VIII virtualization&kvm
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了VIII virtualization&kvm相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
VIII virtualization&kvm
OS将对硬件资源的使用都虚拟成system call,某个进程只要与硬件打交道都要经过kernel提供的接口(system call)
rss(进程启动后必须要位于内存中,绝对不可以被交换出去(不被清出去))
page cache(进程运行时打开的文件,可放到交换分区中(可被清出去))
anon page(进程运行过程当中产生的数据,如堆中的一部分数据)
第一个进程运行打开一个很大的文件,第二个进程运行没有足够的内存时,内核会将第一个进程打开的文件(page cache)统统清出去,之后CPU又切到第一个进程时发现打开的文件没了,产生缺页异常,再重新从硬盘上调取
MMU(memory management unit,线性地址-->物理地址,MMU每次转换都要一级页目录查找、二级页目录查找,再平移计算才得到内存,为加速这个过程有TLB)
CPU通过IO port知道在某时刻与哪个IO打交道(CPU与IO设备交换数据通过IOport实现),IO设备在启动时要向CPU注册它使用的IO port,一个IO设备可使用一片连续的IO port,并注册使用中断号(让IO设备通知CPU有紧急事件要处理)以实现当IO设备上有信号让CPU知道哪个IO设备有信号,而且要通过IO port与这个设备打交道,CPU通过可编程中断控制器让每一个IO设备注册使用中断线上的中断设备号,如网卡上有人ping来一个报文,要将产生的电信号读下来放在内存网络缓冲区,若是disk IO放在disk缓冲区(每个设备都有缓冲区)
站在OS内核角度,kernel认为自己可使用所有硬件:CPU(全量CPU时间片),内存(连续,全部的内存空间0x0000-max,32bitOS内存最开始1M给Bios,16M留给DMA;64bitOS有1G给DMA,这1G内核也能用),I/O(全部可用IO)
VA(virtual address线性地址)
PA(physical address)
虚拟化(将一个物理硬件平台虚拟成多个)
vmware(模拟出一堆硬件设备,每一个硬件设备都是独立平台)
虚拟化要解决的问题(硬件之上的OS,有用户空间、内核空间;vmware虚拟机所模拟出的多个硬件平台上的每一个OS也有用户空间、内核空间;每个内核都意识不到其它主机存在,直接使用硬件设备(内存),这将会覆盖掉其它的正在使用的内存空间,产生资源争用会使系统崩溃,硬件之上的这个OS将内存留一部分给kernel用,其它的给进程用,vmware虚拟机及其它进程使用的内存是高地址内存空间(非0地址空间),关键是每个内核都要使用从0开始的内存地址空间)
guest OS(虚拟出来的虚拟机,内存地址转换要有两次,效率低,多个guest OS要与IO设备(网卡、磁盘)交互)
hypervisor(虚拟机管理程序)
CPU虚拟化(将时间片再分细点,指令分普通指令和特权指令,ring{0,1,2,3},ring0,privileged ring特权环是能运行敏感指令(特权指令)的,进程运行只能运行普通指令(进程在cpu上运行无非将进程的代码转换为cpu上运行的指令),要想用特权指令,如要访问硬盘、访问内存中的数据时通过system call,这时进程要退出,内核在cpu的ring0上运行;guest OS的kernel中同样有普通指令、特权指令,当guest OS上的进程需要运行特权指令(实际上管理虚拟机软件vmware的运行是在用户空间的,所以guest OS是不能运行敏感指令的,不能让虚拟机的内核运行在ring0上,只能运行在ring3上,否则它会将硬件资源视为可全量使用,会清空其它进程的内存、重启系统等操作)又不能运行这显然不合适,每一个kernel都认为自己在ring0上,通过模拟让guest OS认为自己在ring0上,保留一些关键的特权指令(如重启系统等),否则无法保证整个OS的安全性,实际上guest OS并不真正运行特权指令,每次guest OS的进程-->guest OS的内核-->host OS的内核,ring0就是一堆特权指令集来保证各guest OS间是隔离的,当host OS要关机就能控制整个系统关机,不管guest允不允许,host OS的内核才是真正意义的特权阶层,host OS要能监控每一个guest OS执行的指令并判定它能否运行)
X86平台要实现CPU的虚拟化面临的挑战(特权级压缩ring compression,VMM,virtual machine monitor必须要运行在ring0上,为避免guest OS控制系统资源,guestOS不得不降低自身的运行级别在ring3上(特权级不够使用),VMM使用分页或段限制的方式保护物理内存的访问,但64bit模式下段限制不起作用,而分页又不区分ring{0,1,2},为统一和简化VMM的设计,guest OS只能和用户进程一样运行在ring3上,VMM必须监控guest OS对GDT、IDT(CPU寄存器)等特权资源的位置,防止guest OS运行在ring0,同时又要保护降级后的guest OS不受guest进程的主动攻击或无意破坏;特权级别名ring alias,搞一些假的特权指令集告诉guest OS这就是ring0;地址空间压缩address space compression;非特权敏感指令;静默特权失败silentprivilege failure;中断虚拟化interrupt virtualization)
classical virtualization的基本需求(1974,Popek、Goldberg,真正意义的VMM至少需要三个方面的标准:等价执行equivalient execution,除资源可用性及时间上的不同之外,程序在虚拟化环境中及真正环境中的执行是完全相同的;性能performance,指令集中的大部分指令要能直接运行在CPU上;安全safety,VMM要能完全控制系统资源,某个guest OS运行不能影响到其它的guest OS,各guest OS间要实现隔离,且任何一个guest OS要执行特权指令,host OS要能提前捕获对其处理,任何一个guest OS都不能越过host OS对整个物理硬件发出任何特权控制指令)
注:Intel和AMD的CPU(X86)上有模糊地带(普通指令与特权指令间)
CPU硬件虚拟化(Intel:VT-x;AMD:AMD-V;特权级别加入ring-1,guest OS在ring0上,事实上ring0是空出来的一环没有指令,当guestOS试图要在ring0上运行时会触发ring-1,由ring-1决定执行指令、转换并翻译这个指令运行)
内存虚拟化(Intel(EPT,extended page table)和AMD(RVI,rapid virtualization indexing;NPT,nested pagetables)分别通过EPT、RVI技术为虚拟化应用提升shadow MMU(完成VA-->HA一步到位)的性能,降低CPU的占用率,提供良好的吞吐量;并通过标记tagged TLB来避免虚拟机切换时频繁清写flush TLB以提高TLB缓存的命中率(用TLB保存MMU的转换结果)
KVM 还借助于KSM(KernelSame-pageMerging)这个内核特性实现了内存页面共享。KSM 通过扫描每个虚拟机的内存查找各虚拟机间相同的内存页,并将这些内存页合并为一个被各相关虚拟机共享的单独页面。在某虚拟机试图修改此页面中的数据时,KSM 会重新为其提供一个新的页面副本。实践中,运行于同一台物理主机上的具有相同 GuestOS 的虚拟机之间出现相同内存页面的概率是很的,比如共享库、内核或其它内存对象等都有可能表现为相同的内存页,因此,KSM 技术可以降低内存占用进而提高整体性能。
注:将离散的内存地址空间在hypervisor上再整合在一起分给guest OS,guest OS的VA-->guest OS的PA-->host OS的PA(HA);MMU,memory management unit
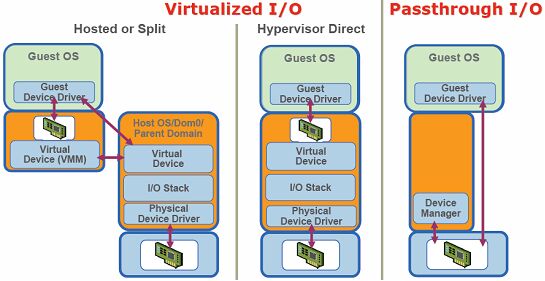
IO设备虚拟化(网卡、硬盘等大多数的IO设备是通过软件(如vmware)模拟(假网卡、假硬盘),guestOS的网卡往外发报文(IP报文本身是独立的),来的报文哪个主机收(guest OS还是host OS),是根据MAC接收报文的,假硬盘上存的数据最终都要到物理硬盘上,在物理硬盘上建立本地回环镜像文件(如用dd命令创建的文件,格式化后能充当swap分区用)与模拟的磁盘建立关联关系,guest OS就把假硬盘当硬盘用,但真正在物理机上表现的是个文件,虚拟的磁盘没物理硬盘性能好,IO要转换两次,若要让guest OS的IO disk性能好点,使用共享存储(iSCSI),guest OS作为client直接使用共享存储;网卡也是这样,模拟一个假网卡与本地的文件建立关联关系,guest OS A同guest OS B之间经网卡通信(或guest OS同host OS通信)借助于OS通过IPC解决(vmware中有虚拟通道),无论使用什么MAC都无所谓,若与外部网络通信,通过bridge、NAT,NAT这种方式是将物理机网卡上的MAC当作网关,源地址转换,类似各guest OS组成网络,要与外部网络通信时将报文发至网关,物理机通过地址转换送到外部网络,外部网络是看不到guest OS的,bridge这种方式将guest OS的虚拟网卡绑定在物理网卡上且让物理网卡运行在混杂模式下(无论目标MAC是不是它都要接收,接收下来转给guest OS,二层代理机制,在二层就转了),bridge这种方式可将物理网卡理解为是switch,host OS的网卡可理解为也是虚拟网卡,guest OS上的网卡也是虚拟网卡,物理网卡接收到报文目标MAC是哪个虚拟网卡就转发到对应的虚拟网卡上(桥接就是网桥,模拟的是switch))
IO虚拟化(Intel和AMD在主板上创建芯片组时,这个芯片组可完成IO虚拟化(在硬件级别上),如Intel:IOMMU,IO设备要映射到当前OS上,为IO分配缓冲区,在passthrough技术上要借助IOMMU)
半虚拟化PV(para virtualization,IO设备虚拟化,guest OS的kernel-->vmware-->host OS的kernel-->物理网卡,性能不好,若直接与host OS的内核打交道则性能会好很多,将中间那步绕过去,模拟的文件该存在让它存在直接绕过它,将host OS网卡的驱动程序做成system call直接输出给虚拟机使用(guest OS-->host OS的system call),这违反虚拟化原则,guest OS就知道它在虚拟化环境中,这种技术叫半虚拟化para virtualization,性能好,直接与硬件打交道速度要快)
完全虚拟化FV(full virtualization,guest OS不认为它在虚拟化环境中;CPU不支持硬件虚拟化技术,要模拟特权指令)
硬件辅助的虚拟化HVM(hardware-assistant VM,CPU支持硬件虚拟化技术,VMM运行在ring-1,guest OS运行在ring0, HVM,hardware-assistant VM,硬件辅助的虚拟化)
PV和HVM整合(guest OS知道自己在虚拟化环境中,只要与硬件打交道,host OS都向guest OS输出system call(将特权指令集也输出为system call)或叫hypercall(hypervisor call),这样性能会好很多,要求在PV下的OS必须要改内核才能使用hypercall(win不能改内核))
PV on HVM(基于HVM的PV技术,把PV中的CPU不用了而用HVM,用IO的PV,这样既利用了CPU的HVM,又利用IO的PV技术,性能会很好)
注:cpu、memory、io都可用PV,有了HVM,cpu的PV将用不着,io的PV能用得上,硬件再辅助,某一种IO设备就那一个,有资源争用
IO穿透技术passthrough I/O(guest OS直接使用独立的网卡)
常见的虚拟化模型:
有宿主机的VMM,VMM要借助于内核才能完成虚拟化(hosted VMM)
硬件之上直接是VMM,这种模型下的VMM称为hypervisor,VMM具备OS的管理机制(VMM自带对CPU、memory等的管理),可理解为是精简的OS只提供虚拟化服务,VMM具备驱动底层硬件的能力(安装前要查看VMM所支持的硬件类型)
注:vmware workstation,vmware server,vmware ESX商业(hypervisor),vmware ESXi(免费,简易版)
Xen提供对CPU、memory、interrupt这三个关键性硬件管理外,其它功能如驱动等都不提供,Xen它自己驱动不了任何硬件设备,要在Xen之上立即安装一个虚拟机(Linux),这个特权Linux提供驱动,提供管理界面,可直接操作底层硬件,Xen中的虚拟机称为Dom{0,1,2,3……}(domain),Dom0为特权虚拟机,通过Dom0来管理其它的Dom{1,2,3}(称为DomU),Dom0要使用CPU、memory、interrupt这三个关键性硬件要通过Xen,而其它的IO设备可直接使用,在Dom0上创建一模拟设备,要通过Xen关联至Dom1上(Dom0将半虚拟化的硬件驱动程序通过Xen的hypercall送给Dom1),Dom1要使用网卡向外发数据要先发至Dom0由Dom0访问硬件网卡,Xen不管理IO等硬件设备,Dom1要使用CPU(或memory或interrupt)则直接由Xen管理,这样一部分要交由Xen管理,一部分交由Dom0管理,Xen是一种半虚拟化的解决方案,就算cpu、memory不支持HVM,Xen照样可高性能运行,若cpu、memory支持HVM,Xen也可使用full virtualization,各硬件是模拟的性能较差,完全虚拟化FV和PV的最大区别,FV中的guest OS的kernel不用修改了,那Xen之上的虚拟机可使用win了(FV的好处),若Dom1是Linux可使用PV on HVM(CPU不虚拟化了使用HVM,而对于其它的IO硬件使用PV))
Qemu(quickemulator,是独立虚拟软件,能独立运行虚拟机,kqemu是该软件的加速软件;常用于模拟器,1M,虚拟化软件,跨平台虚拟,如将硬件CPUx86的模拟成苹果的arm或IBM的power pc,可帮助程序员提供测试环境,好处如底层是X86的CPU,可在guest OS上也使用X86的CPU并进行优化,让其接近硬件CPU的性能运行)
通常Xen和Qemu结合使用,Qemu主要实现为其它guest OS基于软件方式模拟硬件(虚拟网卡、虚拟硬盘等)、本地回环文件(用文件充当虚拟硬盘用),qemu-img支持众多的格式,包括vmware的格式
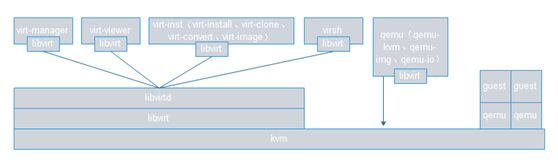
Xend/xm(在Xen上创建虚拟机,安装OS并引导,Xen提供了专门的管理工具Xend/xm,Xend是管理服务,xm是命令(可start、pause、suspend某个虚拟机,完全在CLI下),Xen将其对硬件的管理功能通过API输出给xm这个管理工具,创建好硬件不用重启直接附加在虚拟机上并能让虚拟机识别出来,Xen可虚拟CPU,用xm通过Xen的API创建多个CPU,虚拟机可直接使用,比vmware workstation要强大灵活,通过Xen的API可开发出图形管理工具,有数十种管理工具(CLI下和GUI下),如openstack、cloudstack,这些云平台就是利用虚拟机(Xen)的API提供了能够管理虚拟机进程的管理程序
注:如redhat为Xen提供的管理工具virsh比xm更强大且易用,virsh支持众多虚拟化技术且更通用
KVM(kernel-based VM,基于内核的虚拟机,KVM是内核模块,没有这个模块OS还是本来的OS,这个模块一旦被kernel装载了,OS就摇身变成了hypervisor,KVM可让OS成为hypervisor,KVM取巧利用内核提供的各种驱动,在OS kernel的基础上成为hypervisor,在hypervisor之上跑的是虚拟机(实际上是进程),用ps也能看到,内核自身管理硬件,在内核之上还要提供OS用来管理虚拟机,在硬件之上的 host OS可启动额外的进程(虚拟机),所有的虚拟机都表现为进程,在guest mode(来宾模式)下有user space和kernel space)
kvm(结构简单,分两部分(设备驱动/dev/kvm;针对模拟pc硬件的用户空间组件);
注:百科上的kvm:KVM 是 kernel-based Virtual Machine 的简称,是一个开源的系统虚拟化模块,自Linux2.6.20之后集成在Linux的各个主要发行版本中。它使用Linux自身的调度器进行管理,所以相对于Xen,其核心源码很少。KVM已成为学术界的主流VMM之一。KVM的虚拟化需要硬件支持(如Intel VT技术或者AMD V技术)。是基于硬件的完全虚拟化。而Xen早期则是基于软件模拟的Para-Virtualization,新版本则是基于硬件支持的完全虚拟化。但Xen本身有自己到进程调度器,存储管理模块等,所以代码较为庞大。广为流传的商业系统虚拟化软件VMware ESX系列也是基于软件模拟的Para-Virtualization。
KVM (全称是 Kernel-based Virtual Machine) 是 Linux 下 x86 硬件平台上的全功能虚拟化解决方案,包含一个可加载的内核模块 kvm.ko 提供和虚拟化核心架构和处理器规范模块。
使用 KVM ,可允许运行多个虚拟机,包括 Linux 和 Windows操作系统。每个虚拟机有私有的硬件,包括网卡、磁盘以及图形适配卡等。
KVM如何使用硬件(kernel将CPU时间片分给虚拟机;memory,kernel虚拟化一部分即可;iodevice,管理的OS模拟硬件,虚拟机用网卡时,虚拟机的kernel-->管理的OS模拟的硬件-->真正的kernel-->硬件(类似Xen);模拟硬件借助Qemu,它可虚拟化任何硬件,乍看KVM是多余的,没有KVM,Qemu照样可虚拟化,KVM有Qemu没有的优势,Qemu对CPU的虚拟是在user space通过软件模拟加速实现的,性能再好也无法与kernel性能相比,而KVM是内核模块比Qemu模拟出的硬件性能要好,更能接近硬件性能)
通常使用KVM+Qemu,KVM要求只能装在支持硬件虚拟化的CPU上,而且只能在X86_64平台(Xen若硬件不支持虚拟化可半虚拟化);KVM在2.6.20后直接整合进kernel上,Xen没有;2.6.37以后Xen也加入kernel(注意是运行在Xen上的DomU而非Dom0);3.0以后的kernel运行在Dom0上的Xen也收入内核(也就是3.0以后的kernel可直接使用Xen,3.0之前的kernel要使用Xen得打补丁);redhat2008年收购了KVM(以色列公司的KVM),redhat6.0之后只支持KVM;Xen比KVM强大、稳定,Xen(英国剑桥大学)被Citrix思杰(仅次于vmware第二大虚拟化提供商)收购
redhat(KVM)、citrix(Xen)、vmware(vmware)、microsoft(hyper-V)
KVM(redhat引入virtio(将IO实现PV),支持passthroughI/O)
container(在kernel之上提供了userspace(有对网卡、硬盘的配置程序,可理解为是VM),kernel是公共的,性能比FV和PV要好,对于FV和PV要运行两个kernel,若任何一个VM管理不慎将kernel搞崩溃了,其它VM将不能正常运行,VM间隔离效果没FV和PV好)
openVZ(Linux上的container技术,很多IDC提供VPS(virtualprivate server)时使用openVZ或Xen)
wine(虚拟出win的库,这样win的所有程序都能运行,cywin在win下虚拟linux的库运行linux程序)
注:只要底层有真正硬件,所有硬件都能模拟,Qemu还可跨平台模拟
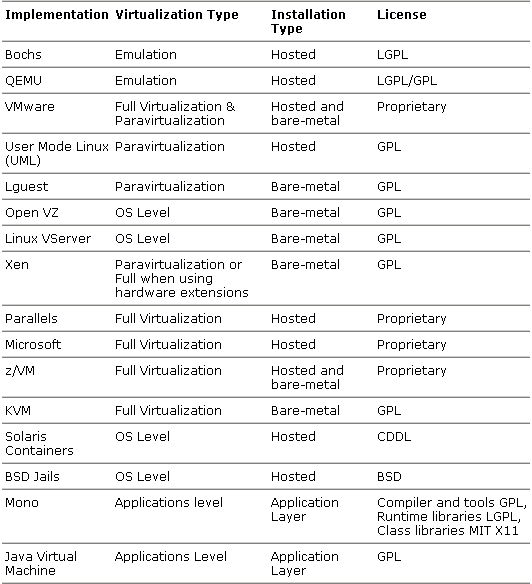
常见的虚拟化技术(virtualization products at a glance):
X86平台虚拟化技术(Intel:VT-x、EPT、IOMMU)
虚拟化中的网络模型(如vmware下的NAT、host-only、bridge、vmnet{1,2,3},NAT模型下可自动分配IP):
可理解为VMM用软件模拟了一个switch,创建的虚拟机VM1只要关联到虚拟网络上,就意味着关联到虚拟的switch上,这个虚拟的switch是连到host OS的虚拟网卡上的(网上邻居可看到vmnet1);host-only,VM1通过虚拟网卡可与物理机通信,不能同外部网络通信,若在物理机上有一dhcp服务指定在物理网卡上,switch不隔离广播报文,那VM{1,2,3}均可获取到地址;虚拟通道是专用网络,如vmnet2是仅模拟了一个switch,物理机上没有对应的虚拟网卡,仅能让在此虚拟通道上的VM{1,2,3}通信;NAT模型下VM{1,2,3}可访问外网,而外网主机不能主动访问VM{1,2,3}除非做DNAT规则要定义在物理主机上(win下的vmware会自动生成规则,而linux下要自己写规则);bridge模型下可理解为物理网卡成为了模拟的switch,所有的报文都通过switch出去,对于发来的报文switch会全部接收下来,再根据MAC判断是哪个网卡上的,是物理网卡还是VM{1,2,3}的网卡,桥接时是不提供dhcp服务的
虚拟机多时,彼此间通信要统一管理会比较麻烦,openstack和cloudstack提供了一种平台,能让物理机随时能加进来,如当前的物理机不够用再加几台进来,正在运行的虚拟机流动的在不同的物理机上运行(实时迁移),某一物理机出问题,其上的虚拟机会迁移到其它物理机上运行,不影响虚拟机的使用,云还能管理网络,虚拟机加进来后要给这个虚拟机分配IP,如何与其它公司的虚拟机隔离,云还要提供存储,云为虚拟机更方便的使用提供了统一管理的接口(IaaS基础架构即服务)
raw格式(优点:寻址简单,访问效率较高,可通过格式转换工具方便的转换为其它格式,可方便的被宿主机挂载,可在不启动VM的情况下和宿主机进行数据传输;缺点:实现简单,不支持压缩、快照、加密、cow等特性,raw格式文件在创建时指定大小之后就占用了宿主机指定大小的空间,而qcow2等稀疏模式的镜像格式可从很小的文件按需增长);
qcow2格式(是qcow的改进,建议使用,是qemu实现的一种VM镜像格式,qcow2文件存储数据的基本单元是cluster,每一个cluster由若干个数据扇区组成,每个数据扇区的大小是512byte,在qcow2中,要定位镜像文件的cluster,需要经过两次地址查询操作,类似于主存二级页表转换机制;更小的存储空间,即使不支持holes FS也可,使用du -h和ll看到的一模一样;copy on write support,where the image only represents changes madeto an underlying disk image,此特性在SUN ZFS表现的淋漓尽致;支持多个snapshot;支持zlib磁盘压缩;支持AES加密
[[email protected] ~]# virsh -h #(management user interface,The virsh program is the main interface for managing virsh guest domains. The program can be used to create,pause, and shutdown domains. It canalso be used to list current domains.)
virsh [options]... [<command_string>]
virsh [options]... <command>[args...]
options:
-c | --connect=URI hypervisorconnection URI
-r | --readonly connectreadonly
-d | --debug=NUM debuglevel [0-4]
-h | --help this help
-q | --quiet quiet mode
-t | --timing printtiming information
-l | --log=FILE outputlogging to file
-v shortversion
-V longversion
--version[=TYPE] version, TYPEis short or long (default short)
-e | --escape <char> setescape sequence for console
commands (non interactive mode):
Domain Management
attach-device attach device from an XML file
attach-disk attach disk device
attach-interface attach network interface
autostart autostart a domain
blkdeviotune Setor query a block device I/O tuning parameters.
blkiotune Getor set blkio parameters
blockcommit Start a block commit operation.
blockcopy Start a block copy operation.
blockjob Manage active block operations
blockpull Populate a disk from its backing image.
blockresize Resize block device of domain.
change-media Change media of CD or floppy drive
console connect to the guest console
cpu-baseline compute baseline CPU
cpu-compare compare host CPU with a CPU described by an XML file
cpu-stats show domain cpu statistics
create create a domain from an XML file
define define (but don‘tstart) a domain from an XML file
desc show or set domain‘s description or title
destroy destroy (stop) a domain
detach-device detach device from an XML file
detach-disk detach disk device
detach-interface detach network interface
domdisplay domain display connection URI
domhostname print the domain‘s hostname
domid convert a domain name or UUID to domain id
domif-setlink setlink state of a virtual interface
domiftune get/set parameters of a virtual interface
domjobabort abort active domain job
domjobinfo domain job information
domname convert a domain id or UUID to domain name
dompmsuspend suspend a domain gracefully using power management functions
dompmwakeup wakeup a domain from pmsuspended state
domuuid convert a domain name or id to domain UUID
domxml-from-native Convert native config to domain XML
domxml-to-native Convert domain XML to native config
dump dump the core of a domain to a file for analysis
dumpxml domain information inXML
edit edit XML configuration for a domain
inject-nmi Inject NMI to the guest
send-key Send keycodes to the guest
managedsave managed save of a domain state
managedsave-remove Remove managed save of a domain
maxvcpus connection vcpu maximum
memtune Getor set memory parameters
migrate migrate domain to another host
migrate-setmaxdowntime setmaximum tolerable downtime
migrate-setspeed Setthe maximum migration bandwidth
migrate-getspeed Getthe maximum migration bandwidth
numatune Getor set numa parameters
reboot reboot a domain
reset reset a domain
restore restore a domain from a saved state in a file
resume resume a domain
save save a domain stateto a file
save-image-define redefine the XML for a domain‘s saved state file
save-image-dumpxml saved state domain information in XML
save-image-edit edit XML for a domain‘s saved state file
schedinfo show/set scheduler parameters
screenshot take a screenshot of a current domain console and store it into a file
setmaxmem change maximum memory limit
setmem change memory allocation
setvcpus change number of virtual CPUs
shutdown gracefully shutdown adomain
start start a (previously defined)inactive domain
suspend suspend a domain
ttyconsole ttyconsole
undefine undefine a domain
update-device update device from an XML file
vcpucount domain vcpu counts
vcpuinfo detailed domain vcpu information
vcpupin control or query domain vcpu affinity
emulatorpin control or query domain emulator affinity
vncdisplay vncdisplay
Domain Monitoring
domblkerror Show errors on block devices
domblkinfo domain block device size information
domblklist list all domain blocks
domblkstat getdevice block stats for a domain
domcontrol domain control interface state
domif-getlink getlink state of a virtual interface
domiflist list all domain virtual interfaces
domifstat getnetwork interface stats for a domain
dominfo domain information
dommemstat getmemory statistics for a domain
domstate domain state
list list domains
Host and Hypervisor
Interface
iface-bridge create a bridge device andattach an existing network device to it
iface-unbridge undefine a bridge device afterdetaching its slave device
Network Filter
Networking
Node Device
Secret
Snapshot
snapshot-create Create a snapshot from XML
snapshot-create-as Create a snapshot from a set of args
snapshot-current Getor set the current snapshot
snapshot-delete Delete a domain snapshot
snapshot-dumpxml Dump XML for a domain snapshot
snapshot-edit edit XML for a snapshot
snapshot-info snapshot information
snapshot-list List snapshots for a domain
snapshot-parent Getthe name of the parent of a snapshot
snapshot-revert Revert a domain to a snapshot
Storage Pool
Storage Volume
Virsh itself
cd change the current directory
connect (re)connect to hypervisor
echo echo arguments
exit quit this interactive terminal
help print help
pwd print the current directory
quit quit this interactive terminal
[[email protected] ~]# qemu-img -h
qemu-img version 0.12.1, Copyright (c) 2004-2008Fabrice Bellard
usage: qemu-img command [command options]
QEMU disk image utility
Command syntax:
check [-f fmt] [--output=ofmt] [-r [leaks |all]] [-T src_cache] filename
create [-f fmt] [-o options] filename [size]
commit [-f fmt] [-t cache] filename
compare [-f fmt] [-F fmt] [-T src_cache] [-p] [-s] filename1 filename2
convert [-c] [-p] [-f fmt] [-t cache] [-Tsrc_cache] [-O output_fmt] [-o options] [-S sparse_size] filename [filename2[...]] output_filename
info [-f fmt] [--output=ofmt] filename
map[-f fmt] [--output=ofmt] filename
snapshot [-l | -a snapshot | -c snapshot | -dsnapshot] filename
rebase [-f fmt] [-t cache] [-T src_cache] [-p] [-u] -b backing_file [-Fbacking_fmt] filename
resize filename [+ | -]size
Command parameters:
‘filename‘ is a disk image filename
‘fmt‘ is the disk image format. It is guessed automatically in mostcases
‘cache‘ is the cache mode used to write the output disk image, the valid
options are: ‘none‘, ‘writeback‘ (default), ‘writethrough‘, ‘directsync‘
and ‘unsafe‘
‘size‘ is the disk image size in bytes. Optional suffixes
‘k‘ or ‘K‘ (kilobyte, 1024), ‘M‘ (megabyte, 1024k), ‘G‘ (gigabyte,1024M)
and T (terabyte, 1024G) are supported. ‘b‘ is ignored.
‘output_filename‘ is the destination disk image filename
‘output_fmt‘ is the destination format
‘options‘ is a comma separated list of format specific options in a
name=value format. Use -o ? for an overview of the options supported bythe
used format
‘-c‘ indicates that target image must be compressed (qcow format only)
‘-u‘ enables unsafe rebasing. It is assumed that old and new backingfile
match exactly. The image doesn‘t need a working backing file before
rebasing in this case (useful for renaming the backing file)
‘-h‘ with or without a command shows this help and lists the supportedformats
‘-p‘ show progress of command (only certain commands)
‘-S‘ indicates the consecutive number of bytes that must contain onlyzeros
for qemu-img to create a sparse image during conversion
‘--output‘ takes the format in which the output must be done (human orjson)
Parameters to checksubcommand:
‘-r‘ tries to repair any inconsistencies that are found during thecheck.
‘-r leaks‘ repairs only cluster leaks, whereas ‘-r all‘ fixes all
kinds of errors, with a higher risk of choosing the wrong fix or
hiding corruption that has already occurred.
Parameters to snapshotsubcommand:
‘snapshot‘ is the name of the snapshot to create, apply or delete
‘-a‘ applies a snapshot (revert disk to saved state)
‘-c‘ creates a snapshot
‘-d‘ deletes a snapshot
‘-l‘ lists all snapshots in the given image
Parameters to compare subcommand:
‘-f‘ first image format
‘-F‘ second image format
‘-s‘ run in Strict mode - fail on different image size or sectorallocation
Supported formats: raw cow qcow vdi vmdkcloop dmg bochs vpc vvfat qcow2 qed vhdx parallels nbd blkdebug null host_cdromhost_floppy host_device file gluster
[[email protected] ~]# qemu-kvm -h
QEMU PC emulator version 0.12.1(qemu-kvm-0.12.1.2-2.491.el6_8.3), Copyright (c) 2003-2008
usage: qemu [options] [disk_image]
‘disk_image‘ is a raw hard image image forIDE hard disk 0
Standard options:
-h or -help display this help and exit
-version display version information and exit
-M machine select emulated machine (-M ? for list)
-cpu cpu select CPU (-cpu ? for list)
-smp n[,maxcpus=cpus][,cores=cores][,threads=threads][,sockets=sockets]
set the number of CPUs to ‘n‘[default=1]
maxcpus= maximum number oftotal cpus, including
offline CPUs for hotplug etc.
cores= number of CPU cores onone socket
threads= number of threads onone CPU core
sockets= number of discretesockets in the system
-numa node[,mem=size][,cpus=cpu[-cpu]][,nodeid=node]
-fda/-fdb file use ‘file‘ as floppy disk 0/1 image
-hda/-hdb file use ‘file‘ as IDE hard disk 0/1 image
-hdc/-hdd file use ‘file‘ as IDE hard disk 2/3 image
-cdrom file use ‘file‘ as IDE cdrom image (cdrom iside1 master)
-drive [file=file][,if=type][,bus=n][,unit=m][,media=d][,index=i]
[,cyls=c,heads=h,secs=s[,trans=t]][,snapshot=on|off]
[,cache=writethrough|writeback|none|directsync|unsafe][,format=f]
[,serial=s][,addr=A][,id=name][,aio=threads|native]
[,readonly=on|off][,copy-on-read=on|off]
use ‘file‘ as a drive image
-set group.id.arg=value
set <arg> parameter foritem <id> of type <group>
i.e. -setdrive.$id.file=/path/to/image
-global driver.prop=value
set a global default for adriver property
-mtdblock file use ‘file‘ as on-board Flash memory image
-sd file use ‘file‘ as SecureDigital card image
-pflash file use ‘file‘ as a parallel flash image
-boot [order=drives][,once=drives][,menu=on|off]
[,reboot-timeout=rb_time][,strict=on|off]
‘drives‘: floppy (a), hard disk(c), CD-ROM (d), network (n)
‘rb_timeout‘: the timeoutbefore guest reboot when boot failed, unit is ms
-snapshot write to temporary filesinstead of disk image files
-m megs set virtual RAM sizeto megs MB [default=128]
-redhat-disable-KSM disable KSM on guest physical memory
-k language use keyboard layout (for example ‘fr‘ forFrench)
-audio-help print list of audio drivers andtheir options
-soundhw c1,... enable audio support
and only specified sound cards(comma separated list)
use -soundhw ? to get the listof supported cards
use -soundhw all to enable allof them
-usb enable the USB driver (will be thedefault soon)
-usbdevice name add the host or guest USB device ‘name‘
-device driver[,prop[=value][,...]]
add device (based on driver)
prop=value,... sets driverproperties
use -device ? to print allpossible drivers
use -device driver,? to printall possible properties
-name string1[,process=string2] set the name of the guest
string1 sets the window title andstring2 the process name (on Linux)
-uuid %08x-%04x-%04x-%04x-%012x
specify machine UUID
Display options:
-nographic disable graphical output and redirectserial I/Os to console
-spice [port=port][,tls-port=secured-port][,x509-dir=<dir>]
[,x509-key-file=<file>][,x509-key-password=<file>]
[,x509-cert-file=<file>][,x509-cacert-file=<file>]
[,x509-dh-key-file=<file>][,addr=addr][,ipv4|ipv6]
[,tls-ciphers=<list>]
[,tls-channel=[main|display|cursor|inputs|record|playback]]
[,plaintext-channel=[main|display|cursor|inputs|record|playback]]
[,sasl][,password=<secret>][,disable-ticketing]
[,image-compression=[auto_glz|auto_lz|quic|glz|lz|off]]
[,jpeg-wan-compression=[auto|never|always]]
[,zlib-glz-wan-compression=[auto|never|always]]
[,streaming-video=[off|all|filter]][,disable-copy-paste]
[,disable-agent-file-xfer][,agent-mouse=[on|off]]
[,playback-compression=[on|off]][,seamless-migration=[on|off]]
enable spice
atleast one of {port, tls-port} is mandatory
-portrait rotate graphical output 90 deg left(only PXA LCD)
-vga [std|cirrus|vmware|qxl|xenfb|none]
select video card type
-full-screen start in full screen
-vnc display start a VNC server on display
i386 target only:
-win2k-hack use it when installing Windows 2000 toavoid a disk full bug
-no-fd-bootchk disable boot signature checking for floppydisks
-no-acpi disable ACPI
-balloon none disable balloon device
-balloon virtio[,addr=str]
enable virtio balloon device(default)
-acpitable[sig=str][,rev=n][,oem_id=str][,oem_table_id=str][,oem_rev=n][,asl_compiler_id=str][,asl_compiler_rev=n][,data=file1[:file2]...]
ACPI table description
-smbios file=binary
Load SMBIOS entry from binaryfile
-smbiostype=0[,vendor=str][,version=str][,date=str][,release=%d.%d]
Specify SMBIOS type 0 fields
-smbios type=1[,manufacturer=str][,product=str][,version=str][,serial=str]
[,uuid=uuid][,sku=str][,family=str]
Specify SMBIOS type 1 fields
Network options:
-netnic[,vlan=n][,macaddr=mac][,model=type][,name=str][,addr=str][,vectors=v]
create a new Network InterfaceCard and connect it to VLAN ‘n‘
-netuser[,vlan=n][,name=str][,net=addr[/mask]][,host=addr][,restrict=y|n]
[,hostname=host][,dhcpstart=addr][,dns=addr][,tftp=dir][,bootfile=f]
[,hostfwd=rule][,guestfwd=rule][,smb=dir[,smbserver=addr]]
connect the user mode networkstack to VLAN ‘n‘, configure its
DHCP server and enabledoptional services
-nettap[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,ifname=name][,script=file][,downscript=dfile][,sndbuf=nbytes][,vnet_hdr=on|off][,vhost=on|off][,vhostfd=h][,vhostforce=on|off]
connect the host TAP networkinterface to VLAN ‘n‘ and use the
network scripts ‘file‘(default=/etc/qemu-ifup)
and ‘dfile‘(default=/etc/qemu-ifdown);
use ‘[down]script=no‘ todisable script execution;
use ‘fd=h‘ to connect to analready opened TAP interface
use ‘sndbuf=nbytes‘ tolimit the size of the send buffer (the
default is disabled ‘sndbuf=0‘to enable flow control set ‘sndbuf=1048576‘)
use vnet_hdr=off to avoidenabling the IFF_VNET_HDR tap flag; use
vnet_hdr=on to make the lack ofIFF_VNET_HDR support an error condition
use vhost=on to enableexperimental in kernel accelerator
(only has effect for virtioguests which use MSIX)
use vhostforce=on to forcevhost on for non-MSIX virtio guests
use ‘vhostfd=h‘ to connect toan already opened vhost net device
-netsocket[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,listen=[host]:port][,connect=host:port]
connect the vlan ‘n‘ to anotherVLAN using a socket connection
-netsocket[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,mcast=maddr:port]
connect the vlan ‘n‘ tomulticast maddr and port
-net dump[,vlan=n][,file=f][,len=n]
dump traffic on vlan ‘n‘ tofile ‘f‘ (max n bytes per packet)
-net none use it alone to have zero networkdevices; if no -net option
is provided, the default is‘-net nic -net user‘
-netdev[user|tap|socket],id=str[,option][,option][,...]
Character device options:
-chardev null,id=id
-chardevsocket,id=id[,host=host],port=host[,to=to][,ipv4][,ipv6][,nodelay]
[,server][,nowait][,telnet] (tcp)
-chardevsocket,id=id,path=path[,server][,nowait][,telnet] (unix)
-chardevudp,id=id[,host=host],port=port[,localaddr=localaddr]
[,localport=localport][,ipv4][,ipv6]
-chardev msmouse,id=id
-chardevvc,id=id[[,width=width][,height=height]][[,cols=cols][,rows=rows]]
-chardev file,id=id,path=path
-chardev pipe,id=id,path=path
-chardev pty,id=id
-chardev stdio,id=id
-chardev serial,id=id,path=path
-chardev tty,id=id,path=path
-chardev parallel,id=id,path=path
-chardev parport,id=id,path=path
-chardevspicevmc,id=id,debug=debug,name=name
Bluetooth(R) options:
-bt hci,null dumb bluetooth HCI - doesn‘t respond tocommands
-bt hci,host[:id]
use host‘s HCI with the givenname
-bt hci[,vlan=n]
emulate a standard HCI invirtual scatternet ‘n‘
-bt vhci[,vlan=n]
add host computer to virtualscatternet ‘n‘ using VHCI
-bt device:dev[,vlan=n]
emulate a bluetooth device‘dev‘ in scatternet ‘n‘
Linux/Multiboot boot specific:
-kernel bzImage use ‘bzImage‘ as kernelimage
-append cmdline use ‘cmdline‘ as kernelcommand line
-initrd file use ‘file‘ as initial ram disk
Debug/Expert options:
-serial dev redirect the serial port to char device‘dev‘
-parallel dev redirect the parallel port to char device‘dev‘
-monitor dev redirect the monitor to char device ‘dev‘
-qmp dev like -monitor but opens in ‘control‘mode.
-monchardev=[name][,mode=readline|control][,default]
-debugcon dev redirect the debug console to char device‘dev‘
-pidfile file write PID to ‘file‘
-singlestep always run in singlestep mode
-S freeze CPU at startup (use ‘c‘ tostart execution)
-realtime [mlock=on|off]
run qemu with realtime features
mlock=on|off controls mlocksupport (default: on)
-gdb dev wait for gdb connection on ‘dev‘
-s shorthand for -gdb tcp::1234
-d item1,... output log to /tmp/qemu.log (use -d ? for alist of log items)
-hdachs c,h,s[,t]
force hard disk 0 physicalgeometry and the optional BIOS
translation (t=none or lba)(usually qemu can guess them)
-L path set the directory for the BIOS, VGABIOS and keymaps
-bios file set the filename for the BIOS
-enable-kvm enable KVM full virtualization support
-machine [type=]name[,prop[=value][,...]]
selects emulated machine(-machine ? for list)
propertyaccel=accel1[:accel2[:...]] selects accelerator
supported accelerators are kvm,tcg (default: kvm:tcg)
dump-guest-core=on|off includeguest memory in a core dump (default=on)
-no-reboot exit instead of rebooting
-no-shutdown stop before shutdown
-loadvm [tag|id]
start right away with a savedstate (loadvm in monitor)
-daemonize daemonize QEMU after initializing
-option-rom rom load a file, rom, into theoption ROM space
-clock force the use of the given methodsfor timer alarm.
To see what timers areavailable use -clock ?
-rtc[base=utc|localtime|date][,clock=host|vm][,driftfix=none|slew]
set the RTC base and clock,enable drift fix for clock ticks
-icount [N|auto]
enable virtual instructioncounter with 2^N clock ticks per
instruction
-watchdog i6300esb|ib700
enable virtual hardwarewatchdog [default=none]
-watchdog-actionreset|shutdown|poweroff|pause|debug|none
action when watchdog fires[default=reset]
-echr chr set terminal escape character instead ofctrl-a
-virtioconsole c
set virtio console
-show-cursor show cursor
-tb-size n set TB size
-incoming p prepare for incoming migration, listen onport p
-nodefaults don‘t create default devices.
-chroot dir Chroot to dir just before starting the VM.
-runas user Change to user id user just before startingthe VM.
-nodefconfig
do not load default configfiles at startup
-readconfig <file>
-writeconfig <file>
read/write config file
-no-kvm disable KVM hardware virtualization
-no-kvm-irqchip disable KVM kernel modePIC/IOAPIC/LAPIC
-no-kvm-pit disable KVM kernel mode PIT
-no-kvm-pit-reinjection disable KVM kernelmode PIT interrupt reinjection
-pcidevicehost=[seg:]bus:dev.func[,dma=none][,name=string]
expose a PCI device to theguest OS.
dma=none: don‘t perform any dmatranslations (default is to use an iommu)
‘string‘ is used in log output.
-nvram FILE provide ia64 nvram contents
-tdf enable guest time driftcompensation
-kvm-shadow-memory MEGABYTES
allocate MEGABYTES for kvmmmu shadowing
-mem-path FILE provide backing storage for guest RAM
-mem-prealloc preallocate guest memory (use with-mempath)
-msg timestamp[=on|off]
change the format of messages
on|off controls leadingtimestamps (default:on)
-object TYPENAME[,PROP1=VALUE1,...]
create an new object of typeTYPENAME setting properties
in the order they arespecified. Note that the ‘id‘
property must be set. These objects are placed in the
‘/objects‘ path.
-dump-vmstate <file>
Output vmstate information inJSON format to file.
Use the scripts/vmstate-static-checker.pyfile to
check for possible regressionsin migration code
by comparing two such vmstatedumps.
During emulation, the following keys areuseful:
ctrl-alt-f toggle full screen
ctrl-alt-n switch to virtual console ‘n‘
ctrl-alt toggle mouse and keyboard grab
When using -nographic, press ‘ctrl-a h‘ toget some help.
[[email protected] ~]# virt-install -h
Usage: virt-install --name NAME --ram RAMSTORAGE INSTALL [options]
Options:
--version showprogram‘s version number and exit
-h,--help show this help messageand exit
--connect=URI Connect tohypervisor with libvirt URI
General Options:
-n NAME, --name=NAME
Name of the guestinstance
-r MEMORY, --ram=MEMORY
Memory to allocate forguest instance in megabytes
--vcpus=VCPUS Number of vcpus to configure for your guest. Ex:
--vcpus 5
--vcpus 5,maxcpus=10
--vcpussockets=2,cores=4,threads=2
--cpuset=CPUSET Set whichphysical CPUs domain can use.
--cpu=CPU CPU model andfeatures. Ex: --cpu coreduo,+x2apic
--description=DESCRIPTION
Human readabledescription of the VM to store in the
generated XML.
--security=SECURITY
Set domain securitydriver configuration.
--numatune=NUMATUNE
Tune NUMA policy forthe domain process.
Installation Method Options:
-c CDROM, --cdrom=CDROM
CD-ROM installationmedia
-l LOCATION, --location=LOCATION
Installation source(eg, nfs:host:/path,
http://host/path,ftp://host/path)
--pxe Boot from thenetwork using the PXE protocol
--import Build guestaround an existing disk image
--init=INIT Path to initbinary for container guest. Ex:
--init /path/to/app (tocontain an application)
--init /sbin/init (fora full OS container)
--livecd Treat theCD-ROM media as a Live CD
-x EXTRA, --extra-args=EXTRA
Additional arguments to pass to theinstall kernel
booted from --location
--initrd-inject=INITRD_INJECTIONS
Add given file to rootof initrd from --location
--os-type=DISTRO_TYPE
The OS type beinginstalled, e.g. ‘linux‘, ‘unix‘,
‘windows‘
--os-variant=DISTRO_VARIANT
The OS variant beinginstalled guests, e.g. ‘fedora6‘,
‘rhel5‘, ‘solaris10‘,‘win2k‘
--boot=BOOTOPTS Optionallyconfigure post-install boot order, menu,
permanent kernel boot,etc.
Storage Configuration:
--disk=DISKOPTS Specify storage with various options. Ex.
--disk path=/my/existing/disk
--diskpath=/my/new/disk,size=5 (in gigabytes)
--disk vol=poolname:volname,device=cdrom,bus=scsi,...
--nodisks Don‘t set upany disks for the guest.
--filesystem=FILESYSTEMS
Pass host directory tothe guest. Ex:
--filesystem/my/source/dir,/dir/in/guest
--filesystemtemplate_name,/,type=template
Networking Configuration:
-w NETWORK, --network=NETWORK
Configure a guestnetwork interface. Ex:
--network bridge=mybr0
--network network=my_libvirt_virtual_net
--networknetwork=mynet,model=virtio,mac=00:11...
--nonetworks Don‘t createnetwork interfaces for the guest.
Graphics Configuration:
--graphics=GRAPHICS
Configure guest displaysettings. Ex:
--graphics vnc
--graphicsspice,port=5901,tlsport=5902
--graphics none
--graphics vnc,password=foobar,port=5910,keymap=ja
--noautoconsole Don‘t automatically try to connect to theguest
console
Device Options:
--serial=SERIALS Configure aguest serial device
--parallel=PARALLELS
Configure a guestparallel device
--channel=CHANNELS Configure aguest communication channel
--console=CONSOLES Configure atext console connection between the guest
and host
--host-device=HOSTDEVS
Configure physical hostdevices attached to the guest
--soundhw=SOUNDHW Configureguest sound device emulation
--watchdog=WATCHDOG
Configure a guestwatchdog device
--video=VIDEO Configureguest video hardware.
--smartcard=SMARTCARD
Configure a guestsmartcard device. Ex:
--smartcardmode=passthrough
--redirdev=REDIRDEV
Configure a guestredirection device. Ex:
--redirdevusb,type=tcp,server=192.168.1.1:4000
--panic=PANIC Configure aguest panic device. Ex:
--panic default
Virtualization Platform Options:
-v, --hvm This guestshould be a fully virtualized guest
-p, --paravirt This guestshould be a paravirtualized guest
--container This guestshould be a container guest
--virt-type=HV_TYPE
Hypervisor name to use(kvm, qemu, xen, ...)
--arch=ARCH The CPUarchitecture to simulate
--machine=MACHINE The machinetype to emulate
--noapic Disables APICfor fully virtualized guest (overrides
value inos-type/os-variant db)
--noacpi Disables ACPIfor fully virtualized guest (overrides
value inos-type/os-variant db)
-u UUID, --uuid=UUID
UUID for the guest.
Miscellaneous Options:
--autostart Have domainautostart on host boot up.
--print-xml Print thegenerated domain XML rather than define the
guest.
--print-step=XMLSTEP
Print XML of a specificinstall step (1, 2, 3, all)
rather than define theguest.
--noreboot Don‘t bootguest after completing install.
--wait=WAIT Time to wait(in minutes)
--dry-run Run throughinstall process, but do not create devices
or define the guest.
--force Forces ‘yes‘ for any applicableprompts, terminates
for all others
-q, --quiet Suppressnon-error output
--prompt Request userinput for ambiguous situations or
required options.
-d, --debug Printdebugging information
操作(KVM):
1、准备:
注:kvm仅可在具有虚拟化功能的cpu上运行,intel-vt技术或amd-v技术;内存方面intel的EPT或amd的RVI
[[email protected] ~]# uname -rm
2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64 x86_64
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.5(Santiago)
[[email protected] ~]# egrep --color "vmx|svm" /proc/cpuinfo #(intel-vt关键字用vmx,amd-v关键字svm)
flags :fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflushdts mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tscarch_perfmon pebs bts xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc aperfmperfunfair_spinlock pni pclmulqdq vmx ssse3 fma cx16pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16crdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm ida arat xsaveopt pln pts dts tpr_shadow vnmi eptvpid fsgsbase bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid
flags :fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflushdts mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tscarch_perfmon pebs bts xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc aperfmperfunfair_spinlock pni pclmulqdq vmx ssse3 fma cx16pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16crdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm ida arat xsaveopt pln pts dts tpr_shadow vnmi eptvpid fsgsbase bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid
flags :fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflushdts mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tscarch_perfmon pebs bts xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc aperfmperfunfair_spinlock pni pclmulqdq vmx ssse3 fma cx16pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16crdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm ida arat xsaveopt pln pts dts tpr_shadow vnmi eptvpid fsgsbase bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid
flags :fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflushdts mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tscarch_perfmon pebs bts xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc aperfmperfunfair_spinlock pni pclmulqdq vmx ssse3 fma cx16pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16crdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm ida arat xsaveopt pln pts dts tpr_shadow vnmi eptvpid fsgsbase bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid
[[email protected] ~]# lsmod | grep kvm
[[email protected] ~]# modprobe kvm #(启用kvm模块)
[[email protected] ~]# modprobe kvm-intel #(是intel加载kvm-intel,是amd加载kvm-amd)
[[email protected] ~]# lsmod | grep kvm
kvm_intel 54285 0
kvm 333172 1 kvm_intel
2、部署kvm环境:
[[email protected] ~]# llepel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 14540 Nov 5 2012epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[[email protected] ~]# rpm -ivhepel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm #(利用epel的yum源安装相关软件包)
[[email protected] ~]# yum -y install libvirt qemu-kvm virt-manager #(KVM 虚拟机的创建依赖qemu-kvm :虽然 kvm 的技术已经相当成熟而且可以对很多东西进行隔离,但是在某些方面还是无法虚拟出真实的机器,比如对网卡的虚拟,那这个时候就需要另外的技术来做补充,而qemu-kvm则是这样一种技术,它补充了 kvm 技术的不足,而且在性能上对 kvm 进行了优化。还可用 virt-manager,virt-viewer 来管理虚拟机;在创建和管理 KVM 虚拟机时还需要 libvirt 这个重要的组件:它是一系列提供出来的库函数,用以其他技术调用,来管理机器上的虚拟机。包括各种虚拟机技术, kvm 、 xen 与 lxc 等,都可以调用 libvirt 提供的 api 对虚拟机进行管理。有这么多的虚拟机技术,它为何能提供这么多的管理功能那。是因为它的设计理念,它是面向驱动的架构设计。对任何一种虚拟机技术都开发设计相对于该技术的驱动。这样不同虚拟机技术就可以使用不同驱动,而且相互直接不会影响,方便扩展。而且 libvirt 提供了多种语言的编程接口,可以直接通过编程,调用 libvirt 提供的对外接口实现对虚拟机的操作。如今流行的云计算中的 IaaS 是与该库联系相当密切的)
Installed:
libvirt.x86_64 0:0.10.2-60.el6 qemu-kvm.x86_64 2:0.12.1.2-2.491.el6_8.3 virt-manager.x86_64 0:0.9.0-31.el6
Dependency Installed:
……
注:libvirt的架构设计思想,在 libvirtapi 之上会有很多个 driver ,对于每一种虚拟机技术都会有一种 driver ,用来充当该虚拟机技术与 libvirt 之间的包装接口。如此设计就可以避免 libvirt 需要设计各种针对不同虚拟机技术的接口,它主要关注底层的实现,提供对外接口调用,而不同的虚拟机技术通过调用 libvirt 提供的接口来完成自己所需要的功能。
[[email protected] ~]# service libvirtd start
Starting libvirtd daemon: libvirtd:relocation error: libvirtd: symbol dm_task_get_info_with_deferred_remove,version Base not defined in file libdevmapper.so.1.02 with link time reference
[FAILED]
[[email protected] ~]# yum-y install device-mapper
[[email protected] ~]# service libvirtd start
Starting libvirtd daemon: [ OK ]
[[email protected] ~]# ifconfig #(libvirtd启动后,会自动创建一个桥设备,相当于vmware中host-only网络设备)
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr00:0C:29:1F:B6:AC
inet addr:10.96.20.113 Bcast:10.96.20.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe1f:b6ac/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:49554 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:16997 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:47453022 (45.2 MiB) TXbytes:1472183 (1.4 MiB)
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr00:0C:29:1F:B6:B6
inet addr:192.168.10.113 Bcast:192.168.10.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe1f:b6b6/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:16561 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:10 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:1380247 (1.3 MiB) TXbytes:636 (636.0 b)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:390 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:390 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:26626 (26.0 KiB) TXbytes:26626 (26.0 KiB)
virbr0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 52:54:00:A4:A9:C5
inet addr:192.168.122.1 Bcast:192.168.122.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:0(0.0 b)
[[email protected] ~]# brctl show #(使用网桥管理命令查看)
bridge name bridgeid STP enabled interfaces
virbr0 8000.525400a4a9c5 yes virbr0-nic
[[email protected] ~]# rpm -ql qemu-kvm
/etc/ksmtuned.conf
/etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-kvm.conf
/etc/rc.d/init.d/ksm
/etc/rc.d/init.d/ksmtuned
/etc/sasl2/qemu-kvm.conf
/etc/sysconfig/ksm
/etc/sysconfig/modules/kvm.modules
/etc/udev/rules.d/80-kvm.rules
/usr/libexec/qemu-kvm
/usr/sbin/ksmtuned
……
[[email protected] ~]# ln -sv /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm /usr/bin/qemu-kvm
`/usr/bin/qemu-kvm‘ ->`/usr/libexec/qemu-kvm‘
[[email protected] ~]# ll /etc/sysconfig/modules/kvm.modules
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 245 Aug 9 10:55 /etc/sysconfig/modules/kvm.modules
[[email protected] ~]# service NetworkManager stop
Stopping NetworkManager daemon: [ OK ]
[[email protected] ~]# chkconfig NetworkManageroff
[[email protected] ~]# virsh iface-bridge eth0 br0 #(使用virsh创建桥设备,关联网卡到桥设备上,类似vmware中创建的物理桥接设备;语法virsh iface-bridge interfacebridge [--no-stp] [delay] [--no-start];virsh iface-unbridgebridge [--no-start])
Created bridge br0 with attached deviceeth0
Bridge interface br0 started
[[email protected] ~]# ifconfig
br0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr00:0C:29:1F:B6:AC
inet addr:10.96.20.113 Bcast:10.96.20.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe1f:b6ac/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:758 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:29 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:55900 (54.5 KiB) TXbytes:2250 (2.1 KiB)
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr00:0C:29:1F:B6:AC
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:54072 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:17300 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:47983909 (45.7 MiB) TXbytes:1514563 (1.4 MiB)
……
[[email protected] ~]# brctl show
bridge name bridgeid STP enabled interfaces
br0 8000.000c291fb6ac yes eth0
virbr0 8000.525400a4a9c5 yes virbr0-nic
[[email protected] ~]# yum -y install tigervnc tigervnc-server #(安装vncviewer)
[[email protected] ~]# rpm -ql tigervnc-server
/etc/rc.d/init.d/vncserver
/etc/sysconfig/vncservers
/usr/bin/Xvnc
/usr/bin/vncconfig
/usr/bin/vncpasswd
/usr/bin/vncserver
/usr/bin/x0vncserver
……
[[email protected] ~]# vncpasswd
Password:
Verify:
[[email protected] ~]# vncserver #(启动vncserver)
New ‘master:1 (root)‘ desktop is master:1
Creating default startup script/root/.vnc/xstartup
Starting applications specified in/root/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /root/.vnc/master:1.log
[[email protected] ~]# vncserver -list
TigerVNC server sessions:
X DISPLAY # PROCESSID
:1 6469
3、在kvm上部署guest os:
方式一(使用qemu-kvm):
[[email protected] ~]# mkdir -pv /kvm/images
mkdir: created directory `/kvm‘
mkdir: created directory `/kvm/images‘
[[email protected] ~]# qemu-img create -f raw /kvm/images/test.raw 5G
Formatting ‘/kvm/images/test.raw‘, fmt=rawsize=5368709120
[[email protected] ~]# ll -h /kvm/images/test.raw
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5.0G Sep 5 18:46 /kvm/images/test.raw
[[email protected] ~]# dd if=/dev/cdrom1 of=/kvm/images/rhel6.iso #(制作安装guest os的光盘镜像)
7526400+0 records in
7526400+0 records out
3853516800 bytes (3.9 GB) copied, 385.314s, 10.0 MB/s
[[email protected] ~]# qemu-kvm -cpu host -smp 1 -m 512 -drive file=/kvm/images/test.raw,if=ide,media=disk,format=raw -drive file=/kvm/images/rhel6.iso,media=cdrom -boot dc -usbdevice tablet #(此命令是在前台运行,占据当前终端,默认位置在/usr/libexec/qemu-kvm已将其链接至/usr/bin/qemu-kvm)
VNC server running on `::1:5900‘
[[email protected] ~]# vncviewer :5900 #(开启另一窗口进入guestos,在前台运行占据当前终端窗口)
TigerVNC Viewer for X version 1.1.0 - builtMay 11 2016 13:00:50
Copyright (C) 1999-2011 TigerVNC Team andmany others (see README.txt)
See http://www.tigervnc.org for informationon TigerVNC.
Mon Sep 5 19:07:08 2016
CConn: connected to host localhost port 5900
CConnection: Server supports RFB protocolversion 3.8
CConnection: Using RFB protocol version 3.8
TXImage: Using default colormap and visual, TrueColor, depth 24.
CConn: Using pixel format depth 24 (32bpp) little-endian rgb888
CConn: Using Tight encoding
[[email protected] ~]# qemu-img info /kvm/images/test.raw
image: /kvm/images/test.raw
file format: raw
virtual size: 5.0G (5368709120 bytes)
disk size: 1.5G
方式二(使用virt-install):
[[email protected] ~]# qemu-img create -f qcow2 /kvm/images/test2.qcow2 5G
Formatting ‘/kvm/images/test2.qcow2‘,fmt=qcow2 size=5368709120 encryption=off cluster_size=65536
[[email protected] ~]# qemu-img info /kvm/images/test2.qcow2
image: /kvm/images/test2.qcow2
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 5.0G (5368709120 bytes)
disk size: 196K
cluster_size: 65536
[[email protected] ~]# qemu-img check /kvm/images/test2.qcow2
No errors were found on the image.
Image end offset: 262144
[[email protected] ~]# ll -h /kvm/images/
total 5.1G
-rw-r--r--. 1 qemu qemu 3.6G Sep 5 03:20 rhel6.iso
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root193K Sep 5 19:32 test2.qcow2
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5.0G Sep 5 19:30 test.raw
[[email protected] ~]# virt-install --name=test2 --ram=512 --vcpus=1 --os-variant=rhel6 --disk path=/kvm/images/test2.qcow2,format=qcow2,size=5,bus=virtio --accelerate --cdrom=/kvm/images/rhel6.iso --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0,port=5911 --network bridge=br0,model=virtio --noautoconsole #(使用qcow2镜像格式,创建guestos时必须要在此处指定其格式和使用virtio驱动,否则系统无法正常安装,会提示virtio block device为0M)
Starting install...
Creating domain... | 0 B 00:00
Domain installation still in progress. You can reconnect to
the console to complete the installationprocess.
[[email protected] ~]# ps aux | grep kvm
root 903 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:58 0:00 [kvm-irqfd-clean]
qemu 9804 0.5 32.0 1370892 321788? Sl 21:20 0:24 /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm -name test2 -S -M rhel6.6.0 -enable-kvm -m512 -realtime mlock=off -smp 1,sockets=1,cores=1,threads=1 -uuid5b4b8e46-3036-31a6-5670-77370675a550 -nodefconfig -nodefaults -chardevsocket,id=charmonitor,path=/var/lib/libvirt/qemu/test2.monitor,server,nowait-mon chardev=charmonitor,id=monitor,mode=control -rtc base=utc -no-shutdown-device ich9-usb-ehci1,id=usb,bus=pci.0,addr=0x4.0x7 -deviceich9-usb-uhci1,masterbus=usb.0,firstport=0,bus=pci.0,multifunction=on,addr=0x4-device ich9-usb-uhci2,masterbus=usb.0,firstport=2,bus=pci.0,addr=0x4.0x1-device ich9-usb-uhci3,masterbus=usb.0,firstport=4,bus=pci.0,addr=0x4.0x2-drive file=/kvm/images/test2.qcow2,if=none,id=drive-virtio-disk0,format=qcow2,cache=none-devicevirtio-blk-pci,scsi=off,bus=pci.0,addr=0x5,drive=drive-virtio-disk0,id=virtio-disk0,bootindex=1-drive if=none,media=cdrom,id=drive-ide0-1-0,readonly=on,format=raw -deviceide-drive,bus=ide.1,unit=0,drive=drive-ide0-1-0,id=ide0-1-0 -netdevtap,fd=22,id=hostnet0,vhost=on,vhostfd=23 -devicevirtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,id=net0,mac=52:54:00:7f:03:2f,bus=pci.0,addr=0x3-chardev pty,id=charserial0 -device isa-serial,chardev=charserial0,id=serial0-device usb-tablet,id=input0 -vnc 0.0.0.0:11 -vga cirrus -devicevirtio-balloon-pci,id=balloon0,bus=pci.0,addr=0x6 -msg timestamp=on
root 9827 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 21:20 0:00 [kvm-pit-wq]
root 12075 0.0 0.0 103256 832 pts/1 S+ 22:34 0:00 grep kvm
在win上使用TigerVNC连接
装完系统后会要求重启,此窗口会关闭
[[email protected] ~]# virsh start test2
Domain test2 started
[[email protected] ~]# virsh list #(#virsh list--all可查看所有domain包括关机的)
Id Name State
----------------------------------------------------
6 test2 running
[[email protected] ~]# ls /etc/libvirt
libvirt.conf libvirtd.conf lxc.conf nwfilter qemu qemu.conf
[[email protected] ~]# ll /etc/libvirt/qemu/ #(自动生成test2.xml,此文件很关键记录着VM的所有配置)
total 8
drwx------. 3 root root 4096 Sep 4 23:58 networks
-rw-------. 1 root root3031 Sep 5 20:27 test2.xml
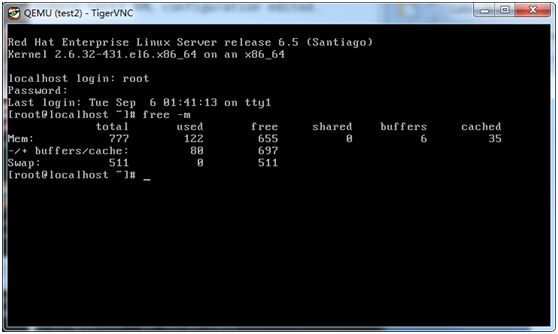
4、更改guest os配置:
注:使用#virsh reboot test2,不能加载新配置,要先用destroy再start
方式一(通过virsh edit DOMAIN直接编辑):
[[email protected] ~]# head -13 /etc/libvirt/qemu/test2.xml
……
<domain type=‘kvm‘>
<name>test2</name>
<uuid>5b4b8e46-3036-31a6-5670-77370675a550</uuid>
<memoryunit=‘KiB‘>524288</memory>
<currentMemoryunit=‘KiB‘>524288</currentMemory>
<vcpu placement=‘static‘>1</vcpu>
[[email protected] ~]# virsh edit test2
<domain type=‘kvm‘>
<name>test2</name>
<uuid>5b4b8e46-3036-31a6-5670-77370675a550</uuid>
<memory unit=‘KiB‘>824288</memory>
<currentMemory unit=‘KiB‘>824288</currentMemory>
[[email protected] ~]# virsh list --all
Id Name State
----------------------------------------------------
6 test2 running
[[email protected]~]# virsh destroy test2
Domain test2 destroyed
[[email protected]~]# virsh list --all
Id Name State
----------------------------------------------------
- test2 shut off
[[email protected] ~]# virsh start test2
Domain test2 started
[[email protected]~]# virsh list
Id Name State
---------------------------------------------------
6 test2 running
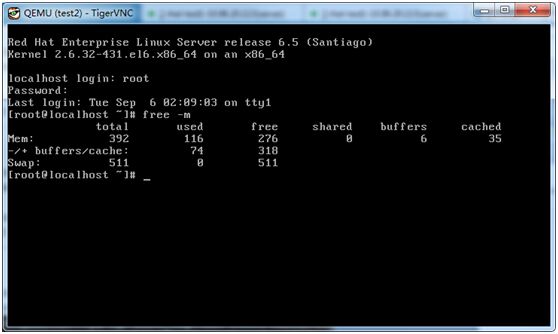
方式二(用dumpxml导出-->通过vim编辑-->用define重新定义domain的xml配置文件):
[[email protected] ~]# virsh dumpxml test2 > test_tmp.xml
[[email protected] ~]# vim test_tmp.xml
<domain type=‘kvm‘ id=‘7‘>
<name>test2</name>
<uuid>5b4b8e46-3036-31a6-5670-77370675a550</uuid>
<memory unit=‘KiB‘>424320</memory>
<currentMemory unit=‘KiB‘>424288</currentMemory>
[[email protected] ~]# cp test_tmp.xml /etc/libvirt/qemu/test2.xml
cp: overwrite`/etc/libvirt/qemu/test2.xml‘? y
[[email protected] ~]# virsh define /etc/libvirt/qemu/test2.xml
Domain test2 defined from/etc/libvirt/qemu/test2.xml
[[email protected] ~]# virsh destroy test2
Domain test2 destroyed
[[email protected] ~]# virsh start test2
Domain test2 started
注:
#qemu-img convert -c -f raw -O qcow2 test.rawtest.qcow2 #(-c,compressed)
#virsh edit test
<disk type=‘file‘ device=‘disk‘>
<driver name=‘qemu‘ type=‘qcow2‘cache=‘none‘/>
<source file=‘/kvm/images/test.qcow2‘/>
<target dev=‘vda‘ bus=‘virtio‘/>
<address type=‘pci‘ domain=‘0x0000‘ bus=‘0x00‘ slot=‘0x05‘function=‘0x0‘/>
</disk>
#virsh start test
本文出自 “Linux运维重难点学习笔记” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://jowin.blog.51cto.com/10090021/1846881
以上是关于VIII virtualization&kvm的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章