数据存储和访问
Posted 金洪光
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据存储和访问相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.SharedPreferences:
通过SharedPreferences可以将NVP(Name/Value Pair,名称/值对)保存在android的文件系统中, 还能够实现不同应用程序间的数据共享.
支持三种访问mode:
私有(MODE_PRIVATE):仅有创建程序有权限对其进行读取或写入
全局读(MODE_WORLD_READABLE):不仅创建程序可以对其进行读取或写入,其他应用程序也读取操作的权限,但没有写入操作的权限
全局写(MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE):创建程序和其他程序都可以对其进行写入操作,但没有读取的权限。
*有的时候需要将SharedPreferences的访问模式设定为即可以全局读,也可以全局写,这样就需要将两种模式写成下面的方式
Public static int MODE = Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE + Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE; //可读可写
SharedPreferences文件位置:
保存在/data/data/<package name>/shared_prefs目录下

-rw-rw-rw”表示SaveSetting.xml可以被创建者、同组用户和其他用户进行读取和写入操作,但不可执行。
-rw-rw ---”,表示仅有创建者和同组用户具有读写文件的权限。
打开SharedPreferences文件:
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = getSharedPreferences(PREFERENCE_NAME, MODE);
写入/编辑SharedPreferences文件:
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = sharedPreferences.edit(); editor.putString("Name", "Tom"); editor.putInt("Age", 20); editor.putFloat("Height", ); editor.commit();
读取 SharedPreferences文件:
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = getSharedPreferences(PREFERENCE_NAME, MODE); String name = sharedPreferences.getString("Name","Default Name"); int age = sharedPreferences.getInt("Age", 20); float height = sharedPreferences.getFloat("Height",);
下面是简单的例子:
package com.example.demo_simplepreference; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Context; import android.content.SharedPreferences; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.EditText; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private EditText nameText; private EditText ageText; private EditText heightText; public static final String PREFERENCE_NAME = "SaveSetting"; public static int MODE = Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE + Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); nameText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.name); ageText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.age); heightText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.height); } @Override public void onStart() { super.onStart(); loadSharedPreferences(); } @Override public void onStop() { super.onStop(); saveSharedPreferences(); } private void loadSharedPreferences() { SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = getSharedPreferences( PREFERENCE_NAME, MODE); String name = sharedPreferences.getString("Name", "Tom"); int age = sharedPreferences.getInt("Age", 20); float height = sharedPreferences.getFloat("Height", (float) 180.5); nameText.setText(name); ageText.setText(String.valueOf(age)); heightText.setText(String.valueOf(height)); } private void saveSharedPreferences() { SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = getSharedPreferences( PREFERENCE_NAME, MODE); SharedPreferences.Editor editor = sharedPreferences.edit(); editor.putString("Name", nameText.getText().toString()); editor.putInt("Age", Integer.parseInt(ageText.getText().toString())); editor.putFloat("Height", Float.parseFloat(heightText.getText().toString())); editor.commit(); } }
运行结果:
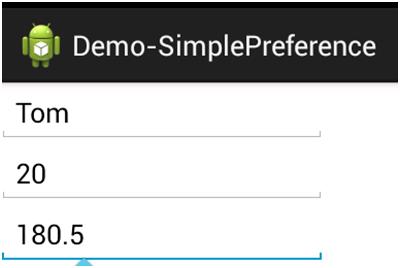
2.File存储:
访问mode:
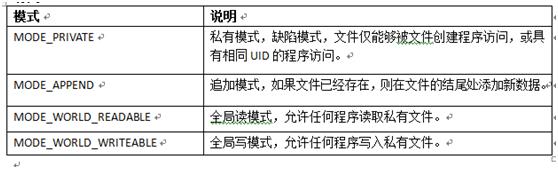
文件保存在:
/data/data/工程(edu.hrbeu.InternalFileDemo)/files/目录下

写入:
String FILE_NAME = "fileDemo.txt"; FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(FILE_NAME,Context.MODE_PRIVATE) String text = “Some data”; fos.write(text.getBytes()); fos.flush(); fos.close();
在调用close()函数关闭文件前,务必要调用flush()函数,将缓冲区内所有的数据写入文件。
读取:
public FileInputStream openFileInput (String name) String FILE_NAME = "fileDemo.txt"; FileInputStream fis = openFileInput(FILE_NAME); byte[] readBytes = new byte[fis.available()]; while(fis.read(readBytes) != -1){ }
下面是简单的例子:
package com.example.demo_internalfiledemo; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Context; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.Environment; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.CheckBox; import android.widget.EditText; import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private TextView labelView; private EditText entryText; private Button readButton; private Button writeButton; private CheckBox appendBox; private EditText displayView; private final static String FILE_NAME = "test.txt"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); labelView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.labelView); appendBox = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.appendBox); entryText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.entryText); readButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.readButton); writeButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.writeButton); displayView = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.displayView); readButton.setOnClickListener(readButtonListener); writeButton.setOnClickListener(writeButtonListener); } OnClickListener writeButtonListener = new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { FileOutputStream fos = null; try { if (appendBox.isChecked()) { fos = openFileOutput(FILE_NAME, Context.MODE_APPEND); } else { fos = openFileOutput(FILE_NAME, Context.MODE_PRIVATE); } String text = entryText.getText().toString(); fos.write(text.getBytes()); labelView.setText("文件写入成功,写入长度:" + text.length()); entryText.setText(""); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (fos != null) { try { fos.flush(); fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }; OnClickListener readButtonListener = new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { displayView.setText(""); FileInputStream fis = null; try { fis = openFileInput(FILE_NAME); if (fis.available() == 0) { return; } byte[] readBytes = new byte[fis.available()]; while (fis.read(readBytes) != -1) { } String text = new String(readBytes); displayView.setText(text); labelView.setText("文件读取成功,文件长度:" + text.length()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; }
运行结果

创建目录:
String path = getFilesDir().getAbsolutePath(); //data/data/project package/files/ String path = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath(); //mnt/sdcard/ File file = new File(path + "/etc2/nihao/wo/jiao/jin"); if (!file.exists()) { file.mkdirs(); }
创建文件
File newFile = new File(path + "/etc2/nihao/wo/jiao/jin/test.txt"); newFile.createNewFile();
写入:
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file2); writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(out)) ; writer.write("123123") ; writer.close() ;
读取:
FileInputStream out = new FileInputStream (file2); reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(out)) ; String input = null; //每读一行进行一次写入动作 while(!(input = bufReader.readLine()).equals("quit")) { //Do something.. } bufReader.close();
资源文件访问:
通过stream可以访问任何res文件夹中的文件。
Resources resources = this.getResources(); InputStream inputStream = inputStream = resources.openRawResource(R.raw.raw_file);
也可以通过XmlPullParser访问xml文件夹中的xml文件
XmlPullParser parser = resources.getXml(R.xml.person); String msg = ""; try { while (parser.next() != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { String people = parser.getName(); String name = null; String age = null; String height = null; if ((people != null) && people.equals("person")) { int count = parser.getAttributeCount(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { String attrName = parser.getAttributeName(i); String attrValue = parser.getAttributeValue(i); if ((attrName != null) && attrName.equals("name")) { name = attrValue; } else if ((attrName != null) && attrName.equals("age")) { age = attrValue; } else if ((attrName != null) && attrName.equals("height")) { height = attrValue; } } if ((name != null) && (age != null) && (height != null)) { msg += "姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age + ",身高:" + height + "\\n"; } } } } catch (Exception e) { Log.e("ResourceFileDemo", e.getMessage(), e); }
XmlPullParser的XML事件类型 :
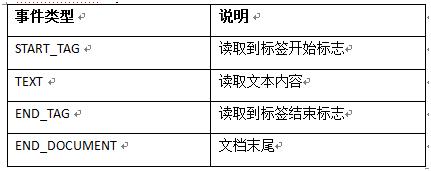
XMLPull相关参考:http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/8036340
以上是关于数据存储和访问的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章