69.Android之天气预报app
Posted chaoer
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了69.Android之天气预报app相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
最近买了本书《android第一行代码》,通篇看了下感觉不错,书本最后有个实战项目酷欧天气,闲来无事就照着敲了一遍代码,主要在请求天气接口和背景优化做了些小改动,现在来记录下。
(1) android studio完成代码目录结构
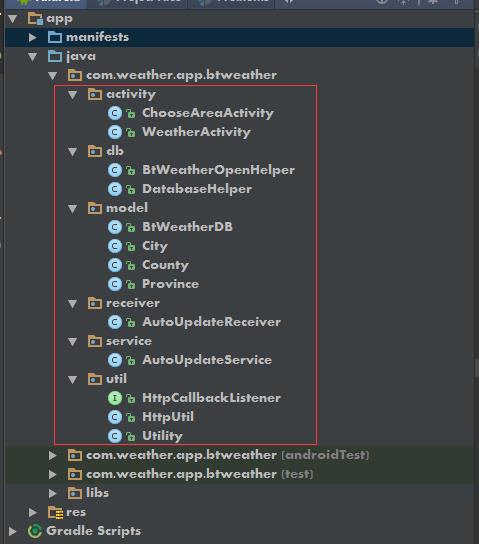
其中activity包存放天气所有活动有关的代码,db包用于存放所有数据库相关的代码,model包存放所有模型相关的代码,receiver包用于存放所有广播接收器相关的代码,service包用于存放所有服务相关的代码,util包用于存放所有工具相关的代码。
(2) 创建好数据库和表
在db包下新建一个BtWeatherOpenHelper类,这里我准备建立三张表,Provice、City、County,分别用于存放省、市、县,代码如下:
1 public class BtWeatherOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper { 2 3 /** 4 * Province表建表语句 5 */ 6 public static final String CREATE_PROVINCE = "create table Province (" 7 + "id integer primary key autoincrement," 8 + "province_name text," 9 + "province_code text)"; 10 11 /** 12 * City表建表语句 13 */ 14 public static final String CREATE_CITY = "create table City (" 15 + "id integer primary key autoincrement," 16 + "city_name text, " 17 + "city_code text, " 18 + "province_id integer)"; 19 20 /** 21 * County表建表语句 22 */ 23 public static final String CREATE_COUNTY = "create table County (" 24 + "id integer primary key autoincrement, " 25 + "county_name text, " 26 + "county_code text, " 27 + "city_id integer)"; 28 29 30 public BtWeatherOpenHelper(Context context, String name, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int version) { 31 super(context, name, factory, version); 32 } 33 34 @Override 35 public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) { 36 db.execSQL(CREATE_PROVINCE); // 创建Province表 37 db.execSQL(CREATE_CITY); // 创建City表 38 db.execSQL(CREATE_COUNTY); // 创建County表 39 } 40 41 @Override 42 public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) { 43 44 } 45 }
对于Province建表语句里,其中id是自增长主键,province_name表示省名,province_code表示省级代号;
对于City建表语句里,其中id是自增长主键,city_name表示城市名,city_code表示市级代号,province_id是City表关联Province表的外键;
对于County建表语句里,其中id是自增长主键,county_name表示县名,county_code表示县级代号,city_id是County表关联City表的外键。
接下来我们要在每张表写一个对应的实体类,这样方便我们后续的开发工作。因此,在model包下新建一个Province类,如下:
1 public class Province { 2 private int id; 3 private String provinceName; 4 private String provinceCode; 5 6 7 public int getId() { 8 return id; 9 } 10 11 public void setId(int id) { 12 this.id = id; 13 } 14 15 public String getProvinceName() { 16 return provinceName; 17 } 18 19 public void setProvinceName(String provinceName) { 20 this.provinceName = provinceName; 21 } 22 23 public String getProvinceCode() { 24 return provinceCode; 25 } 26 27 public void setProvinceCode(String provinceCode) { 28 this.provinceCode = provinceCode; 29 } 30 }
同理也在model包下新建一个City和County类,可以看到实体类的内容非常简单,基本就是生成数据库表对应字段的get和set方法就可以了。接着我们还需要创建一个BtWeatherDB类,这个类会把一些常用的数据库操作封装起来,以方便我们后面实用,代码如下:
1 public class BtWeatherDB { 2 /** 3 * 数据库名 4 */ 5 public static final String DB_NAME = "Bt_weather"; 6 7 /** 8 * 数据库版本 9 */ 10 public static final int VERSION = 1; 11 private static BtWeatherDB btWeatherDB; 12 private SQLiteDatabase db; 13 14 /** 15 * 将构造方法私有化 16 */ 17 private BtWeatherDB(Context context){ 18 BtWeatherOpenHelper dbHelper = new BtWeatherOpenHelper(context,DB_NAME,null,VERSION); 19 db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase(); 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 获取BtWeatherDB的实例 24 */ 25 public synchronized static BtWeatherDB getInstance(Context context){ 26 if (btWeatherDB == null){ 27 btWeatherDB = new BtWeatherDB(context); 28 } 29 return btWeatherDB; 30 } 31 32 /** 33 * 将Province实例存储到数据库 34 */ 35 public void saveProvince(Province province){ 36 if (province != null){ 37 ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); 38 values.put("province_name",province.getProvinceName()); 39 values.put("province_code",province.getProvinceCode()); 40 db.insert("Province",null,values); 41 } 42 } 43 44 /** 45 * 从数据库获取全国所有省份信息 46 */ 47 public List<Province> loadProvince(){ 48 List<Province> list = new ArrayList<Province>(); 49 Cursor cursor = db.query("Province",null,null,null,null,null,null); 50 if (cursor.moveToFirst()){ 51 do{ 52 Province province = new Province(); 53 province.setId(cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("id"))); 54 province.setProvinceName(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("province_name"))); 55 province.setProvinceCode(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("province_code"))); 56 list.add(province); 57 } while(cursor.moveToNext()); 58 } 59 if (cursor != null){ 60 cursor.close(); 61 } 62 return list; 63 } 64 65 /** 66 * 将City实例存储到数据库 67 */ 68 public void saveCity(City city){ 69 if (city != null){ 70 ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); 71 values.put("city_name",city.getCityName()); 72 values.put("city_code",city.getCityCode()); 73 values.put("province_id",city.getProvinceId()); 74 db.insert("City",null,values); 75 } 76 } 77 78 /** 79 * 将数据库读取某省下所有的城市信息 80 */ 81 public List<City> loadCities(int provinceId){ 82 List<City> list = new ArrayList<City>(); 83 Cursor cursor = db.query("City",null,"province_id = ?", 84 new String[]{String.valueOf(provinceId)},null,null,null); 85 86 if (cursor.moveToFirst()){ 87 do{ 88 City city = new City(); 89 city.setId(cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("id"))); 90 city.setCityName(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("city_name"))); 91 city.setCityCode(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("city_code"))); 92 city.setProvinceId(provinceId); 93 list.add(city); 94 }while (cursor.moveToNext()); 95 } 96 if (cursor != null){ 97 cursor.close(); 98 } 99 return list; 100 } 101 102 /** 103 * 将County实例存储到数据库 104 */ 105 public void saveCounty(County county){ 106 if (county != null){ 107 ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); 108 values.put("county_name",county.getCountyName()); 109 values.put("county_code",county.getCountyCode()); 110 values.put("city_id",county.getCityId()); 111 db.insert("County",null,values); 112 } 113 } 114 115 /** 116 * 从数据库读取某城市下所有的县信息 117 */ 118 public List<County> loadCounties(int cityId){ 119 List<County> list = new ArrayList<County>(); 120 Cursor cursor = db.query("County",null,"City_id = ?", 121 new String[] {String.valueOf(cityId)},null,null,null); 122 if (cursor.moveToFirst()){ 123 do{ 124 County county = new County(); 125 county.setId(cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("id"))); 126 county.setCountyName(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("county_name"))); 127 county.setCountyCode(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("county_code"))); 128 county.setCityId(cityId); 129 list.add(county); 130 } while(cursor.moveToNext()); 131 } 132 if (cursor != null){ 133 cursor.close(); 134 } 135 return list; 136 } 137 }
从上面可以看到,BtWeatherDB是一个单例类,我们将它的构造方法私有化,并提供一个getInstance()方法来获取BtWeatherDB的实例,这样就可以保证全局范围内只有一个BtWeathereDB的实例。接下来我们在BtWeatherDB中提供了六组方法,saveProvince()、loadProvince()、saveCity()、loadCities()、saveCounty()、loadCounties(),分别用于存储省份数据、读取所有省份数据、存储城市数据、读取某省内所有城市数据、存储县数据、读取某市内所有县的数据。
(3) 遍历全国省市县数据
我们知道,全国省市县的数据都是通过网络请求服务器端获得的,因此这里和服务器的交互必不可少,所以我们在util包下先增加一个HttpUtil类,代码如下:
1 public class HttpUtil { 2 public static void sendHttpRequest(final String address, final HttpCallbackListener listener){ 3 new Thread( new Runnable() { 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 HttpURLConnection connection = null; 7 try{ 8 URL url = new URL(address); 9 connection = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection(); 10 connection.setRequestMethod("GET"); 11 connection.setConnectTimeout(8000); 12 connection.setReadTimeout(8000); 13 InputStream in = connection.getInputStream(); 14 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in)); 15 StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder(); 16 String line; 17 while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null){ 18 response.append(line); 19 } 20 if (listener != null){ 21 // 回调onFinish()方法 22 listener.onFinish(response.toString()); 23 } 24 }catch (Exception e){ 25 if (listener != null){ 26 // 回调onError()方法 27 listener.onError(e); 28 } 29 }finally { 30 if (connection != null){ 31 connection.disconnect(); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }).start(); 36 } 37 }
HttpUtil类中使用到了HttpCallbackListener接口来回调服务返回的结果,因此我们需要在util包下添加这个接口,如下:
1 public interface HttpCallbackListener { 2 void onFinish(String response); 3 4 void onError(Exception e); 5 }
另外,由于服务器返回的省市县数据都是“代号|城市,代号|城市”这种格式的,所以我们最好在提供一个工具类来解析和处理这种数据,故在util包下新建一个Utility类,代码如下:
1 public class Utility { 2 3 /** 4 * 解析和处理服务器返回的省级数据 5 */ 6 public synchronized static boolean handleProvinceResponse(BtWeatherDB btWeatherDB,String response){ 7 if (!(TextUtils.isEmpty(response))){ 8 String[] allProvince = response.split(","); 9 if (allProvince != null && allProvince.length > 0){ 10 for (String p : allProvince){ 11 String[] array = p.split("\\\\|"); 12 Province province = new Province(); 13 province.setProvinceCode(array[0]); 14 province.setProvinceName(array[1]); 15 // 将解析出来的数据存储到Province类 16 btWeatherDB.saveProvince(province); 17 } 18 return true; 19 } 20 } 21 return false; 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * 解析和处理服务器返回的市级数据 26 */ 27 public static boolean handleCitiesResponse(BtWeatherDB btWeatherDB,String response,int provinceId){ 28 if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(response)){ 29 String[] allCities = response.split(","); 30 if (allCities != null && allCities.length > 0){ 31 for (String c: allCities){ 32 String[] array = c.split("\\\\|"); 33 City city = new City(); 34 city.setCityCode(array[0]); 35 city.setCityName(array[1]); 36 city.setProvinceId(provinceId); 37 // 将解析出来的数据存储到City类 38 btWeatherDB.saveCity(city); 39 } 40 return true; 41 } 42 } 43 return false; 44 } 45 46 /** 47 * 解析和处理服务器返回的县级数据 48 */ 49 public static boolean handleCountiesResponse(BtWeatherDB btWeatherDB,String response,int CityId){ 50 if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(response)){ 51 String[] allCounties = response.split(","); 52 if (allCounties != null && allCounties.length > 0){ 53 for (String c: allCounties){ 54 String[] array = c.split("\\\\|"); 55 County county = new County(); 56 county.setCountyCode(array[0]); 57 county.setCountyName(array[1]); 58 county.setCityId(CityId); 59 btWeatherDB.saveCounty(county); 60 } 61 return true; 62 } 63 } 64 return false; 65 } 66 67 /** 68 * 解析服务器返回的JSON数据,并将解析出的数据存储到本地 69 */ 70 public static void handleWeatherResponse(Context context,String response){ 71 try{ 72 JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(response); 73 JSONObject weatherInfo = jsonObject.getJSONObject("weatherinfo"); 74 String cityName = weatherInfo.getString("city"); 75 String weatherCode = weatherInfo.getString("cityid"); 76 String temp1 = weatherInfo.getString("temp1"); 77 String temp2 = weatherInfo.getString("temp2"); 78 String weatherDesp = weatherInfo.getString("weather"); 79 String publishTime = weatherInfo.getString("ptime"); 80 saveWeatherInfo(context, cityName, weatherCode, temp1, temp2, weatherDesp, publishTime); 81 } catch (JSONException e){ 82 e.printStackTrace(); 83 } 84 } 85 86 /** 87 * 将服务器返回的所有的天气信息存储到SharePreferences文件中 88 */ 89 public static void saveWeatherInfo(Context context, String cityName, String weatherCode, String temp1, String temp2, 90 String weatherDesp, String publishTime){ 91 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年M月d日", Locale.CANADA); 92 SharedPreferences.Editor editor = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(context).edit(); 93 editor.putBoolean("city_selected",true); 94 editor.putString("city_name",cityName); 95 editor.putString("weather_code",weatherCode); 96 editor.putString("temp1",temp1); 97 editor.putString("temp2",temp2); 98 editor.putString("weather_desp",weatherDesp); 99 editor.putString("publish_time",publishTime); 100 editor.putString("current_date",sdf.format(new Date())); 101 editor.commit(); 102 } 103 }
可以看到,我们提供了 handleProvinceResponse()、handleCitiesResponse()、handleCountiesResponse()、handleWeatherResponse()、saveWeatherInfo()这五个方法,分别用于解析和处理服务器返回的省级、市级、县级数据,用于JSON格式的天气信息解析出来和保存天气信息到文件里。
然后我们写下界面,在res/layout目录中新建choose_area.xml布局,代码如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical"> 6 7 <RelativeLayout 8 android:layout_width="match_parent" 9 android:layout_height="50dp" 10 android:background="#484E61"> 11 12 <TextView 13 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 14 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 15 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 16 android:textColor="#fff" 17 android:textSize="24sp" 18 android:id="@+id/title_text"/> 19 </RelativeLayout> 20 21 <ListView 22 android:layout_width="match_parent" 23 android:layout_height="match_parent" 24 android:id="@+id/list_view"> 25 </ListView> 26 27 </LinearLayout>
接下来最关键一步,就是要编写用于遍历省市县数据的活动了,在activity包下新建ChooseAreaActivity继承于Activity,代码如下:
1 public class ChooseAreaActivity extends Activity { 2 3 以上是关于69.Android之天气预报app的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章