Android Programming: Pushing the Limits -- Chapter 6: Services and Background Tasks
Posted yarightok
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android Programming: Pushing the Limits -- Chapter 6: Services and Background Tasks相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
什么时候使用Service:

@、任何与用户界面无关的操作,可移到后台线程,然后由一个Service来控制这个线程。
服务类型:
@、First is the one that performs work for the application independent of the user’s input.
如:后台执行的音乐播放器。
@、The other type of Service is one that’s directly triggered by an action from the user.
如:照片分享应用的拍照上传服务。 完成后系统自动终止服务。
@、Service的生命周期:
1、 对于Service来说,总是会被执行的两个回调方法:onCreate和onDestroy。
2、 在onCreate中完成大部分初始化工作,在onDestroy中完成大部分清理工作。
3、 由于onCreate,onDestroy都是在主线程执行,应此要把长时间运行的操作移到后台线程中。
开启服务:
@、Context.startService:

1、 如果需要提供给外部调用,则需要配置intent-filter。
2、 调用Context.startService会触发onStartCommand,系统根据onStartCommand的返回值决定服务被关闭后是否重启。
3、 START_STICKY:系统因某些原因,如内存不足,关闭服务,如果服务的onStartCommand返回START_STICKY,则系统会重启服务,不过参数Intent传入的是null。这种情况,可能需要在onDestroy中对数据进行保存。(音乐播放器)
4、 START_NOT_STICKY:服务被系统关闭后,不会被重启。(上传服务)
5、 START_REDELIVER_INTENT:类似START_STICKY,但是参数Intent传入的是初始的Intent。
6、 可通过BroadcastReceiver方式将结果回馈给Activity。
7、 此方式需要通过调用Service.stopSelf()或者Context.stopService()来停止服务。
8、 实例,演示Service.stopSelf()

public class MyMusicPlayer extends Service implements MediaPlayer.OnCompletionListener{ public static final String ACTION_ADD_TO_QUEUE = "com.example.lsp.myactivity.ADD_TO_QUEUE"; private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Uri> mTrackQueue; private MediaPlayer mMediaPlayer; public IBinder onBind(Intent intent){ return null; } @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); mTrackQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Uri>(); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { String action = intent.getAction(); if(ACTION_ADD_TO_QUEUE.equals(action)){ Uri trackUri = intent.getData(); addTrackToQueue(trackUri); } return START_NOT_STICKY; } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); if(mMediaPlayer != null){ mMediaPlayer.release(); mMediaPlayer = null; } } /** * Add track to end of queue if already palying, * otherwise create a new MediaPlayer and start playing. */ private synchronized void addTrackToQueue(Uri trackUri){ if(mMediaPlayer == null){ try{ mMediaPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(this, trackUri); mMediaPlayer.setOnCompletionListener(this); mMediaPlayer.prepare(); mMediaPlayer.start(); }catch (IOException e){ stopSelf(); } }else{ mTrackQueue.offer(trackUri); } } // Track completed, start playing next or stop service... @Override public void onCompletion(MediaPlayer mp) { mMediaPlayer.reset(); Uri nextTrackUri = mTrackQueue.poll(); if(nextTrackUri != null){ try{ mMediaPlayer.setDataSource(this, nextTrackUri); mMediaPlayer.prepare(); mMediaPlayer.start(); }catch (IOException e){ stopSelf(); } }else{ stopSelf(); } } }
@、Context.bindService:
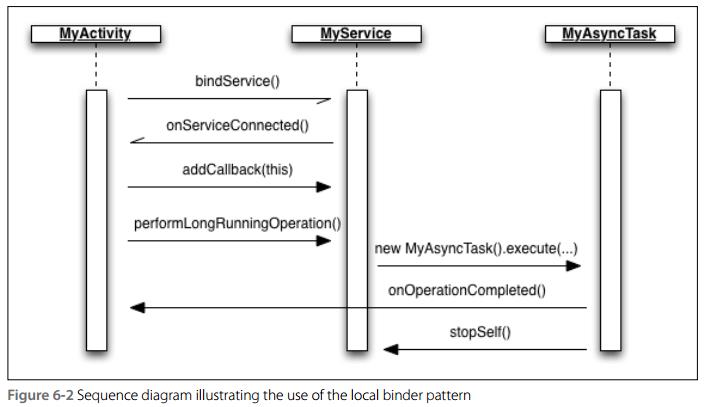
1、 此方法用于同一应用内组件拥有Service对象,然后通过Service对象直接访问Service方法。这种方式叫local binder。
2、 如果是跨应用调用Service,则需要AIDL。
3、 任何不属于当前前台运行的应用的Service都有可能被系统终止掉(为了free RAM)。想要在用户退出应用后,Service能够进行运行,可调用Service.startForeground()方法。
4、 当最后一个client断开连接(Context.unbindService()),服务将自动停止,除非在对后一个client断开连接后调用Service.startForeground()来保持Service alive。这也是为什么正确地调用Service.stopForeground()如此重要。
后台运行:
@、IntentService:
1、 IntentService通过Handler的方式来实现后台运行。
2、 自定义Service继承IntentService,实现onHandleIntent方法:根据入参Intent的action(intent.getAction()),实现多action的切换。
3、 多次调用时,以队列的方式处理,即onHandleIntent一次只处理一个intent。
4、 实例:

public class MyIntentService extends IntentService { private static final String NAME = MyIntentService.class.getSimpleName(); public static final String ACTION_UPLOAD_PHOTO = "com.example.lsp.myactivity.UPLOAD_PHOTO"; public static final String EXTRA_PHOTO = "bitmapPhoto"; public static final String ACTION_SEND_MASSAGE = "com.example.lsp.myactivity.SEND_MESSAGE"; public static final String EXTRA_MESSAGE = "messageText"; public static final String EXTRA_RECIPIENT = "messageRecipient"; public MyIntentService(){ super(NAME); // We don\'t want intents redelivered in case we\'re shut down unexpectedly setIntentRedelivery(false); } /** * This methos is executed on its own thread, one intent at a time... */ @Override protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) { String action = intent.getAction(); if(ACTION_SEND_MASSAGE.equals(action)){ String messageText = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_MESSAGE); String messageRecipient = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_RECIPIENT); sendMessage(messageRecipient, messageText); }else if(ACTION_UPLOAD_PHOTO.equals(action)){ Bitmap photo = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_PHOTO); uploadPhoto(photo); } } private void sendMessage(String messageRecipient, String messageText){ // TODO Make network call... // TODO Send a broadcast that operation is completed } private void uploadPhoto(Bitmap photo){ // TODO Make network call... // TODO Send a broadcast that operation is completed //sendBroadcast(new Intent(BROADCAST_UPLOAD_COMPLETED)); } }
@、ExecutorService:
1、 实现操作并行执行。
2、 自定义服务类,继承Service类。
3、 添加ExecutorService对象作为成员变量。
4、 在自定义服务类中创建私有类,并实现Runnable接口,由此类来完成具体的功能操作。
5、 在onStartCommand()方法中通过ExecutorSerive的execute方法执行操作。
6、 实例:

public class MediaTranscoder extends Service { private static final int NOTIFICATION_ID = 1001; public static final String ACTION_TRANSCODE_MEDIA = "com.example.lsp.myactivity.TRANSCODE_MEDIA"; public static final String EXTRA_OUTPUT_TYPE = "outputType"; private ExecutorService mExecutorService; private int mRunningJobs = 0; private final Object mLock = new Object(); private boolean mIsForeground = false; public IBinder onBind(Intent intent){ return null; } @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); mExecutorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { String action = intent.getAction(); if(ACTION_TRANSCODE_MEDIA.equals(action)){ String outputType = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_OUTPUT_TYPE); // Start new job and increase the running job counter synchronized(mLock){ TranscodeRunnable transcodeRunnable = new TranscodeRunnable(intent.getData(), outputType); mExecutorService.execute(transcodeRunnable); mRunningJobs++; startForegroundIfNeeded(); } } return START_NOT_STICKY; } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); mExecutorService.shutdownNow(); synchronized (mLock){ mRunningJobs = 0; stopForegroundIfAllDone(); } } public void startForegroundIfNeeded(){ if(!mIsForeground){ Notification notification = buildNotificatin(); startForeground(NOTIFICATION_ID, notification); mIsForeground = true; } } private Notification buildNotificatin(){ Notification notification = null; // TODO Build the notification here return notification; } private void stopForegroundIfAllDone(){ if(mRunningJobs == 0 && mIsForeground){ stopForeground(true); mIsForeground = false; } } private class TranscodeRunnable implements Runnable{ private Uri mInData; private String mOutputType; private TranscodeRunnable(Uri inData, String outputType){ mInData = inData; mOutputType = outputType; } @Override public void run() { // TODO Perform transcoding here... //Decrease counter when we\'re done.. synchronized (mLock){ mRunningJobs--; stopForegroundIfAllDone(); } } } }
服务通信:
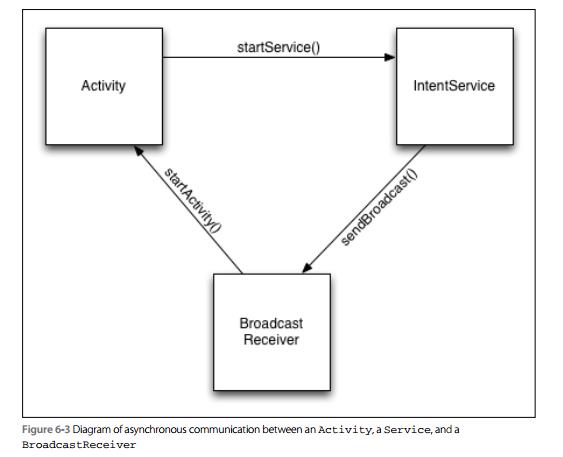
@、使用BroadcastReceiver的方式
@、在bindService()模式的基础上,增加回调接口来实现通信
1、实例:

public class MyLocalService extends Service { private static final int NOTIFICATION_ID = 1001; private LocalBinder mLocalBinder = new LocalBinder(); private Callback mCallback; public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return mLocalBinder; } public void performLongRunningOperation(MyComplexDataObject dataObject) { new MyAsyncTask().execute(dataObject); } public void setCallback(Callback callback) { mCallback = callback; } public class LocalBinder extends Binder { public MyLocalService getService() { return MyLocalService.this; } } public interface Callback { void onOperationProgress(int progress); void onOperationCompleted(MyComplexResult complexResult); } private final class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<MyComplexDataObject, Integer, MyComplexResult> { @Override protected void onPreExecute() { super.onPreExecute(); startForeground(NOTIFICATION_ID, buildNotification()); } @Override protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) { if(mCallback != null && values.length > 0) { for (Integer value : values) { mCallback.onOperationProgress(value); } } } @Override protected MyComplexResult doInBackground(MyComplexDataObject... myComplexDataObjects) { MyComplexResult complexResult = new MyComplexResult(); // Actual operation left out for brevity... return complexResult; } @Override protected void onPostExecute(MyComplexResult myComplexResult) { if(mCallback != null ) { mCallback.onOperationCompleted(myComplexResult); } stopForeground(true); } @Override protected void onCancelled(MyComplexResult complexResult) { super.onCancelled(complexResult); stopForeground(true); } } private Notification buildNotification() { Notification notification = null; // Create a notification for the service.. return notification; } }

public class MyActivity extends Activity implements ServiceConnection, MyLocalService.Callback { private MyLocalService mService; /** * Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main_activity); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); Intent bindIntent = new Intent(this, MyLocalService.class); bindService(bindIntent, this, BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); if (mService != null) { mService.setCallback(null); // Important to avoid memory leaks unbindService(this); } } public void onTriggerLongRunningOperation(View view) { if(mService != null) { mService.performLongRunningOperation(new MyComplexDataObject()); } } @Override public void onOperationProgress(int progress) { // TODO Update user interface with progress.. } @Override public void onOperationCompleted(MyComplexResult complexResult) { // TODO Show result to user... } @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) { mService = ((MyLocalService.LocalBinder) iBinder).getService(); mService.setCallback(this); // Once we have a reference to the service, we can update the UI and // enable buttons that should otherwise be disabled. findViewById(R.id.trigger_operation_button).setEnabled(true); } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) { // Disable the button as we are loosing the reference to the service. findViewById(R.id.trigger_operation_button).setEnabled(false); mService = null; } }
附加资源:
Google’s changes to the Service API at
http://android-developers.blogspot.se/2010/02/service-api-changes-starting-with.html
Dianne Hackborn at
http://android-developers.blogspot.se/2010/04/multitaskingandroid-way.html
以上是关于Android Programming: Pushing the Limits -- Chapter 6: Services and Background Tasks的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
