1, sync_with_stdio(), tie()的应用
Posted let_go
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了1, sync_with_stdio(), tie()的应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、sync_with_stdio()
这个函数是一个“是否兼容stdio”的开关,C++为了兼容C,保证程序在使用了std::printf和std::cout的时候不发生混乱,将输出流绑在了一起。
在IO之前将stdio接触绑定,可以大大提高IO效率。在操作大数据时,cin,cout的速率也能很快了。
现在,我们通过比较解除绑定前后cin,printf的速率来实际体验下sync_with_stdio()的作用。
首先,我们先产生1000万个随机数作为测试数据。然后,分别用cin,scanf来读取数据,比较其效率
- data.cpp,产生1000万个随机数存贮在data.txt中,大概55M左右
 View Code1 /* 2 本程序实现的功能: 3 生成1000万个可能重复的随机数,用作测试数据 4 并计算生成这些数据所用的时间 5 */ 6 #include <iostream> 7 #include <ctime> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define SELF_RAND_MAX 0x7FFFFFFF 10 int main() 11 { 12 13 clock_t start_time = clock(); 14 15 srand(unsigned(time(0))); 16 17 const int MAX = 10000000; 18 const int MIN = 1000; 19 20 freopen("data.txt","w",stdout); 21 22 for(int i = 0; i < 10000000; ++i){ 23 unsigned long data = rand() % (MAX - MIN + 1) + MIN; 24 cout << data << \' \'; 25 } 26 fclose(stdout); 27 freopen("time.txt","w",stdout); 28 cout << endl 29 << "---the end---" 30 << endl; 31 //CLOCKS_PER_SEC控制精度,在windows环境下是1000,linux下是多少? 32 //简单地说windows下是毫秒级,而linux下好像是纳秒级 33 cout << "elapsed time:" << double(clock() - start_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC 34 << \'s\' << endl; 35 fclose(stdout); 36 }
View Code1 /* 2 本程序实现的功能: 3 生成1000万个可能重复的随机数,用作测试数据 4 并计算生成这些数据所用的时间 5 */ 6 #include <iostream> 7 #include <ctime> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define SELF_RAND_MAX 0x7FFFFFFF 10 int main() 11 { 12 13 clock_t start_time = clock(); 14 15 srand(unsigned(time(0))); 16 17 const int MAX = 10000000; 18 const int MIN = 1000; 19 20 freopen("data.txt","w",stdout); 21 22 for(int i = 0; i < 10000000; ++i){ 23 unsigned long data = rand() % (MAX - MIN + 1) + MIN; 24 cout << data << \' \'; 25 } 26 fclose(stdout); 27 freopen("time.txt","w",stdout); 28 cout << endl 29 << "---the end---" 30 << endl; 31 //CLOCKS_PER_SEC控制精度,在windows环境下是1000,linux下是多少? 32 //简单地说windows下是毫秒级,而linux下好像是纳秒级 33 cout << "elapsed time:" << double(clock() - start_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC 34 << \'s\' << endl; 35 fclose(stdout); 36 }
- test.cpp, 测试程序,读取data.txt中的数据,比较cin, printf的效率
 View Code1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <ctime> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void scanf_read(); 6 void cin_read(); 7 8 const int MAXIN = 10000000; 9 int numbers[MAXIN]; 10 11 int main () { 12 iostream::sync_with_stdio(false); 13 cin.tie(nullptr); 14 cout.tie(nullptr); 15 clock_t start_time = clock(); 16 //do something 17 scanf_read(); 18 //cin_read(); 19 cout << "read time:" 20 << double(clock() - start_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC 21 << endl; 22 } 23 24 void scanf_read() { 25 freopen("data.txt","r",stdin); 26 for (int i = 0; i < MAXIN; ++i) { 27 scanf("%d", &numbers[i]); 28 } 29 } 30 31 32 void cin_read() { 33 freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin); 34 for (int i = 0; i < MAXIN; ++i) { 35 cin >> numbers[i]; 36 } 37 }
View Code1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <ctime> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void scanf_read(); 6 void cin_read(); 7 8 const int MAXIN = 10000000; 9 int numbers[MAXIN]; 10 11 int main () { 12 iostream::sync_with_stdio(false); 13 cin.tie(nullptr); 14 cout.tie(nullptr); 15 clock_t start_time = clock(); 16 //do something 17 scanf_read(); 18 //cin_read(); 19 cout << "read time:" 20 << double(clock() - start_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC 21 << endl; 22 } 23 24 void scanf_read() { 25 freopen("data.txt","r",stdin); 26 for (int i = 0; i < MAXIN; ++i) { 27 scanf("%d", &numbers[i]); 28 } 29 } 30 31 32 void cin_read() { 33 freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin); 34 for (int i = 0; i < MAXIN; ++i) { 35 cin >> numbers[i]; 36 } 37 }运行结果(win7 32 i3处理器,mingw 4.9.2):
- 解除绑定前
通过scanf来读取1000万个随机数需要的时间:16.323s
通过cin来读取1000万个随机数需要的时间:24.361s
我们可以看到,cin的读取时间整整比scanf满了8秒。
- 解除绑定后
通过scanf读取1000万个数据需要的时间:16.29s。
通过cin来读取1000万个随机数需要的时间:4.946s,我们看到cin的读取时间整整缩短了20秒,比scanf的读取时间还快乐10秒。
- 解除绑定,并cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr)
通过cin来读取1000万个随机数需要的时间:4.861s,数值上来看,比只解除绑定好像快了一丢丢。但效果不明显。这里提到了tie()函数,下面就来看看tie()函数。
二、tie()
tie()用来绑定stream,空参数则返回当前的输出流指针。
直接上程序,看看其是如何表现的。
- tie.cpp, 测试tie的实现效果。
 View Code1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <fstream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main () { 6 ostream *prevstr; 7 ofstream ofs; 8 9 ofs.open("test.txt"); 10 cout << "Output to the screen" << endl; 11 12 *cin.tie() << "Output to the screem, too" << endl; //null parameters, return the default output stream, i.e. cout 13 14 prevstr = cin.tie(&ofs); // cin bind to ofs, and return the pre output stream, i.e. cout 15 *cin.tie() << "Output to the file, test.txt" << endl; 16 17 *cin.tie(prevstr) << "Output to the file, too"; 18 *cin.tie() << "Output to the screen, again"; 19 20 ofs.close(); 21 22 return 0; 23 24 }
View Code1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <fstream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main () { 6 ostream *prevstr; 7 ofstream ofs; 8 9 ofs.open("test.txt"); 10 cout << "Output to the screen" << endl; 11 12 *cin.tie() << "Output to the screem, too" << endl; //null parameters, return the default output stream, i.e. cout 13 14 prevstr = cin.tie(&ofs); // cin bind to ofs, and return the pre output stream, i.e. cout 15 *cin.tie() << "Output to the file, test.txt" << endl; 16 17 *cin.tie(prevstr) << "Output to the file, too"; 18 *cin.tie() << "Output to the screen, again"; 19 20 ofs.close(); 21 22 return 0; 23 24 }运行结果(环境同一):
控制台输出:
Output to the screen Output to the screen, too Output to the screen, again文件输出:
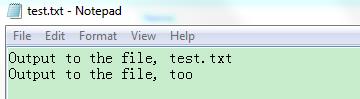
对照程序结果,我们可以很清楚的明白tie()的作用。就不多讲了。
PS:Open live writer怎么添加“代码插入”插件啊!!!看见有人用SyntaxHighlighter,自己折腾半天也没把SyntaxHighlighter和Open live writer整合在一起,傻傻的在网页上编辑。
以上是关于1, sync_with_stdio(), tie()的应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
