广度优先深度优先搜索算法——面试题
Posted nogos
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了广度优先深度优先搜索算法——面试题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
广度优先搜索(Breadth-first Search)
BFS在求解最短路径或者最短步数上有很多的应用。应用最多的是在走迷宫上。

分析
树的定义本身就是一种递归定义,因此对于树相关的算法题,递归是最好的解决思路(在递归深度允许的情况下)。
递归版
public class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return root==null||isMirror(root.left,root.right);
}
private boolean isMirror(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p==null&&q==null)
return true;
if(p==null||q==null)
return false;
if(p.val!=q.val)
return false;
return isMirror(p.left,q.right)&&isMirror(p.right,q.left);
}
}public class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode left, right;
if(root.left!=null){
if(root.right==null) return false;
stack.push(root.left);
stack.push(root.right);
}
else if(root.right!=null){
return false;
}
while(!stack.empty()){
if(stack.size()%2!=0) return false;
right = stack.pop();
left = stack.pop();
if(right.val!=left.val) return false;
if(left.left!=null){//左子树的左子树和右子树的右子树比较
if(right.right==null) return false;
stack.push(left.left);
stack.push(right.right);
}
else if(right.right!=null){
return false;
}
if(left.right!=null){//左子树的右子树和右子树的左子树比较
if(right.left==null) return false;
stack.push(left.right);
stack.push(right.left);
}
else if(right.left!=null){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}

分析
层次遍历可以利用队列实现。
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> levels = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null)
return levels;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode> nextQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);//记录层次遍历的结果
if (node.left != null)
nextQueue.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
nextQueue.add(node.right);
}
queue = nextQueue;
levels.add(list);
}
return levels;
}
}
分析
与上一题的唯一区别:节点遍历的顺序会交替变换,我们只需要用一个变量标记每次遍历的顺序即可。
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> levels = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null)
return levels;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
int mark = 0;//遍历方向的标记
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode> nextqueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
nextqueue.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
nextqueue.add(node.right);
}
queue = nextqueue;
if (mark == 1)//不同标记不同方向
Collections.reverse(list);
mark = (mark + 1) % 2;
levels.add(list);
}
return levels;
}
}
分析
与上上题的唯一区别:将结果集逆序。
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> levels=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null)return levels;
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode> nextQueue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)nextQueue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)nextQueue.add(node.right);
}
queue=nextQueue;
levels.add(list);
}
Collections.reverse(levels);//将结果集逆序即可
return levels;
}
}
递归版
public class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
return doMinDepth(root);
}
public int doMinDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) return 1;
int leftDepth=doMinDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth=doMinDepth(root.right);
return 1+Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
}利用后序遍历可以遍历所有从根节点的路径。
public class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
Map<TreeNode,Boolean> visit=new HashMap<TreeNode,Boolean>();
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){//后续遍历
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.peek();
if(p.left==null&&p.right==null){
min=Math.min(min, stack.size());
}
if(p.right!=null){//具有右子树
if(visit.get(p)==null){//第一次出现在栈顶
visit.put(p, true);
//处理右子树
p=p.right;
}
else{//第二次出现在栈顶
stack.pop();
p=null; //右子树已经处理过了
}
}else{
stack.pop();
p=null;
}
}
return min;
}
}
分析
初始化:location=0(<row=0,col=0>)。利用宽度优先遍历算法,搜寻从location(<row,col>)出发所有连通的'O’。然后判定连通集合是否被包围,如果被包围则全部置为‘X’,否则全部标记为未被包围。然后,从下一个可能被包围的location开始继续上述步骤,直到找不到下一个可能被包围的location,算法结束。
public class Solution {
private void doSolve(char[][] board,HashSet<Integer> unSurrounded,int location){
int m=board.length,n=board[0].length;
while(location<m*n){//找到第一个可能被包围的'O'
int r=location/n,c=location%n;
if(board[r][c]=='O'&&!unSurrounded.contains(location)){
break;
}
location++;
}
if(location==m*n)return;//处理完毕
//宽度优先遍历
HashSet<Integer> founded=new HashSet<Integer>();//所有搜索到的
HashSet<Integer> current=new HashSet<Integer>();//当前元素
founded.add(location);
current.add(location);
while(true){
HashSet<Integer> newLocations=new HashSet<Integer>();
for(Integer i:current){
int r=i/n,c=i%n;
//依次考虑上下左右的位置
if(r>0&&board[r-1][c]=='O'&&!founded.contains(i-n)){
founded.add(i-n);newLocations.add(i-n);}//上
if(r<m-1&&board[r+1][c]=='O'&&!founded.contains(i+n)){
founded.add(i+n);newLocations.add(i+n);}//下
if(c>0&&board[r][c-1]=='O'&&!founded.contains(i-1)){
founded.add(i-1);newLocations.add(i-1);}//左
if(c<n-1&&board[r][c+1]=='O'&&!founded.contains(i+1)){
founded.add(i+1);newLocations.add(i+1);}//右
}
if(newLocations.size()==0){
break;
}else{
current=newLocations;//只有新增的位置,才能搜索到新增位置
}
}
//检查是否被包含
boolean surrounded=true;
for(Integer i:founded){
int r=i/n,c=i%n;
if(r==0||r==m-1||c==0||c==n-1){
surrounded=false;
break;
}
}
if(surrounded){
for(Integer i:founded){
int r=i/n,c=i%n;
board[r][c]='X';
}
}else{
for(Integer i:founded){
unSurrounded.add(i);
}
}
doSolve(board,unSurrounded,location);//递归求解
}
public void solve(char[][] board) {
if(board.length==0||board[0].length==0)return;
HashSet<Integer> unSurrounded=new HashSet<Integer>();//未被包围的'O'
doSolve(board,unSurrounded,0);
}
}
分析
该问题等价于层次遍历过程中,每一层的末尾元素。
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null)
return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Queue<TreeNode> nextQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode last=null;//记录每层末尾的元素
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
last=node;
if (node.left != null)
nextQueue.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
nextQueue.add(node.right);
}
queue = nextQueue;
res.add(last.val);
}
return res;
}
}
分析
依然是宽度优先遍历,思路几乎与上上题一致。从location开始搜索连通集合,然后将连通集合标记为已找到的island。然后,寻找下一个可能是island的location,继续上述搜索过程,直到找不到可能的island。
private int findIslands(char[][] grid,HashSet<Integer> islandLocation,int location){
int m=grid.length,n=grid[0].length;
while(location<m*n){//找到第一个可能是island的'1'
int r=location/n,c=location%n;
if(grid[r][c]=='1'&&!islandLocation.contains(location)){
break;
}
location++;
}
if(location==m*n) return 0;//处理完毕
//宽度优先遍历
HashSet<Integer> founded=new HashSet<Integer>();//所有搜索到的'1'
HashSet<Integer> current=new HashSet<Integer>();//当前元素
founded.add(location);
current.add(location);
while(true){
HashSet<Integer> newLocations=new HashSet<Integer>();
for(Integer i:current){
int r=i/n,c=i%n;
//依次考虑上下左右的位置
if(r>0&&grid[r-1][c]=='1'&&!founded.contains(i-n)){
founded.add(i-n);newLocations.add(i-n);}//上
if(r<m-1&&grid[r+1][c]=='1'&&!founded.contains(i+n)){
founded.add(i+n);newLocations.add(i+n);}//下
if(c>0&&grid[r][c-1]=='1'&&!founded.contains(i-1)){
founded.add(i-1);newLocations.add(i-1);}//左
if(c<n-1&&grid[r][c+1]=='1'&&!founded.contains(i+1)){
founded.add(i+1);newLocations.add(i+1);}//右
}
if(newLocations.size()==0){
break;
}else{
current=newLocations;//只有新增的位置,才能搜索到新增位置
}
}
for(Integer i:founded){//标记为island
islandLocation.add(i);
}
return 1+findIslands(grid,islandLocation,location);//递归求解
}
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if(grid.length==0||grid[0].length==0)return 0;
HashSet<Integer> islandLocation=new HashSet<Integer>();
return findIslands(grid,islandLocation,0);
}
深度优先搜索(Depth-first Search)
在我们遇到的一些问题当中,有些问题我们不能够确切的找出数学模型,即找不出一种直接求解的方法,解决这一类问题,我们一般采用搜索的方法解决。搜索就是用问题的所有可能去试探,按照一定的顺序、规则,不断去试探,直到找到问题的解,试完了也没有找到解,那就是无解,试探时一定要试探完所有的情况(实际上就是穷举);深度优先搜索(回溯法)作为最基本的搜索算法,其采用了一种“一直向下走,走不通就掉头”的思想(体会“回溯”二字),相当于采用了先根遍历的方法来构造搜索树。
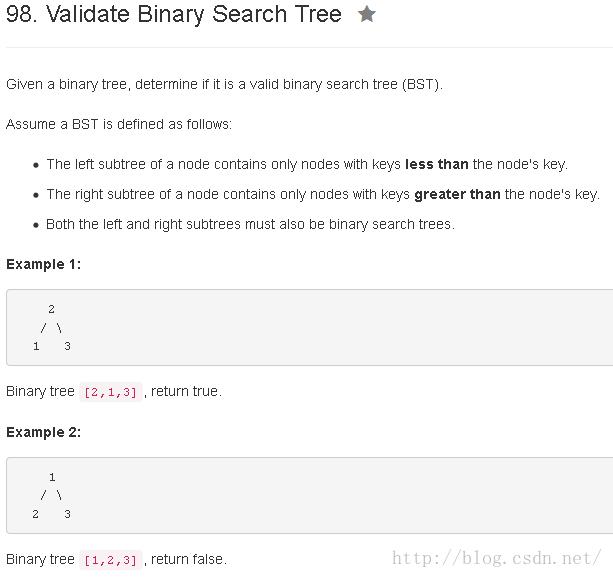
分析
方案一:中序遍历
因为二叉查找数的中序遍历是递增的,我们可以利用这个性质进行验证。
public class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
//查找树的中序遍历为递增的
if(root==null)return true;
TreeNode pre=null;//上一个节点
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.pop();
if(pre==null||pre.val<p.val){
pre=p;
}else{
return false;
}
if(p.right!=null){//处理右子树
p=p.right;
}else{//处理上一层
p=null;
}
}
return true;
}
}public class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);//验证树中节点的值域
}
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, long minVal, long maxVal) {
if (root == null) return true;
if (root.val >= maxVal || root.val <= minVal) return false;//检查根节点的值是否在值域内
//根据根节点的值,限定子树节点的值域
return isValidBST(root.left, minVal, root.val)
&& isValidBST(root.right, root.val, maxVal);
}
}分析
方案一:中序遍历
假如,正常的中序遍历结果为1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8。交换后的中序遍历结果变成1,7,3,4,5,6,2,8,我们如何找到两个颠倒位置的元素呢?
不难发现,重前往后第一个波峰,和从后往前第一个波谷。对于边界,假定最左边有个负无穷的元素,最右边有个正无穷的元素。
空间复杂度为O(n),时间复杂度为O(n)。
public class Solution {
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
//查找树的中序遍历为递增,先获取中序遍历,再定位交换位置
if(root==null)return ;
List<TreeNode> list=new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.pop();
list.add(p);
if(p.right!=null){//处理右子树
p=p.right;
}else{//处理上一层
p=null;
}
}
TreeNode firstNode=null;
TreeNode secondNode=null;
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){//从前往后找到第一个小大小
if(i==0){
if(list.get(i).val>list.get(i+1).val){
firstNode=list.get(i);
break;
}
}else{
if(list.get(i-1).val<list.get(i).val&&list.get(i).val>list.get(i+1).val){
firstNode=list.get(i);
break;
}
}
}
for(int i=list.size()-1;i>=0;i--){//从后往前找到第一个大小大
if(i==list.size()-1){
if(list.get(i-1).val>list.get(i).val){
secondNode=list.get(i);
break;
}
}else{
if(list.get(i-1).val>list.get(i).val&&list.get(i).val<list.get(i+1).val){
secondNode=list.get(i);
break;
}
}
}
int t=firstNode.val;firstNode.val=secondNode.val;secondNode.val=t;//交换
}
}方案二
方案一的解决思路非常直观,但是却需要O(n)的空间复杂度。如果能在中序遍历过程中标记错位的节点,空间复杂度就降为O(1)。
注:这里所说的O(1)空间复杂度,应该不考虑迭代过程中的栈空间,特此说明。

见讨论区:https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/2200/an-elegent-o-n-time-complexity-and-o-1-space-complexity-algorithm/2
public class Solution {
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
//查找树的中序遍历为递增,先获取中序遍历,再定位交换位置
if(root==null)return ;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode firstNode=null;
TreeNode secondNode=null;
TreeNode p=root;
TreeNode preNode=null;//前驱
TreeNode prePreNode=null;//前驱的前驱
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.pop();
if(preNode!=null){
//标记第一个小大小
if(firstNode==null&&preNode.val>p.val
&&(prePreNode==null||prePreNode.val<preNode.val)){
firstNode=preNode;
}
//标记最后一个大小大
if(prePreNode!=null){
if(prePreNode.val>preNode.val&&preNode.val<p.val){
secondNode=preNode;
}
}
if(p.right==null&&stack.isEmpty()){//最后一个节点特殊处理
if(preNode.val>p.val){
secondNode=p;
}
}
}
prePreNode=preNode;preNode=p;
if(p.right!=null){//处理右子树
p=p.right;
}else{//处理上一层
p=null;
}//这里为了阐述思路,其实可以简化为 p=p.right;
}
int t=firstNode.val;firstNode.val=secondNode.val;secondNode.val=t;//交换
}
}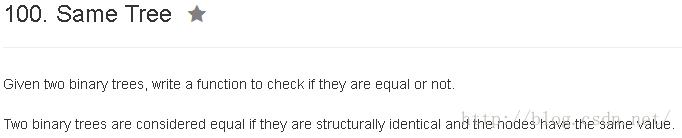
public class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null&&q==null)
return true;
if(p==null||q==null)
return false;
return p.val==q.val&&isSameTree(p.left,q.left)&&isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
}
递归版
public class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return root==null||isMirror(root.left,root.right);
}
private boolean isMirror(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p==null&&q==null)
return true;
if(p==null||q==null)
return false;
if(p.val!=q.val)
return false;
return isMirror(p.left,q.right)&&isMirror(p.right,q.left);
}
}
public class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode left, right;
if(root.left!=null){
if(root.right==null) return false;
stack.push(root.left);
stack.push(root.right);
}
else if(root.right!=null){
return false;
}
while(!stack.empty()){
if(stack.size()%2!=0) return false;
right = stack.pop();
left = stack.pop();
if(right.val!=left.val) return false;
if(left.left!=null){//左子树的左子树和右子树的右子树比较
if(right.right==null) return false;
stack.push(left.left);
stack.push(right.right);
}
else if(right.right!=null){
return false;
}
if(left.right!=null){//左子树的右子树和右子树的左子树比较
if(right.left==null) return false;
stack.push(left.right);
stack.push(right.left);
}
else if(right.left!=null){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}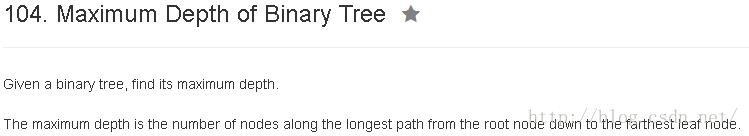
分析
递归版
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
return doMaxDepth(root);
}
public int doMaxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) return 1;
int leftDepth=doMaxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth=doMaxDepth(root.right);
return 1+Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
}二叉树的后序遍历(深度优先遍历)可以访问到所有从根节点出发的路径,我们只需要在遍历过程中记录最大深度即可。
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
Map<TreeNode,Boolean> visit=new HashMap<TreeNode,Boolean>(); //标记节点访问情况
if(root==null) return 0;
int max=1;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
max=Math.max(max, stack.size());//记录最大深度
p=stack.peek();
if(p.right!=null){
if(visit.get(p)==null){
visit.put(p, true);
p=p.right;
}
else{
visit.remove(p);//移除
stack.pop();
p=null;
}
}else{
stack.pop();
p=null;
}
}
return max;
}
}
public class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int n=preorder.length;
if(n==0)return null;
return doBuildTree(preorder,0,n-1,inorder,0,n-1);
}
public TreeNode doBuildTree(int[] preorder,int s1,int e1, int[] inorder,int s2,int e2){
if(e1<s1)return null;
int rootindex = 0;//根节点在中序序列中的位置
for(int i=s2;i<=e2;i++){
if(inorder[i]==preorder[s1]){
rootindex=i;
break;
}
}
int leftCount=rootindex-s2;//左子树节点个数
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[s1]);
root.left=doBuildTree(preorder,s1+1,s1+leftCount,inorder,s2,rootindex-1);
root.right=doBuildTree(preorder,s1+leftCount+1,e1,inorder,rootindex+1,e2);
return root;
}
}
public class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
int n=inorder.length;
if(n==0)return null;
return doBuildTree(inorder,0,n-1,postorder,0,n-1);
}
public TreeNode doBuildTree(int[] inorder,int s1,int e1, int[] postorder,int s2,int e2){
if(e1<s1)return null;
int rootindex = 0;
for(int i=s1;i<=e1;i++){
if(inorder[i]==postorder[e2]){
rootindex=i;
break;
}
}
int leftCount=rootindex-s1;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[e2]);
root.left=doBuildTree(inorder,s1,rootindex-1,postorder,s2,s2+leftCount-1);
root.right=doBuildTree(inorder,rootindex+1,e1,postorder,s2+leftCount,e2-1);
return root;
}
}
public class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
if(n==0)return null;
return doSortedArrayToBST(nums,0,n-1);
}
public TreeNode doSortedArrayToBST(int[] nums,int start,int end) {
if(end<start)return null;
int mid=(start+end)/2;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left=doSortedArrayToBST(nums,start,mid-1);
root.right=doSortedArrayToBST(nums,mid+1,end);
return root;
}
}
分析
基本思路不变。只是链表失去随机存取特性,寻找划分点的时候需要线性查找。
public class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
ListNode p=head;
int n=0;
while(p!=null){
p=p.next;
n++;
}
return buildBST(head,n);
}
private TreeNode buildBST(ListNode head,int length){
if(length==0)return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(-1);
if(length==1){
root.val=head.val;
return root;
}
int index=1;
int mid=(1+length)/2;
ListNode midNode=head;
while(index<mid){
midNode=midNode.next;
index++;
}
root.val=midNode.val;
root.left=buildBST(head,mid-1);
root.right=buildBST(midNode.next,length-mid);
return root;
}
}
public class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return lengthOfTree(root)!=-1;
}
private int lengthOfTree(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return 0;
int leftLength=lengthOfTree(root.left);
int rightLength=lengthOfTree(root.right);
if(leftLength==-1||rightLength==-1)return -1;
if(Math.abs(leftLength-rightLength)>1)return -1;
return Math.max(leftLength, rightLength)+1;
}
}
递归版
public class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
return doMinDepth(root);
}
public int doMinDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) return 1;
int leftDepth=doMinDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth=doMinDepth(root.right);
return 1+Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
}
public class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
Map<TreeNode,Boolean> visit=new HashMap<TreeNode,Boolean>();
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){//后续遍历
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.peek();
if(p.left==null&&p.right==null){
min=Math.min(min, stack.size());
}
if(p.right!=null){//具有右子树
if(visit.get(p)==null){//第一次出现在栈顶
visit.put(p, true);
p=p.right;
}
else{//第二次出现在栈顶
visit.remove(p);
stack.pop();
p=null;
}
}else{
stack.pop();
p=null;
}
}
return min;
}
}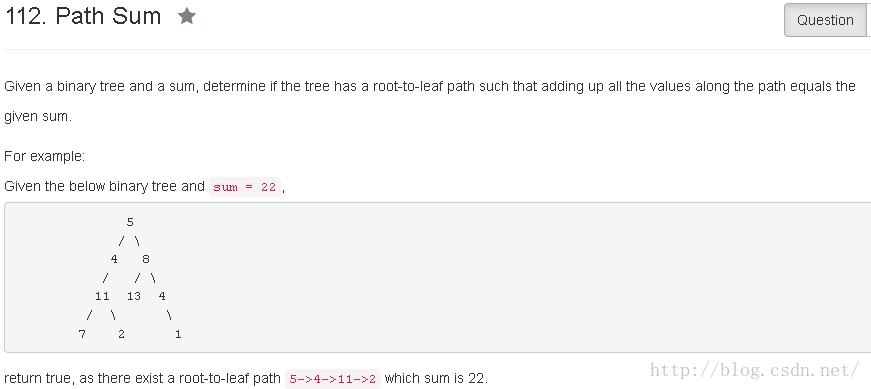
递归版
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root==null) return false;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null&&sum==root.val){
return true;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left,sum-root.val)||hasPathSum(root.right,sum-root.val);
}
}
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null){
return false;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
Map<TreeNode,Boolean> visit=new HashMap<TreeNode,Boolean>();
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode p=root;
int currentSum=0;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){//后续遍历
while(p!=null){
currentSum+=p.val;
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.peek();
if(p.left==null&&p.right==null){
if(currentSum==sum)return true;
}
if(p.right!=null){//具有右子树
if(visit.get(p)==null){//第一次出现在栈顶
visit.put(p, true);
p=p.right;
}
else{//第二次出现在栈顶
visit.remove(p);
stack.pop();
currentSum-=p.val;
p=null;
}
}else{
currentSum-=p.val;
stack.pop();
p=null;
}
}
return false;
}
}
递归版
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
pathSumUtil(paths, new ArrayList<Integer>(), root, sum);
return paths;
}
private void pathSumUtil(List<List<Integer>> paths, List<Integer> currList, TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
sum = sum - root.val;
currList.add(root.val);
if (sum == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
paths.add(new ArrayList<>(currList));//copy
}
pathSumUtil(paths, new ArrayList<>(currList), root.left, sum);
pathSumUtil(paths, new ArrayList<>(currList), root.right, sum);
}
}迭代版
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null) return res;
Map<TreeNode,Boolean> visit=new HashMap<TreeNode,Boolean>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
int nowSum=0;
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
nowSum+=p.val;
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.peek();
if(p.left==null&&p.right==null&&sum==nowSum){
List<Integer> r=new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(Object i:stack.toArray())
r.add((Integer)((TreeNode)i).val);
res.add(r);
}
if(p.right!=null){
if(visit.get(p)==null){
visit.put(p, true);
//第一次处理右子树
p=p.right;
}
else{
visit.remove(p);
nowSum-=p.val;
stack.pop();
p=null;
}
}else{
nowSum-=p.val;
stack.pop();
p=null;
}
}
return res;
}
}
分析
递归版
public class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return;
doFlatten(root);
}
private TreeNode doFlatten(TreeNode root){//保证root!=null ,返回尾部节点
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null)return root;
if(root.left==null){
TreeNode rightLast=doFlatten(root.right);
root.right=root.right;
root.left=null;
return rightLast;
}
if(root.right==null){
TreeNode leftLast=doFlatten(root.left);
root.right=root.left;
root.left=null;
return leftLast;
}
TreeNode leftLast=doFlatten(root.left);
TreeNode rightLast=doFlatten(root.right);
leftLast.right=root.right;
root.right=root.left;
root.left=null;
return rightLast;
}
}链表中的元素顺序即为先序遍历后的顺序。
public class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return;
List<TreeNode> list=new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
list.add(p);
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.pop();
p=p.right;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
TreeNode node=list.get(i);
node.left=null;
if(i==list.size()-1){
node.right=null;
}else{
node.right=list.get(i+1);
}
}
}
}

递归版
public class Solution {
public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) {
if(root==null)
return;
if(root.left!=null){
root.left.next=root.right;//将当前节点的左右子树关联
if(root.next != null)//将同一级别的相邻树关联
root.right.next = root.next.left;
} <pre name="code" class="java"> connect(root.right);
迭代版
我们可以层次遍历树,遍历过程中将同一级别的节点串联起来。
public class Solution {
public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) {
if(root==null) return;
LinkedList<TreeLinkNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeLinkNode>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<TreeLinkNode> list=new ArrayList<TreeLinkNode>(queue);
for(int i=0;i<list.size()-1;i++){//将同一级的节点串联
list.get(i).next=list.get(i+1);
}
LinkedList<TreeLinkNode> nextQueue=new LinkedList<TreeLinkNode>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeLinkNode node=queue.poll();
if(node.left!=null)nextQueue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)nextQueue.add(node.right);
}
queue=nextQueue;
}
}
}
递归版
public class Solution {
public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) {
if(root==null)
return;
//将当前节点的左右子树关联
if(root.left!=null){//
root.left.next=root.right;
}
//将同一级别的相邻树关联
TreeLinkNode pre=root.right!=null?root.right:root.left;
TreeLinkNode nextTree=root.next;//相邻树
TreeLinkNode post=null;
while(nextTree!=null&&post==null){
post=nextTree.left!=null?nextTree.left:nextTree.right;
nextTree=nextTree.next;
}
if(pre!=null){
pre.next=post;
}
connect(root.right);//这里的顺序很关键
connect(root.left); //这里的顺序很关键
}
}迭代版(与上一题相同)
public class Solution {
public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) {
if(root==null) return;
LinkedList<TreeLinkNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeLinkNode>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<TreeLinkNode> list=new ArrayList<TreeLinkNode>(queue);
for(int i=0;i<list.size()-1;i++){//将同一级的节点串联
list.get(i).next=list.get(i+1);
}
LinkedList<TreeLinkNode> nextQueue=new LinkedList<TreeLinkNode>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeLinkNode node=queue.poll();
if(node.left!=null)nextQueue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)nextQueue.add(node.right);
}
queue=nextQueue;
}
}
}
public class Solution {
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res=doMaxPathSum(root);
return res.get(1);
}
//结果集中,第一个元素表示单向路径最大和,第二个元素表示最大路径和
public List<Integer> doMaxPathSum(TreeNode root){
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root==null){
res.add(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
res.add(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
return res;
}
List<Integer> leftRes=doMaxPathSum(root.left);
List<Integer> rightRes=doMaxPathSum(root.right);
int maxPath=root.val;
if(Math.max(leftRes.get(0),rightRes.get(0))>0) maxPath+=Math.max(leftRes.get(0),rightRes.get(0));
res.add(maxPath);
int maxSum=root.val;
if(leftRes.get(0)>0)maxSum+=leftRes.get(0);
if(rightRes.get(0)>0)maxSum+=rightRes.get(0);
res.add(Math.max(maxSum,Math.max(leftRes.get(1),rightRes.get(1))));
return res;
}
}
方案一
public class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, 0);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return sum * 10 + root.val;
return dfs(root.left, sum * 10 + root.val) +
dfs(root.right, sum * 10 + root.val);
}
}
以上是关于广度优先深度优先搜索算法——面试题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章