Java 深浅拷贝
Posted 邗影
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java 深浅拷贝相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
2016-07-02
1深拷贝:不仅拷贝对象,而且对象所引用地址的内容一块拷贝。改变一个对象的某个属性,并不影响另一个对象所引用的内容。
2浅拷贝:仅拷贝对象本身,并不对所引用(所指的)内容进行拷贝,当对一个对象做改变的时候,另一个对象的相应属性也做同样的改变。
3深拷贝要重写clone函数。implements Cloneable。
浅拷贝:
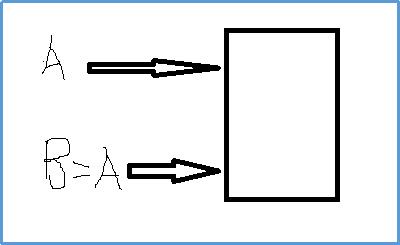
深拷贝
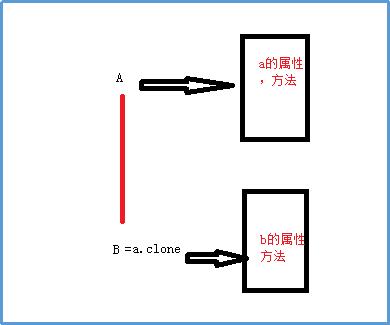
这个代码是借鉴的(记得是这样的,标注---借鉴资源)
class Professor0 implements Cloneable { String name; int age; Professor0(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone();//调用父类的 } } class Student0 implements Cloneable { String name;// 常量对象。 int age; Professor0 p;// 学生1和学生2的引用值都是一样的。 Student0(String name, int age, Professor0 p) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.p = p; } /* public Object clone() { Student0 o = null; try { o = (Student0) super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); } return o; }*/ } public class qiancopy { public static void main(String[] args) { Professor0 p = new Professor0("perfesser0", 50); Student0 s1 = new Student0("stu1", 18, p); System.out.println("学生s1的姓名:" + s1.name + "\\n学生s1教授的姓名:" + s1.p.name + "," + "\\n学生s1教授的年纪" + s1.p.age+"......end");// 学生1的教授 Student0 s2 =s1; s2.p.name = "s2copys"; s2.p.age = 30; s2.name = "s2"; s2.age = 45; System.out.println("学生s1的姓名:" + s1.name+ "\\n学生s1的年龄:" + s1.age + "\\n学生s1教授的姓名:" + s1.p.name + "," + "\\n学生s1教授的年纪" + s1.p.age+"...end"); System.out.println("学生s2的姓名:" + s2.name+ "\\n学生s2的年龄:" + s2.age + "\\n学生s2教授的姓名:" + s2.p.name + "," + "\\n学生s2教授的年纪" + s2.p.age+"...end");// 学生1的教授 } }
class Professor implements Cloneable { String name; int age; Professor(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Object clone() { Object o = null; try { o = super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); } return o; } } class Student implements Cloneable { String name; int age; Professor p; Student(String name, int age, Professor p) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.p = p; } public Object clone() { Student o = null; try { o = (Student) super.clone();//stu 深拷贝 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); } o.p = (Professor) p.clone();//professer深拷贝 return o; } } public class shencopy { public static void main(String args[]) { Professor p = new Professor("professer1", 50); Student s1 = new Student("stu1", 18, p); System.out.println("学生s1的姓名:" + s1.name+ "\\n学生s1的年龄:" + s1.age + "\\n学生s1教授的姓名:" + s1.p.name + "," + "\\n学生s1教授的年纪" + s1.p.age+"......end");// 学生1的教授 Student s2 = (Student) s1.clone(); s2.name = "s2copys"; s2.age = 30; s2.p.name = "stu2"; s2.p.age = 30; System.out.println("学生s1的姓名:" + s1.name+ "\\n学生s1的年龄:" + s1.age + "\\n学生s1教授的姓名:" + s1.p.name + "," + "\\n学生s1教授的年纪" + s1.p.age+"......end");// 学生1的教授 System.out.println("学生s2的姓名:" + s2.name+ "\\n学生s2的年龄:" + s2.age + "\\n学生s2教授的姓名:" + s2.p.name + "," + "\\n学生s2教授的年纪" + s2.p.age+"......end");// 学生2的教授 } }
以上是关于Java 深浅拷贝的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章