43Java动态代理一——动态类Proxy的使用
Posted JustDo
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了43Java动态代理一——动态类Proxy的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.什么是动态代理?
答:动态代理可以提供对另一个对象的访问,同时隐藏实际对象的具体事实。代理一般会实现它所表示的实际对象的接口。代理可以访问实际对象,但是延迟实现实际对象的部分功能,实际对象实现系统的实际功能,代理对象对客户隐藏了实际对象。客户不知道它是与代理打交道还是与实际对象打交道。
2.为什么使用动态代理?
答:因为动态代理可以对请求进行任何处理
3.使用它有哪些好处?
答:因为动态代理可以对请求进行任何处理
4.哪些地方需要动态代理?
答:不允许直接访问某些类;对访问要做特殊处理等
目前Java开发包中包含了对动态代理的支持,但是其实现只支持对接口的的实现。 其实现主要通过java.lang.reflect.Proxy类和java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler接口。
Proxy类主要用来获取动态代理对象,InvocationHandler接口用来约束调用者实现
以下为模拟案例,通过动态代理实现在方法调用前后向控制台输出两句字符串
目录结构
<br/>
定义一个HelloWorld接口
2
3 /**
4 * 定义一个HelloWorld接口
5 *
6 * @author jiqinlin
7 *
8 */
9 publicinterface HelloWorld {
10 publicvoid sayHelloWorld();
11 }
<br/>
类HelloWorldImpl是HelloWorld接口的实现
2
3 /**
4 * 类HelloWorldImpl是HelloWorld接口的实现
5 *
6 * @author jiqinlin
7 *
8 */
9 publicclass HelloWorldImpl implements HelloWorld{
10
11 publicvoid sayHelloWorld() {
12 System.out.println("HelloWorld!");
13 }
14
15 }
HelloWorldHandler是 InvocationHandler接口实现
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
4 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
5
6 /**
7 * 实现在方法调用前后向控制台输出两句字符串
8 *
9 * @author jiqinlin
10 *
11 */
12 publicclass HelloWorldHandler implements InvocationHandler{
13 //要代理的原始对象
14 private Object obj;
15
16 public HelloWorldHandler(Object obj) {
17 super();
18 this.obj = obj;
19 }
20
21 /**
22 * 在代理实例上处理方法调用并返回结果
23 *
24 * @param proxy 代理类
25 * @param method 被代理的方法
26 * @param args 该方法的参数数组
27 */
28 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
29 Object result =null;
30 //调用之前
31 doBefore();
32 //调用原始对象的方法
33 result=method.invoke(obj, args);
34 //调用之后
35 doAfter();
36 return result;
37 }
38
39 privatevoid doBefore(){
40 System.out.println("before method invoke");
41 }
42
43 privatevoid doAfter(){
44 System.out.println("after method invoke");
45 }
46
47 }
测试类
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
publicclass HelloWorldTest {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
HelloWorld helloWorld=new HelloWorldImpl();
InvocationHandler handler=new HelloWorldHandler(helloWorld);
//创建动态代理对象
HelloWorld proxy=(HelloWorld)Proxy.newProxyInstance(
helloWorld.getClass().getClassLoader(),
helloWorld.getClass().getInterfaces(),
handler);
proxy.sayHelloWorld();
}
}
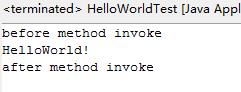
运行结果为:
案例二
Calculator.java
1 import java.math.BigDecimal; 2 3 4 public interface Calculator { 5 6 //加法 7 BigDecimal add(String a,String b); 8 9 //减法 10 BigDecimal sub(String a,String b); 11 12 //乘法 13 BigDecimal mul(String a,String b); 14 15 //除法 16 BigDecimal div(String a,String b); 17 }
SimpleCalculator.java
1 import java.math.BigDecimal; 2 3 4 public class SimpleCalculator implements Calculator{ 5 6 @Override 7 public BigDecimal add(String a, String b) { 8 9 BigDecimal n1=new BigDecimal(a); 10 BigDecimal n2=new BigDecimal(b); 11 12 return n1.add(n2); 13 } 14 15 @Override 16 public BigDecimal sub(String a, String b) { 17 BigDecimal n1=new BigDecimal(a); 18 BigDecimal n2=new BigDecimal(b); 19 20 return n1.subtract(n2); 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public BigDecimal mul(String a, String b) { 25 BigDecimal n1=new BigDecimal(a); 26 BigDecimal n2=new BigDecimal(b); 27 28 return n1.multiply(n2); 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 public BigDecimal div(String a, String b) { 33 BigDecimal n1=new BigDecimal(a); 34 BigDecimal n2=new BigDecimal(b); 35 36 return n1.divide(n2); 37 } 38 39 }
SimpleCalculatorLoggingProxy.java
1 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 2 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 3 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 4 5 6 public class SimpleCalculatorLoggingProxy { 7 8 private Calculator target; 9 10 public SimpleCalculatorLoggingProxy(Calculator target){ 11 this.target=target; 12 } 13 14 public Calculator getProxy(){ 15 Calculator proxy=null; 16 17 // 18 ClassLoader loader=target.getClass().getClassLoader(); 19 20 Class[] interfaces=new Class[]{Calculator.class}; 21 22 InvocationHandler handle=new InvocationHandler() { 23 24 @Override 25 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 26 throws Throwable { 27 System.out.println("正在执行"+method.getName()+"方法,参数为"+args[0]+","+args[1]); 28 return method.invoke(target, args); 29 } 30 }; 31 32 proxy= (Calculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, handle); 33 return proxy; 34 } 35 36 }
测试代码:
1 Calculator target=new SimpleCalculator(); 2 3 Calculator proxy=new SimpleCalculatorLoggingProxy(target).getProxy(); 4 5 System.out.println(proxy.add("1", "2")); 6 7 System.out.println(proxy.div("3", "2"));
输出结果:
正在执行add方法,参数为1,2
3
正在执行div方法,参数为3,2
1.5
以上是关于43Java动态代理一——动态类Proxy的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章