Spring 源码学习
Posted 可爱的呆子
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring 源码学习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
spring最核心的理念是IOC,包括AOP也要屈居第二,那么IOC到底是什么呢,四个字,控制反转
一、什么是Ioc/DI?
IoC 容器:最主要是完成了完成对象的创建和依赖的管理注入等等。
先从我们自己设计这样一个视角来考虑:
所谓控制反转,就是把原先我们代码里面需要实现的对象创建、依赖的代码,反转给容器来帮忙实现。那么必然的我们需要创建一个容器,同时需要一种描述来让容器知道需要创建的对象与对象的关系。这个描述最具体表现就是我们可配置的文件。
对象和对象关系怎么表示?
可以用 xml , properties 文件等语义化配置文件表示。
描述对象关系的文件存放在哪里?
可能是 classpath , filesystem ,或者是 URL 网络资源, servletContext 等。
回到正题,有了配置文件,还需要对配置文件解析。
不同的配置文件对对象的描述不一样,如标准的,自定义声明式的,如何统一? 在内部需要有一个统一的关于对象的定义,所有外部的描述都必须转化成统一的描述定义。
如何对不同的配置文件进行解析?需要对不同的配置文件语法,采用不同的解析器
二、 Spring IOC体系结构?
(1) BeanFactory
Spring Bean的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的Bean工厂,也即IOC容器为开发者管理对象间的依赖关系提供了很多便利和基础服务。
首先是BeanFactory ,它会根据定义好的不同的依赖选择不同的设计模式(主要有单例和原型模式)来返回bean,他们有不同的作用域,spring 2.0以后,作用域更加复杂。
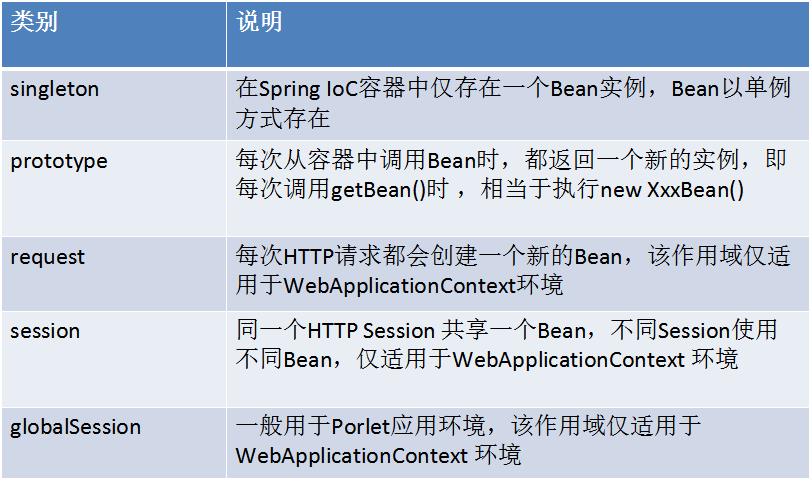
1 public interface BeanFactory {
2
3 //对FactoryBean的转义定义,因为如果使用bean的名字是一个factoryBean那么返回就是一个factory
5 String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
6
7 //根据bean的名字,获取在IOC容器中得到bean实例
8 Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
9
10 //根据bean的名字和Class类型来得到bean实例,增加了类型安全验证机制。
11 Object getBean(String name, Class requiredType) throws BeansException;
12
13 //提供对bean的检索,看看是否在IOC容器有这个名字的bean
14 boolean containsBean(String name);
15
16 //根据bean名字得到bean实例,并同时判断这个bean是不是单例
17 boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
18
19 //得到bean实例的Class类型
20 Class getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
21
22 //得到bean的别名,如果根据别名检索,那么其原名也会被检索出来
23 String[] getAliases(String name);
24
}
在Spring中有许多的IOC容器的实现供用户选择和使用,其相互关系如下:
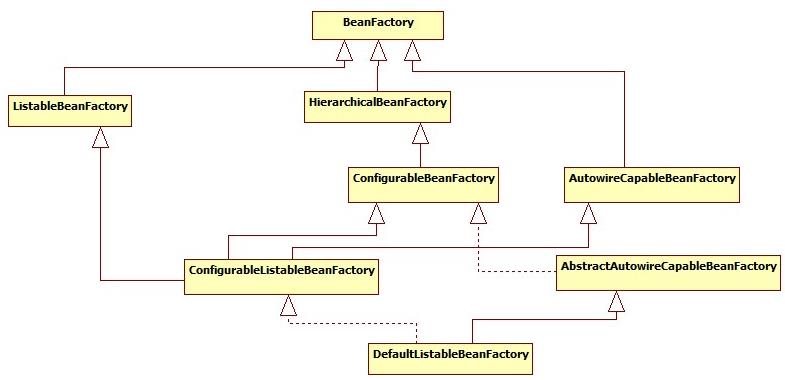
其中BeanFactory作为最顶层的一个接口类,它定义了IOC容器的基本功能规范,BeanFactory 有三个子类:ListableBeanFactory、HierarchicalBeanFactory 和AutowireCapableBeanFactory。但是从上图中我们可以发现最终的默认实现类是 DefaultListableBeanFactory,他实现了所有的接口。那为何要定义这么多层次的接口呢?查阅这些接口的源码和说明发现,每个接口都有他使用的场合,它主要是为了区分在 Spring 内部在操作过程中对象的传递和转化过程中,对对象的数据访问所做的限制。例如 ListableBeanFactory 接口表示这些 Bean 是可列表的,而 HierarchicalBeanFactory 表示的是这些 Bean 是有继承关系的,也就是每个Bean 有可能有父 Bean。AutowireCapableBeanFactory 接口定义 Bean 的自动装配规则。这四个接口共同定义了 Bean 的集合、Bean 之间的关系、以及 Bean 行为.
这个类BeanFactory是spring中所有bean工厂,也就是俗称的IOC容器的祖先,各种IOC容器都只是它的实现或者为了满足特别需求的扩展实现,包括我们平时用的最多的ApplicationContext。从上面的方法就可以看出,这些工厂的实现最大的作用就是根据bean的名称亦或类型等等,来返回一个bean的实例。
一个工厂如果想拥有这样的功能,那么它一定需要以下几个因素:
1.需要持有各种bean的定义,否则无法正确的完成bean的实例化。
2.需要持有bean之间的依赖关系,否则在bean实例化的过程中也会出现问题。例如上例,如果我们只是各自持有Person和Company,却不知道他们的依赖关系,那么在Company初始化以后,调用open方法时,就会报空指针。这是因为Company其实并没有真正的被正确初始化。
3.以上两种都要依赖于我们所写的依赖关系的定义,暂且认为是XML文件(其实可以是各种各样的),那么我们需要一个工具来完成XML文件的读取。
我目前想到的,只需要满足以上三种条件,便可以创建一个bean工厂,来生产各种bean。当然,spring有更高级的做法,以上只是我们直观的去想如何实现IOC。
其实在上述过程中仍旧有一些问题,比如第一步,我们需要持有bean的定义,如何持有?这是一个问题。我们知道spring的XML配置文件中,有一个属性是lazy-init,这就说明,bean在何时实例化我们是可以控制的。这个属性默认是false,但是我们可以将这个属性设置为true,也就是说spring容器初始化以后,配置了延迟加载的各种bean都还未产生,它们只在需要的时候出现。
所以我们无法直接的创建一个Map<String,Object>来持有这些bean的实例,在这里要注意,我们要储存的是bean的定义,而非实例。
那么接下来,又是一个祖宗级别的接口要出现了,来看BeanDefinition。
(2) BeanDefinition
这个便是spring中的bean定义接口,所以其实我们工厂里持有的bean定义,就是一堆这个玩意,或者是他的实现类和子接口。这个接口并非直接的祖宗接口,他所继承的两个接口一个是core下面的AttributeAccessor,继承这个接口就以为这我们的bean定义接口同样具有处理属性的能力,而另外一个是beans下面的BeanMetadataElement,字面翻译这个接口就是bean的元数据元素,它可以获得bean的配置定义的一个元素。在XML文件中来说,就是会持有一个bean标签。
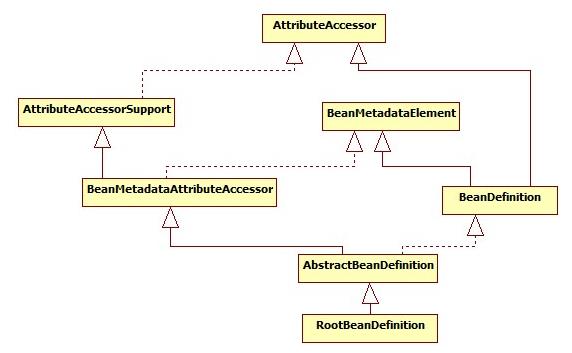
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config; import org.springframework.beans.BeanMetadataElement; import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues; import org.springframework.core.AttributeAccessor; public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement { String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON; String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE; int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0; int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1; int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2; String getParentName(); void setParentName(String parentName); String getBeanClassName(); void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName); String getFactoryBeanName(); void setFactoryBeanName(String factoryBeanName); String getFactoryMethodName(); void setFactoryMethodName(String factoryMethodName); String getScope(); void setScope(String scope); boolean isLazyInit(); void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit); String[] getDependsOn(); void setDependsOn(String[] dependsOn); boolean isAutowireCandidate(); void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate); boolean isPrimary(); void setPrimary(boolean primary); ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues(); MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues(); boolean isSingleton(); boolean isPrototype(); boolean isAbstract(); int getRole(); String getDescription(); String getResourceDescription(); BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); } 复制代码
仔细观看,能发现beanDefinition中有两个方法分别是String[] getDependsOn()和void setDependsOn(String[] dependsOn),这两个方法就是获取依赖的beanName和设置依赖的beanName,这样就好办了,只要我们有一个BeanDefinition,就可以完全的产生一个完整的bean实例。
那么知道了上述两个接口,我相信不少人甚至不看源码都已经猜到spring是如何做的了。没错,就是让bean工厂持有一个Map<String,BeanDefinition>,这样就可以在任何时候我们想用哪个bean,取到它的bean定义,我们就可以创造出一个新鲜的实例。
接口当然不可能持有这样一个对象,那么这个对象一定是在BeanFactory的某个实现类或者抽象实现类当中所持有的,上面我们说了BeanFactory的继承关系,我们发现最终的默认实现类是 DefaultListableBeanFactory。
(3)DefaultListableBeanFactory
它的源码为:
package org.springframework.beans.factory.support;
/**
* Default implementation of the
* based on bean definition objects.
*
* <p>Can be used as a standalone bean factory, or as a superclass for custom
* bean factories. Note that readers for specific bean definition formats are
* typically implemented separately rather than as bean factory subclasses:.
*
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
private static Class<?> javaxInjectProviderClass = null;
static {
ClassLoader cl = DefaultListableBeanFactory.class.getClassLoader();
try {
javaxInjectProviderClass = cl.loadClass("javax.inject.Provider");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - Provider interface simply not supported then.
}
}
/** Map from serialized id to factory instance */
private static final Map<String, Reference<DefaultListableBeanFactory>> serializableFactories =
new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Reference<DefaultListableBeanFactory>>(8);
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>(64);
/** Map of singleton and non-singleton bean names keyed by dependency type */
private final Map<Class<?>, String[]> allBeanNamesByType = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, String[]>(64);
/** Map of singleton-only bean names keyed by dependency type */
private final Map<Class<?>, String[]> singletonBeanNamesByType = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, String[]>(64);
/** List of bean definition names, in registration order */
private final List<String> beanDefinitionNames = new ArrayList<String>();
/**
* Create a new DefaultListableBeanFactory.
*/
public DefaultListableBeanFactory() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a new DefaultListableBeanFactory with the given parent.
* @param parentBeanFactory the parent BeanFactory
*/
public DefaultListableBeanFactory(BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) {
super(parentBeanFactory);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of ListableBeanFactory interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {
Assert.notNull(requiredType, "Required type must not be null");
String[] beanNames = getBeanNamesForType(requiredType);
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
ArrayList<String> autowireCandidates = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (getBeanDefinition(beanName).isAutowireCandidate()) {
autowireCandidates.add(beanName);
}
}
if (autowireCandidates.size() > 0) {
beanNames = autowireCandidates.toArray(new String[autowireCandidates.size()]);
}
}
if (beanNames.length == 1) {
return getBean(beanNames[0], requiredType);
}
else if (beanNames.length > 1) {
T primaryBean = null;
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
T beanInstance = getBean(beanName, requiredType);
if (isPrimary(beanName, beanInstance)) {
if (primaryBean != null) {
throw new NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException(requiredType, beanNames.length,
"more than one \'primary\' bean found of required type: " + Arrays.asList(beanNames));
}
primaryBean = beanInstance;
}
}
if (primaryBean != null) {
return primaryBean;
}
throw new NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException(requiredType, beanNames);
}
else if (getParentBeanFactory() != null) {
return getParentBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType);
}
else {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(requiredType);
}
}
}
其中
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
让bean工厂持有一个Map<String,BeanDefinition>,这样就可以在任何时候我们想用哪个bean,取到它的bean定义,我们就可以创造出一个新鲜的实例。
那么从现在来看,我们需要什么才能把Map填充呢?也就是初始化bean工厂呢,或者说建立IOC容器。我首先列出来以下几步。
1.需要一个File指向我们的XML文件(本文的配置文件都已XML为例,因为这是我们最熟悉的),专业点可以叫资源定位,简单点可以说我们需要一些工具来完成找到XML文件的所在位置。
2.需要一个Reader来读取我们的XML文件,专业点叫DOM解析,简单点说,就是把XML文件的各种定义都给拿出来。
3.需要将读出来的数据都设置到Map当中。
那么从现在来看,我们需要什么才能把Map填充呢?也就是初始化bean工厂呢,或者说建立IOC容器。
1.需要一个File指向我们的XML文件(本文的配置文件都已XML为例,因为这是我们最熟悉的),专业点可以叫资源定位,简单点可以说我们需要一些工具来完成找到XML文件的所在位置。
2.需要一个Reader来读取我们的XML文件,专业点叫DOM解析,简单点说,就是把XML文件的各种定义都给拿出来。
3.需要将读出来的数据都设置到Map当中。
这三步总结起来就是定位、解析、注册。
(4)定位、解析、注册
spring提供了许多IOC容器的实现。比如XmlBeanFactory,ClasspathXmlApplicationContext等。其中XmlBeanFactory就是针对最基本的ioc容器的实现,这个IOC容器可以读取XML文件定义的BeanDefinition(XML文件中对bean的描述),如果说XmlBeanFactory是容器中的屌丝,ApplicationContext应该算容器中的高帅富.
XmlBeanFactory源码如下:
package org.springframework.beans.factory.xml; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; /** * Convenience extension of {@link DefaultListableBeanFactory} that reads bean definitions * from an XML document. Delegates to {@link XmlBeanDefinitionReader} underneath; effectively * equivalent to using an XmlBeanDefinitionReader with a DefaultListableBeanFactory. * * <p>The structure, element and attribute names of the required XML document * are hard-coded in this class. (Of course a transform could be run if necessary * to produce this format). "beans" doesn\'t need to be the root element of the XML * document: This class will parse all bean definition elements in the XML file.*/ @Deprecated @SuppressWarnings({"serial", "all"}) public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory { private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this); /** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException { this(resource, null); } /** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException { super(parentBeanFactory); this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } }
直接上代码,我们还使用Person类作为一个Bean。
package com.springframework.beans.test; public class Person { public void work(){ System.out.println("I am working"); } }
我们还需要写一个简单的XML文件,beans.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.springframework.beans.test.Person"></bean> </beans>
下面是我们根据上述的思路写一段程序。
package com.springframework.beans.test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; public class TestDefaultListableBeanFactory { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml"); DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); XmlBeanDefinitionReader xmlBeanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(defaultListableBeanFactory); xmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(classPathResource); System.out.println("numbers: " + defaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanDefinitionCount()); ((Person)defaultListableBeanFactory.getBean("person")).work(); } }
对于xmlbeanfactory,代码为:
//根据Xml配置文件创建Resource资源对象,该对象中包含了BeanDefinition的信息 ClassPathResource resource =new ClassPathResource("application-context.xml"); //创建DefaultListableBeanFactory DefaultListableBeanFactory factory =new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); //创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader读取器,用于载入BeanDefinition。之所以需要BeanFactory作为参数,是因为会将读取的信息回调配置给factory XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader =new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); //XmlBeanDefinitionReader执行载入BeanDefinition的方法,最后会完成Bean的载入和注册。完成后Bean就成功的放置到IOC容器当中,以后我们就可以从中取得Bean来使用 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
第一行完成了我们的第一步,即资源定位,采用classpath定位,因为我的beans.xml文件是放在src下面的。
第二行创建了一个默认的bean工厂。
第三行创建了一个reader,从名字就不难看出,这个reader是用来读取XML文件的。这一步要多说一句,其中将我们创建的defaultListableBeanFactory作为参数传给了reader的构造函数,这里是为了第四步读取XML文件做准备。
第四行使用reader解析XML文件,并将读取的bean定义回调设置到defaultListableBeanFactory当中。其实回调这一步就相当于我们上述的注册这一步。
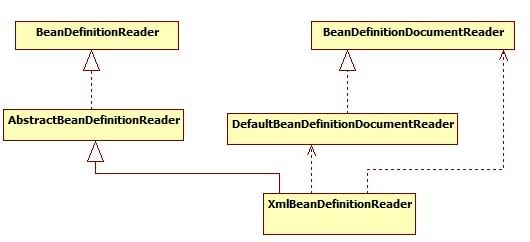
(1)Bean 的解析
Bean 的解析 过程非常复杂,功能被分的很细,因为这里需要被扩展的地方很多,必须保证有足够的灵活性,以应对可能的变化。Bean 的解析主要就是对 Spring 配置文件的解析。这个解析过程主要通过下图中的类完成:
这个时候defaultListableBeanFactory已经被正确初始化了,我们已经可以使用它的一些方法了,比如上面所使用的获取bean个数,以及获得一个bean实例的方法。
1.1
对于ApplicationContext ,代码为
package com.springframework.beans.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestApplicationContext {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:beans.xml");
System.out.println("numbers: " + applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionCount());
((Person)applicationContext.getBean("person")).work();
}
}
1.2
具体我们在new一个FileSystemXmlApplicationContext对象的时候,spring到底做了哪些事情呢,
先看其构造函数:
调用构造函数:
/**
* Create a new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions
* from the given XML files and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param configLocations array of file paths
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
*/public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, null);
}
实际调用
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
通过分析FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的源代码可以知道,在创建FileSystemXmlApplicationContext容器时,构造方法做以下两项重要工作:
1 首先,调用父类容器的构造方法(super(parent)方法)为容器设置好Bean资源加载器。(其继承体系如下)
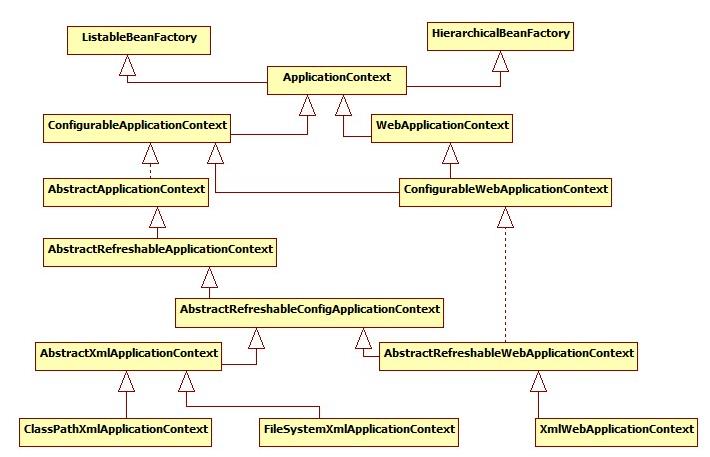
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean { //静态初始化块,在整个容器创建过程中只执行一次 static { //为了避免应用程序在Weblogic8.1关闭时出现类加载异常加载问题,加载IoC容 //器关闭事件(ContextClosedEvent)类 ContextClosedEvent.class.getName(); } //FileSystemXmlApplicationContext调用父类构造方法调用的就是该方法 public AbstractApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { this.parent = parent; this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver(); } //获取一个Spring Source的加载器用于读入Spring Bean定义资源文件 protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() { // AbstractApplicationContext继承DefaultResourceLoader,也是一个S //Spring资源加载器,其getResource(String location)方法用于载入资源 return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this); } …… }
AbstractApplicationContext构造方法中调用PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver的构造方法创建Spring资源加载器:
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
//设置Spring的资源加载器
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
在设置容器的资源加载器之后,接下来FileSystemXmlApplicationContet执行setConfigLocations方法通过调用其父类AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext的方法进行对Bean定义资源文件的定位,该方法的源码如下:
//处理单个资源文件路径为一个字符串的情况
public void setConfigLocation(String location) {
//String CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS = ",; /t/n";
//即多个资源文件路径之间用” ,; /t/n”分隔,解析成数组形式
setConfigLocations(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(location, CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
//解析Bean定义资源文件的路径,处理多个资源文件字符串数组
public void setConfigLocations(String[] locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
// resolvePath为同一个类中将字符串解析为路径的方法
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
通过这两个方法的源码我们可以看出,我们既可以使用一个字符串来配置多个Spring Bean定义资源文件,也可以使用字符串数组,即下面两种方式都是可以的:
a. ClasspathResource res = new ClasspathResource(“a.xml,b.xml,……”);
多个资源文件路径之间可以是用” ,; /t/n”等分隔。
b. ClasspathResource res = new ClasspathResource(newString[]{“a.xml”,”b.xml”,……});
至此,Spring IoC容器在初始化时将配置的Bean定义资源文件定位为Spring封装的Resource。
1.3
refresh方法,便是IOC容器初始化的入口。
Spring IoC容器对Bean定义资源的载入是从refresh()函数开始的,refresh()是一个模板方法,refresh()方法的作用是:在创建IoC容器前,如果已经有容器存在,则需要把已有的容器销毁和关闭,以保证在refresh之后使用的是新建立起来的IoC容器。refresh的作用类似于对IoC容器的重启,在新建立好的容器中对容器进行初始化,对Bean定义资源进行载入
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext通过调用其父类AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()函数启动整个IoC容器对Bean定义的载入过程:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
2 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
3 //调用容器准备刷新的方法,获取容器的当时时间,同时给容器设置同步标识
4 prepareRefresh();
5 //告诉子类启动refreshBeanFactory()方法,Bean定义资源文件的载入从
6 //子类的refreshBeanFactory()方法启动
7 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
8 //为BeanFactory配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等
9 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
10 try {
11 //为容器的某些子类指定特殊的BeanPost事件处理器
12 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
13 //调用所有注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的Bean
14 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
15 //为BeanFactory注册BeanPost事件处理器.
16 //BeanPostProcessor是Bean后置处理器,用于监听容器触发的事件
17 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
18 //初始化信息源,和国际化相关.
19 initMessageSource();
20 //初始化容器事件传播器.
21 initApplicationEventMulticaster();
22 //调用子类的某些特殊Bean初始化方法
23 onRefresh();
24 //为事件传播器注册事件监听器.
25 registerListeners();
26 //初始化所有剩余的单态Bean.
27 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
28 //初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件
29 finishRefresh();
30 }
31 catch (BeansException ex) {
32 //销毁以创建的单态Bean
33 destroyBeans();
34 //取消refresh操作,重置容器的同步标识.
35 cancelRefresh(ex);
36 throw ex;
37 }
38 }
39 }
refresh()方法主要为IoC容器Bean的生命周期管理提供条件,Spring IoC容器载入Bean定义资源文件从其子类容器的refreshBeanFactory()方法启动,所以整个refresh()中“ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory =obtainFreshBeanFactory();”这句以后代码的都是注册容器的信息源和生命周期事件,载入过程就是从这句代码启动
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//这里使用了委派设计模式,父类定义了抽象的refreshBeanFactory()方法,具体实现调用子类容器的refreshBeanFactory()方法
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
该方法中第一句便调用了另外一个refreshBeanFactory方法,这个方法是AbstractApplicationContext中的抽象方法,具体的实现并没有在这个抽象类中实现,而是留给了子类,我们追踪到这个子类当中去看一下。该方法又子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext实现,我们来看
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
方法加上了final关键字,也就是说此方法不可被重写,可以很清楚的看到,IOC容器的初始化就是在这个方法里发生的,第一步先是判断有无现有的工厂,有的话便会将其摧毁,否则,就会创建一个默认的bean工厂,也就是前面提到的DefaultListableBeanFactory,注意看loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);这里,当我们创建了一个默认的bean工厂以后,便是载入bean的定义。这与我们上一章所使用的原始的创建bean工厂的方式极为相似。
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中只定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,容器真正调用的是其子类AbstractXmlApplicationContext对该方法的实现,AbstractXmlApplicationContext的主要源码如下:
1.4
loadBeanDefinitions方法是由AbstractXmlApplicationContext抽象类实现的。
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context\'s
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
1.5
第一行首先定义了一个reader,很明显,这个就是spring为读取XML配置文件而定制的读取工具,这里AbstractXmlApplicationContext间接实现了ResourceLoader接口,所以该方法的第二行才得以成立,最后一行便是真正载入bean定义的过程。我们追踪其根源,可以发现最终的读取过程正是由reader完成的,代码如下。
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
1.6
这个方法中不难发现,try块中的代码才是载入bean定义的真正过程,我们一步一步的扒开bean定义的载入,spring将资源返回的输入流包装以后传给了doLoadBeanDefinitions方法,我们进去看看发生了什么。
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);
Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
可以看到,spring采用documentLoader将资源转换成了Document接口,这正是我们熟知的SAX对XML解析的重要接口之一,这下不难理解了,可以想象出spring一定是根据XSD文件规定的XML格式,解析了XML文件中的各个节点以及属性。尽管如此,我们还是跟着registerBeanDefinitions方法进去看看。
XmlBeanDefinitionReader类中的doLoadBeanDefinitions方法是从特定XML文件中实际载入Bean定义资源的方法,该方法在载入Bean定义资源之后将其转换为Document对象,接下来调用registerBeanDefinitions启动Spring IoC容器对Bean定义的解析过程,registerBeanDefinitions方法源码如下:
1 //按照Spring的Bean语义要求将Bean定义资源解析并转换为容器内部数据结构 2 public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 3 //得到BeanDefinitionDocumentReader来对xml格式的BeanDefinition解析 4 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); 5 //获得容器中注册的Bean数量 6 int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); 7 //解析过程入口,这里使用了委派模式,BeanDefinitionDocumentReader只是个接口,//具体的解析实现过程有实现类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader完成 8 documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); 9 //统计解析的Bean数量 10 return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; 11 } 12 //创建BeanDefinitionDocumentReader对象,解析Document对象 13 protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() { 14 return BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.cast(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass)); }
1.7解析文件与注册的具体实现
1解析与注册的分界点
按照Spring的Bean规则对Document对象解析的过程是在接口BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的实现类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader中实现的。BeanDefinitionDocumentReader接口通过registerBeanDefinitions方法调用其实现类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader对Document对象进行解析,解析的代码如下:
//根据Spring DTD对Bean的定义规则解析Bean定义Document对象
2 public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
3 //获得XML描述符
4 this.readerContext = readerContext;
5 logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
6 //获得Document的根元素
7 Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
8 //具体的解析过程由BeanDefinitionParserDelegate实现,
9 //BeanDefinitionParserDelegate中定义了Spring Bean定义XML文件的各种元素
10 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate = createHelper(readerContext, root);
11 //在解析Bean定义之前,进行自定义的解析,增强解析过程的可扩展性
12 preProcessXml(root);
13 //从Document的根元素开始进行Bean定义的Document对象
14 parseBeanDefinitions(root, delegate);
15 //在解析Bean定义之后,进行自定义的解析,增加解析过程的可扩展性
16 postProcessXml(root);
17 }
18 //创建BeanDefinitionParserDelegate,用于完成真正的解析过程
19 protected BeanDefinitionParserDelegate createHelper(XmlReaderContext readerContext, Element root) {
20 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(readerContext);
21 //BeanDefinitionParserDelegate初始化Document根元素
22 delegate.initDefaults(root);
23 return delegate;
24 }
25 //使用Spring的Bean规则从Document的根元素开始进行Bean定义的Document对象
26 protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
27 //Bean定义的Document对象使用了Spring默认的XML命名空间
28 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
29 //获取Bean定义的Document对象根元素的所有子节点
30 NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
31 for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
32 Node node = nl.item(i);
33 //获得Document节点是XML元素节点
34 if (node instanceof Element) {
35 Element ele = (Element) node;
36 //Bean定义的Document的元素节点使用的是Spring默认的XML命名空间
37 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
38 //使用Spring的Bean规则解析元素节点
39 parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
40 }
41 else {
42 //没有使用Spring默认的XML命名空间,则使用用户自定义的解//析规则解析元素节点
43 delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
44 }
45 }
46 }
47 }
48 else {
49 //Document的根节点没有使用Spring默认的命名空间,则使用用户自定义的
50 //解析规则解析Document根节点
51 delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
52 }
53 }
54 //使用Spring的Bean规则解析Document元素节点
55 private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
56 //如果元素节点是<Import>导入元素,进行导入解析
57 if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
58 importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
59 }
60 //如果元素节点是<Alias>别名元素,进行别名解析
61 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
62 processAliasRegistration(ele);
63 }
64 //元素节点既不是导入元素,也不是别名元素,即普通的<Bean>元素,
65 //按照Spring的Bean规则解析元素
66 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
67 processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
68 }
69 }
70 //解析<Import>导入元素,从给定的导入路径加载Bean定义资源到Spring IoC容器中
71 protected void importBeanDefinitionResource(Element ele) {
72 //获取给定的导入元素的location属性
73 String location = ele.getAttribute(RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE);
74 //如果导入元素的location属性值为空,则没有导入任何资源,直接返回
75 if (!StringUtils.hasText(location)) {
76 getReaderContext().error("Resource location must not be empty", ele);
77 return;
78 }
79 //使用系统变量值解析location属性值
80 location = SystemPropertyUtils.resolvePlaceholders(location);
81 Set<Resource> actualResources = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(4);
82 //标识给定的导入元素的location是否是绝对路径
83 boolean absoluteLocation = false;
84 try {
85 absoluteLocation = ResourcePatternUtils.isUrl(location) || ResourceUtils.toURI(location).isAbsolute();
86 }
87 catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
88 //给定的导入元素的location不是绝对路径
89 }
90 //给定的导入元素的location是绝对路径
91 if (absoluteLocation) {
92 try {
93 //使用资源读入器加载给定路径的Bean定义资源
94 int importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(location, actualResources);
95 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
96 logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]");
97 }
98 }
99 catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
100 getReaderContext().error(
101 "Failed to import bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]", ele, ex);
102 }
103 }
104 else {
105 //给定的导入元素的location是相对路径
106 try {
107 int importCount;
108 //将给定导入元素的location封装为相对路径资源
109 Resource relativeResource = getReaderContext().getResource().createRelative(location);
110 //封装的相对路径资源存在
111 if (relativeResource.exists()) {
112 //使用资源读入器加载Bean定义资源
113 importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(relativeResource);
114 actualResources.add(relativeResource);
115 }
116 //封装的相对路径资源不存在
117 else {
118 //获取Spring IoC容器资源读入器的基本路径
119 String baseLocation = getReaderContext().getResource().getURL().toString();
120 //根据Spring IoC容器资源读入器的基本路径加载给定导入
121 //路径的资源
122 importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(
123 StringUtils.applyRelativePath(baseLocation, location), actualResources);
124 }
125 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
126 logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]");
127 }
128 }
129 catch (IOE以上是关于Spring 源码学习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
