android自定义控件之飞入飞出控件
Posted zero-27
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了android自定义控件之飞入飞出控件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
最近呢,本人辞职了,在找工作期间,不幸碰到了这个求职淡季,另外还是大学生毕业求职的高峰期,简历发了无数份却都石沉大海,宝宝心里那是一个苦啊!翻着过去的代码,本人偶然找到了一个有意思的控件,那时本人还没有写博客的习惯,现在补上,先看效果图:
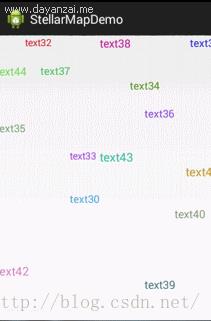
然后看用法代码:
StellarMap stellarMap = (StellarMap) findViewById(R.id.stellar);
// 设置数据
RecommendAdapter adapter = new RecommendAdapter();
stellarMap.setAdapter(adapter);
// 首页选中
stellarMap.setGroup(0, true);
// 拆分屏幕
stellarMap.setRegularity(15, 20);class RecommendAdapter implements Adapter {
/** 默认组数 */
public static final int PAGESIZE = 15;
@Override
public int getGroupCount() {
// 数据分组
int groupCount = data.size() / PAGESIZE;
// 最后一组
if (data.size() % PAGESIZE != 0) {
return groupCount + 1;
}
return groupCount;
}
@Override
public int getCount(int group) {
// 最后一组
if (data.size() % PAGESIZE != 0) {
if (group == getGroupCount() - 1) {
return data.size() % PAGESIZE;
}
}
return PAGESIZE;
}
@Override
public View getView(int group, int position, View convertView) {
TextView tv = new TextView(MainActivity.this);
int index = group * PAGESIZE + position;
tv.setText(data.get(index));
// 随机大小
Random random = new Random();
// 14-17
int size = random.nextInt(4) + 14;
tv.setTextSize(size);
// 随机颜色
int alpha = 255;
int red = random.nextInt(190) + 30;
int green = random.nextInt(190) + 30;
int blue = random.nextInt(190) + 30;
int argb = Color.argb(alpha, red, green, blue);
tv.setTextColor(argb);
return tv;
}
@Override
public int getNextGroupOnPan(int group, float degree) {
if(group == getGroupCount() - 1){
group = -1;
}
return group + 1;
}
@Override
public int getNextGroupOnZoom(int group, boolean isZoomIn) {
if(group == getGroupCount() - 1){
group = -1;
}
return group + 1;
}
}代码都很简单,我简单说一下,getGroupCount返回一共有多少组,getCount返回一组有多少个元素,getView就不说了,getNextGroupOnPan返回下一个需要放大动画的组数,getNextGroupOnZoom返回下一个需要错小动画的组数。
接下来才是正餐,我们看看StellarMap的实现,StellarMap继承于FrameLayout:
/** 构造方法 */
public StellarMap(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
}
public StellarMap(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public StellarMap(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}这个大家应该都很熟,自定义View需要实现的三个构造方法。
/** 初始化方法 */
private void init() {
mGroupCount = 0;
mHidenGroupIndex = -1;
mShownGroupIndex = -1;
mHidenGroup = new RandomLayout(getContext());
mShownGroup = new RandomLayout(getContext());
addView(mHidenGroup, new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT));
mHidenGroup.setVisibility(View.GONE);
addView(mShownGroup, new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT));
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(this);
setOnTouchListener(this);
// 设置动画
mZoomInNearAnim = AnimationUtil.createZoomInNearAnim();
mZoomInNearAnim.setAnimationListener(this);
mZoomInAwayAnim = AnimationUtil.createZoomInAwayAnim();
mZoomInAwayAnim.setAnimationListener(this);
mZoomOutNearAnim = AnimationUtil.createZoomOutNearAnim();
mZoomOutNearAnim.setAnimationListener(this);
mZoomOutAwayAnim = AnimationUtil.createZoomOutAwayAnim();
mZoomOutAwayAnim.setAnimationListener(this);
}代码很清晰,简单说一下,mGroupCount是组数,mHidenGroupIndex是隐藏的组数角标,mShownGroupIndex是显示的组数角标,另外创建了两个RandomLayout,它继承于ViewGroup,用于实现View的随机放入,之后创建手势监听和触摸监听,下面就是四个不同的动画。
按照代码执行顺序来,下一步是设置Adapter:
/** 设置本Adapter */
public void setAdapter(Adapter adapter) {
mAdapter = adapter;
mGroupCount = mAdapter.getGroupCount();
if (mGroupCount > 0) {
mShownGroupIndex = 0;
}
setChildAdapter();
}可见这里初始化了组数,并调用了setChildAdapter方法:
/** 为子Group设置Adapter */
private void setChildAdapter() {
if (null == mAdapter) {
return;
}
mHidenGroupAdapter = new RandomLayout.Adapter() {
// 取出本Adapter的View对象给HidenGroup的Adapter
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView) {
return mAdapter.getView(mHidenGroupIndex, position, convertView);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mAdapter.getCount(mHidenGroupIndex);
}
};
mHidenGroup.setAdapter(mHidenGroupAdapter);
mShownGroupAdapter = new RandomLayout.Adapter() {
// 取出本Adapter的View对象给ShownGroup的Adapter
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView) {
return mAdapter.getView(mShownGroupIndex, position, convertView);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mAdapter.getCount(mShownGroupIndex);
}
};
mShownGroup.setAdapter(mShownGroupAdapter);
}该方法为子视图创建Adapter,也就是RandomLayout,我们看看它的实现:
/** 构造方法 */
public RandomLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}/** 初始化方法 */
private void init() {
mLayouted = false;
mRdm = new Random();
setRegularity(1, 1);
mFixedViews = new HashSet<View>();
mRecycledViews = new LinkedList<View>();
}在init方法中,mLayouted表示该视图是否已经onlayout,mFixedViews存放已经确定位置的View ,mRecycledViews记录被回收的View,以便重复利用,setRegularity(1, 1)方法仅仅只是初始化,会被重新调用,我们后面讲,setAdapter方法就相当简单了:
/** 设置数据源 */
public void setAdapter(Adapter adapter) {
this.mAdapter = adapter;
}再回到使用代码上,下一句是stellarMap.setGroup(0, true),我们看看实现:
/** 给指定的Group设置动画 */
public void setGroup(int groupIndex, boolean playAnimation) {
switchGroup(groupIndex, playAnimation, mZoomInNearAnim, mZoomInAwayAnim);
}/** 给下一个Group设置进出动画 */
private void switchGroup(int newGroupIndex, boolean playAnimation, Animation inAnim,
Animation outAnim) {
if (newGroupIndex < 0 || newGroupIndex >= mGroupCount) {
return;
}
// 把当前显示Group角标设置为隐藏的
mHidenGroupIndex = mShownGroupIndex;
// 把下一个Group角标设置为显示的
mShownGroupIndex = newGroupIndex;
// 交换两个Group
RandomLayout temp = mShownGroup;
mShownGroup = mHidenGroup;
mShownGroup.setAdapter(mShownGroupAdapter);
mHidenGroup = temp;
mHidenGroup.setAdapter(mHidenGroupAdapter);
// 刷新显示的Group
mShownGroup.refresh();
// 显示Group
mShownGroup.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// 启动动画
if (playAnimation) {
if (mShownGroup.hasLayouted()) {
mShownGroup.startAnimation(inAnim);
}
mHidenGroup.startAnimation(outAnim);
} else {
mHidenGroup.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}switchGroup方法正是StellarMap的核心方法,通过交换show和hide的角标与adapter,完成显示和隐藏的切换,并开启过度动画。
最后一行代码,stellarMap.setRegularity(15, 20)方法:
/** 设置隐藏组和显示组的x和y的规则 */
public void setRegularity(int xRegularity, int yRegularity) {
mHidenGroup.setRegularity(xRegularity, yRegularity);
mShownGroup.setRegularity(xRegularity, yRegularity);
}用于设置屏幕的分割,再看RandomLayout的setRegularity方法:
/** 设置mXRegularity和mXRegularity,确定区域的个数 */
public void setRegularity(int xRegularity, int yRegularity) {
if (xRegularity > 1) {
this.mXRegularity = xRegularity;
} else {
this.mXRegularity = 1;
}
if (yRegularity > 1) {
this.mYRegularity = yRegularity;
} else {
this.mYRegularity = 1;
}
this.mAreaCount = mXRegularity * mYRegularity;// 个数等于x方向的个数*y方向的个数
this.mAreaDensity = new int[mYRegularity][mXRegularity];// 存放区域的二维数组
}这里保存了屏幕被分割的快数,并创建了一个二维数组,定位具体的位置,它的onLayout便是区域分布的关键:
/** 确定子View的位置,这个就是区域分布的关键 */
@Override
public void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
final int count = getChildCount();
// 确定自身的宽高
int thisW = r - l - this.getPaddingLeft() - this.getPaddingRight();
int thisH = b - t - this.getPaddingTop() - this.getPaddingBottom();
// 自身内容区域的右边和下边
int contentRight = r - getPaddingRight();
int contentBottom = b - getPaddingBottom();
// 按照顺序存放把区域存放到集合中
List<Integer> availAreas = new ArrayList<Integer>(mAreaCount);
for (int i = 0; i < mAreaCount; i++) {
availAreas.add(i);
}
int areaCapacity = (count + 1) / mAreaCount + 1; // 区域密度,表示一个区域内可以放几个View,+1表示至少要放一个
int availAreaCount = mAreaCount; // 可用的区域个数
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) { // gone掉的view是不参与布局
continue;
}
if (!mFixedViews.contains(child)) {// mFixedViews用于存放已经确定好位置的View,存到了就没必要再次存放
LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 先测量子View的大小
int childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(this.getMeasuredWidth(), MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);// 为子View准备测量的参数
int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(this.getMeasuredHeight(), MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// 子View测量之后的宽和高
int childW = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childH = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 用自身的高度去除以分配值,可以算出每一个区域的宽和高
float colW = thisW / (float) mXRegularity;
float rowH = thisH / (float) mYRegularity;
while (availAreaCount > 0) { // 如果使用区域大于0,就可以为子View尝试分配
int arrayIdx = mRdm.nextInt(availAreaCount);// 随机一个list中的位置
int areaIdx = availAreas.get(arrayIdx);// 再根据list中的位置获取一个区域编号
int col = areaIdx % mXRegularity;// 计算出在二维数组中的位置
int row = areaIdx / mXRegularity;
if (mAreaDensity[row][col] < areaCapacity) {// 区域密度未超过限定,将view置入该区域
int xOffset = (int) colW - childW; // 区域宽度 和 子View的宽度差值,差值可以用来做区域内的位置随机
if (xOffset <= 0) {// 说明子View的宽比较大
xOffset = 1;
}
int yOffset = (int) rowH - childH;
if (yOffset <= 0) {// 说明子View的高比较大
yOffset = 1;
}
// 确定左边,等于区域宽度*左边的区域
params.mLeft = getPaddingLeft() + (int) (colW * col + mRdm.nextInt(xOffset));
int rightEdge = contentRight - childW;
if (params.mLeft > rightEdge) {// 加上子View的宽度后不能超出右边界
params.mLeft = rightEdge;
}
params.mRight = params.mLeft + childW;
params.mTop = getPaddingTop() + (int) (rowH * row + mRdm.nextInt(yOffset));
int bottomEdge = contentBottom - childH;
if (params.mTop > bottomEdge) {// 加上子View的宽度后不能超出右边界
params.mTop = bottomEdge;
}
params.mBottom = params.mTop + childH;
if (!isOverlap(params)) {// 判断是否和别的View重叠了
mAreaDensity[row][col]++;// 没有重叠,把该区域的密度加1
child.layout(params.mLeft, params.mTop, params.mRight, params.mBottom);// 布局子View
mFixedViews.add(child);// 添加到已经布局的集合中
break;
} else {// 如果重叠了,把该区域移除,
availAreas.remove(arrayIdx);
availAreaCount--;
}
} else {// 区域密度超过限定,将该区域从可选区域中移除
availAreas.remove(arrayIdx);
availAreaCount--;
}
}
}
}
mLayouted = true;
}说实在的,这么长的代码分析起来着实有点费劲,必要的部分我加了注释,这里就不多说了。
在StellarMap中加入了手势,用于用户滑动的时候给与交互:
@Override
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY) {
int centerX = getMeasuredWidth() / 2;
int centerY = getMeasuredWidth() / 2;
int x1 = (int) e1.getX() - centerX;
int y1 = (int) e1.getY() - centerY;
int x2 = (int) e2.getX() - centerX;
int y2 = (int) e2.getY() - centerY;
if ((x1 * x1 + y1 * y1) > (x2 * x2 + y2 * y2)) {
zoomOut();
} else {
zoomIn();
}
return true;
}/** 给Group设置动画入 */
public void zoomIn() {
final int nextGroupIndex = mAdapter.getNextGroupOnZoom(mShownGroupIndex, true);
switchGroup(nextGroupIndex, true, mZoomInNearAnim, mZoomInAwayAnim);
}
/** 给Group设置出动画 */
public void zoomOut() {
final int nextGroupIndex = mAdapter.getNextGroupOnZoom(mShownGroupIndex, false);
switchGroup(nextGroupIndex, true, mZoomOutNearAnim, mZoomOutAwayAnim);
}可见最后还是调回了我们的switchGroup方法。
本文最后附上Demo以供参考。
以上是关于android自定义控件之飞入飞出控件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章