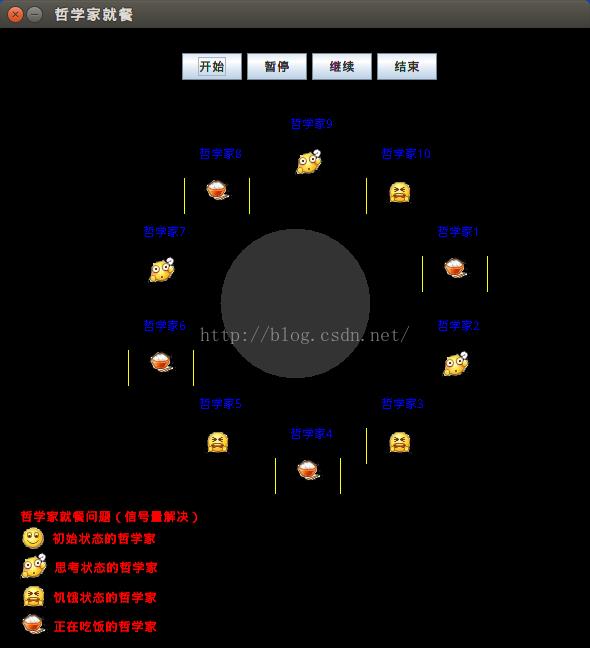
6.若继续添加限制,要求在一时刻只能有4个哲学家就餐,则可以再添加另外一个信号量(比如房间资源)。哲学家在竞争筷子之前,必须先进入一个房间才能参与下一步竞争。房间类的设计如下:
/*
* 限制多个哲学家同时就餐,增设一间房间, 哲学家在准备就餐之前,必须先进入该房间, 若人数超过房间容量,则阻塞该线程
*/
public class Room
{
private static int capacity; //房间的容量上限
public Room(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public synchronized void enter() {
while (capacity == 0) {
try {
wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
capacity--;
}
public synchronized void exit() {
capacity++;
notify();
}
}
同时,设置房间上限(Dinner类的Room字段的初始化)
private static Room room = new Room(4);//房间锁变量,用于控制同时就餐的人数修改哲学家线程的run()方法,竞争筷子资源前先进入一个房间,放下筷子的时候需要退出房间,代码如下:
public void run() {
while (true) {
think();//哲学家思考
try {
sleep((int) ((rand.nextFloat() + 0.5) * 3000));
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
room.enter();//进入房间
eat();//哲学家就餐
try {
sleep((int) ((rand.nextFloat() + 0.5) * 4000));
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
room.exit();//离开房间
}
}
可以观察到,在同一时刻最多只有4个哲学家在就餐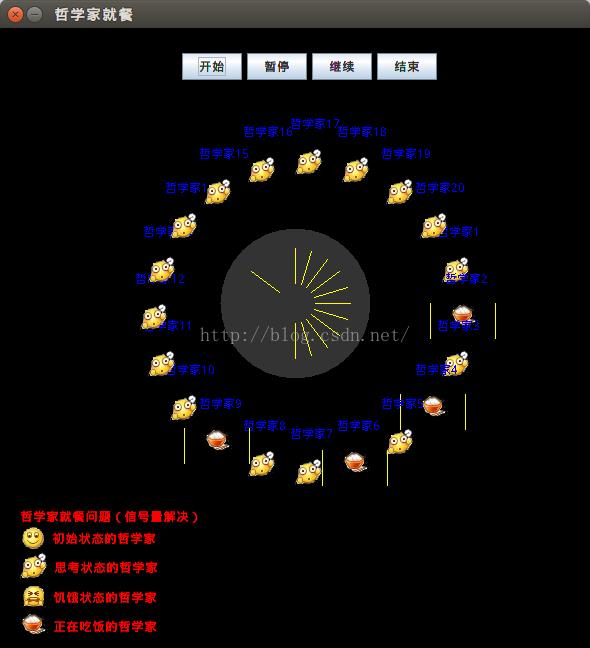
以上是关于信号量解决哲学家就餐问题(GUI动态演示)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章