C和指针 第十二章 结构体 习题
Posted 日拱一卒,功不唐捐
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C和指针 第十二章 结构体 习题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
12.3 重新编写12.7,使用头和尾指针分别以一个单独的指针传递给函数,而不是作为一个节点的一部分
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
//指针fwd指向前一个节点,bwd指向后一个节点
typedef struct NODE {
struct NODE *fwd;
struct NODE *bwd;
int value;
} Node;
/*传入指向 头部和尾部节点的指针 的指针,四种情况
* 插入到表头,
* 插入到表尾,
* 插入到空表中,
* 插入到表中,前三个都需要修改headPtr或tailPtr指针
*/
int doubleLinklistInsert(Node **headPtr, Node **tailPtr, int value)
{
Node *this = *headPtr;
Node *newNode;
while( this != NULL && this -> value < value){
this = this -> fwd;
}
newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode -> value = value;
if(this == NULL){
//插入到表尾,或者空表中
if(this == *headPtr){
//插入到空表
*headPtr = newNode;
*tailPtr = newNode;
newNode -> fwd = NULL;
newNode -> bwd = NULL;
}else{
//插入到表尾
newNode -> fwd = NULL;
//原来的表尾元素为当前节点的前节点
newNode -> bwd = *tailPtr;
(*tailPtr) -> fwd = newNode;
//更新尾节点指针
*tailPtr = newNode;
}
}else{
//插入到表头,或者表中
if(this == *headPtr){
//插入到表头
newNode -> bwd = NULL;
//原来的表头变成第二个节点
newNode -> fwd = *headPtr;
(*headPtr) -> bwd = newNode;
//更新表头
*headPtr = newNode;
}else{
//插入到非空表中this位置的前面
newNode -> fwd = this;
newNode -> bwd = this -> bwd;
this -> bwd -> fwd = newNode;
this -> bwd = newNode;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
int main()
{
Node third;
Node second;
Node first;
third = (Node){NULL, &second, 4};
second = (Node){&third, &first, 2};
first = (Node){&second, NULL, 1};
Node *head = &first;
Node *tail = &third;
doubleLinklistInsert(&head, &tail, 35);
doubleLinklistInsert(&head, &tail, 3);
doubleLinklistInsert(&head, &tail, -10);
Node *rootPtr = head;
while(rootPtr != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", rootPtr -> value);
rootPtr = rootPtr -> fwd;
}
return 0;
}
运行:
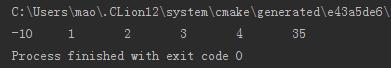
12.4 编写函数反序排列单链表所有节点。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef struct Node {
struct Node *next;
int value;
} Linklist;
Linklist *sll_reverse(Linklist *first)
{
if(first == NULL){
return NULL;
}
Linklist *current = first;
Linklist *next;
Linklist *pre;
Linklist *morePre = NULL;
while((next = current -> next) != NULL){
//循环移动当前指向的节点
pre = current;
current = next;
//修改前一节点的next指针为前前节点
pre -> next = morePre;
//移动前前节点morePre的指针
morePre = pre;
}
//如果为单个节点之间返回
if(current == first){
return first;
}else{
//修改最后一个节点的指针,作为头指针返回原来的最后一个节点的位置
current -> next = pre;
return current;
}
}
int main()
{
Linklist third = {NULL, 4};
Linklist second = {&third, 3};
Linklist first = {&second, 2};
Linklist *head = &first;
head = sll_reverse(head);
while (head != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", head -> value);
head = head -> next;
}
return 0;
}
运行:
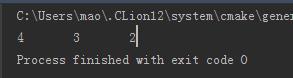
12.5 编写程序,从一个单链表中删除一个节点,第一个参数为指向链表头部的指针的指针
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef struct Node {
struct Node *next;
int value;
} Linklist;
//从first指向的链表中删除节点node
int sll_delete(Linklist **first, Linklist *node)
{
Linklist **ptr = first;
//Ptr为指向 next字段的 指针
while(*ptr != NULL && *ptr != node){
ptr = &((*ptr) -> next);
}
//如果没有找到
if(*ptr == NULL){
return FALSE;
}else{
//如果找到了,变更前节点指向
*ptr = (*ptr) -> next;
//释放节点内存
free(*ptr);
return FALSE;
}
}
int main()
{
Linklist third = {NULL, 3};
Linklist second = {&third, 2};
Linklist first = {&second, 1};
Linklist *headPtr = &first;
Linklist *head = headPtr;
while (head != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", head -> value);
head = head -> next;
}
printf("\\n");
sll_delete(&headPtr, &second);
head = headPtr;
while (head != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", head -> value);
head = head -> next;
}
printf("\\n");
sll_delete(&headPtr, &first);
head = headPtr;
while (head != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", head -> value);
head = head -> next;
}
printf("\\n");
sll_delete(&headPtr, &third);
head = headPtr;
while (head != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", head -> value);
head = head -> next;
}
return 0;
}
运行:
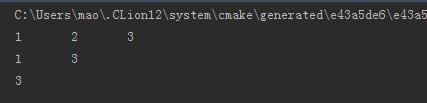
12.6 双链表中移除节点,第一个参数为指向链表头部的指针,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef struct Node {
struct Node *next;
int value;
} Linklist;
//从first指向的链表中删除节点node
int sll_delete(Linklist *first, Linklist *node)
{
Linklist *pre = NULL;
Linklist *cur = first;
while(cur != NULL && cur != node){
pre = cur;
cur = cur -> next;
}
//如果没有找到
if(cur == NULL){
return FALSE;
}else if(cur == first){
//此时first是传值传入,只可以修改头指针指向的值,修改为第二个节点
*first = *(cur -> next);
free(node);
return TRUE;
}else{
pre -> next = cur -> next;
free(node);
return TRUE;
}
}
int main()
{
Linklist third = {NULL, 3};
Linklist second = {&third, 2};
Linklist first = {&second, 1};
Linklist *headPtr = &first;
Linklist *head = headPtr;
while (head != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", head -> value);
head = head -> next;
}
printf("\\n");
sll_delete(headPtr, &second);
head = headPtr;
while (head != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", head -> value);
head = head -> next;
}
printf("\\n");
sll_delete(headPtr, &first);
while (headPtr != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", headPtr -> value);
headPtr = headPtr -> next;
}
printf("\\n");
sll_delete(headPtr, &third);
head = headPtr;
while (head != NULL){
printf("%d\\t", head -> value);
head = head -> next;
}
printf("\\n");
return 0;
}
运行:
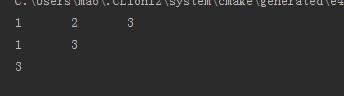
12.7 建立单词索引表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define EXIST 1
#define NOEXIST 0
typedef struct Wordlist {
struct Wordlist *nextWord;
char *word;
} wordlist;
typedef struct Alphalist {
struct Alphalist *nextAlpha;
//单个单词链表的指针
wordlist * wlPtr;
char alpha;
} alphalist;
int isExist(wordlist *listPtr, char *string)
{
wordlist *current = listPtr;
while(current != NULL){
if(strcmp(string, current -> word) == 0){
return EXIST;
}
current = current -> nextWord;
}
return NOEXIST;
}
int wordInsert(wordlist **listPtr, char *string)
{
wordlist **current = listPtr;
wordlist *new;
char *temp;
while(*current != NULL){
//按字符排序进行插入
if(strcmp(string, (*current) -> word) < 0){
//生成new节点,插入到current之前,current为指向nextWord字段的指针
new = (wordlist *)malloc(sizeof(wordlist));
temp = (char *)malloc(strlen(string));
if(temp == NULL){
return FALSE;
}
strcpy(temp, string);
new -> word = temp;
//new指向 *current
new -> nextWord = *current;
//更新 *current为当前插入点
*current = new;
return TRUE;
}
//循环到下一点
current = &(*current) -> nextWord;
}
//循环玩整个列表后,还未找到,则末尾追加上
temp = (char *)malloc(strlen(string));
if(temp == NULL){
return FALSE;
}
strcpy(temp, string);
new = (wordlist *)malloc(sizeof(wordlist));
new -> word = temp;
new -> nextWord = NULL;
*current = new;
return TRUE;
}
int WordAlphaListInsert(alphalist *ptr, char *string)
{
char headCh = string[0];
alphalist *current = ptr;
wordlist *wl;
wordlist **rootPtr;
char *temp;
//通过首字符查找wordlist
while (current -> alpha != headCh){
current = current -> nextAlpha;
}
//已经存在
if(isExist(current -> wlPtr, string) == EXIST){
return FALSE;
}else{
//如果wordlist为NULL空,则创建初始单词链表
if(current -> wlPtr == NULL){
wl = (wordlist *)malloc(sizeof(wordlist));
//第一个节点,nextword为NULL
wl -> nextWord = NULL;
//申请内存拷贝字符串
temp = (char *)malloc(strlen(string));
if(temp == NULL){
return FALSE;
}
strcpy(temp, string);
wl ->word = temp;
current -> wlPtr = wl;
}else{
//如果有单词表,则插入单词
rootPtr = &(current -> wlPtr);
wordInsert(rootPtr, string);
}
return TRUE;
}
}
//打印链表内容
void printList(alphalist *list)
{
alphalist *currentAl = list;
wordlist *currentWl;
while (currentAl != NULL){
printf("%c:\\n", currentAl -> alpha);
currentWl = currentAl -> wlPtr;
while (currentWl != NULL){
printf("%s \\t", currentWl -> word);
currentWl = currentWl -> nextWord;
}
printf("\\n-----------------------\\n");
currentAl = currentAl -> nextAlpha;
}
}
int main()
{
char z;
alphalist *pre = NULL;
alphalist *current;
//创建字母和单词列表
for(z = 122; z > 96; z--){
current = (alphalist *)malloc(sizeof(alphalist));
current -> alpha = z;
current -> wlPtr = NULL;
current -> nextAlpha = pre;
pre = current;
}
//插入单词
WordAlphaListInsert(current, "yang");
WordAlphaListInsert(current, "xun");
WordAlphaListInsert(current, "xan");
WordAlphaListInsert(current, "xzn");
WordAlphaListInsert(current, "wu");
WordAlphaListInsert(current, "ya");
WordAlphaListInsert(current, "yz");
printList(current);
return 0;
}
运行:

以上是关于C和指针 第十二章 结构体 习题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章