HDU 1272 小希的迷宫
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HDU 1272 小希的迷宫相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
小希的迷宫
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 38890 Accepted Submission(s): 11933
Problem Description
上
次Gardon的迷宫城堡小希玩了很久(见Problem
B),现在她也想设计一个迷宫让Gardon来走。但是她设计迷宫的思路不一样,首先她认为所有的通道都应该是双向连通的,就是说如果有一个通道连通了房
间A和B,那么既可以通过它从房间A走到房间B,也可以通过它从房间B走到房间A,为了提高难度,小希希望任意两个房间有且仅有一条路径可以相通(除非走
了回头路)。小希现在把她的设计图给你,让你帮忙判断她的设计图是否符合她的设计思路。比如下面的例子,前两个是符合条件的,但是最后一个却有两种方法从
5到达8。
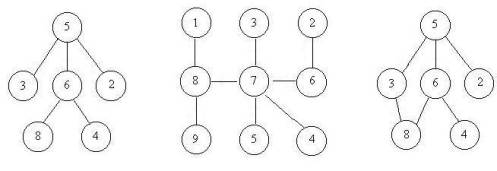

Input
输入包含多组数据,每组数据是一个以0 0结尾的整数对列表,表示了一条通道连接的两个房间的编号。房间的编号至少为1,且不超过100000。每两组数据之间有一个空行。
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
Output
对于输入的每一组数据,输出仅包括一行。如果该迷宫符合小希的思路,那么输出"Yes",否则输出"No"。
Sample Input
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
Sample Output
Yes
Yes
No
Author
Gardon
Source
Recommend
lxj
我的做法是不断把点对加到集合中,在加入之前先判断点对是否属于同一个集合,如果属于同一个集合,那么图就存在回来,图对应的迷宫就不符合小希的思路。
另外还要判断图是否是连通的。
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <queue> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int maxn = 100050; 6 7 int f[maxn]; 8 bool vis[maxn]; 9 typedef pair<int, int> P; 10 vector<P> v; 11 12 int sf(int x){ return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = sf(f[x]); } 13 int main() 14 { 15 int a, b, n = 0; 16 while (scanf("%d%d", &a, &b) == 2 && a != -1 && b != -1) 17 { 18 if (a&&b) 19 { 20 v.push_back(P(a, b)); 21 n = max(a, n); 22 n = max(b, n); 23 } 24 else 25 { 26 bool flag = true; 27 int cnt = 0;//连通 28 if (n == 0) { printf("Yes\n"); continue; } 29 memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); 30 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) f[i] = i; 31 for (vector<P>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 32 { 33 if (!vis[it->first]){ cnt++; vis[it->first] = true; } 34 if (!vis[it->second]){ cnt++; vis[it->second] = true; } 35 int q = sf(it->first); int w = sf(it->second); 36 if (q != w){ cnt--; f[q] = w; } 37 else{ flag = false; break; } 38 } 39 if (flag && cnt==1) printf("Yes\n"); 40 else printf("No\n"); 41 42 //清空和重置 43 v.clear(); 44 n = 0; 45 } 46 } 47 }
以上是关于HDU 1272 小希的迷宫的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章