1 C++中使用vector来表示二维数组
- 声明一个二维数组:
vector<vector<int>> dp(row, vector<int>(col));
将变量dp初始化为一个含有row个元素的vector对象,其中每个元素又都是含有col个元素的vector对象。内部的vector对象的基类型为int,外部vector对象的基类型为 vector< int >。
- 获取数组的row和col
vector<vector<int>>& grid
int row = grid.size();
int col = grid.at(0).size();
2 自己动手写一个Grid类
尽管使用嵌套的vector对象能够代表二维数组,但是这种方法很不便利,因此考虑到自己写一个Grid类。
- 代码实现
开发环境:VS2017
/*
以Class Template的形式实现Matrix
*/
#pragma once
template <typename ValueType>
class Grid
{
public:
class GridRow;
Grid(); //默认的构造函数
Grid(int row,int col);
~Grid();
int numRows() const;
int numCols() const;
void resize(int row,int col);
bool inBounds(int row, int col) const;
ValueType get(int row, int col);
const ValueType& get(int row, int col) const;
void set(int row, int col, ValueType value);
GridRow operator[](int row);
const GridRow operator[](int row) const;
void deepCopy(const Grid& src)
{
int n = src.m_icol * src.m_irow;
this->element = new ValueType[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
this->element[i] = src.element[i];
}
this->m_icol = src.m_icol;
this->m_irow = src.m_irow;
}
Grid & operator=(const Grid& src)
{
if (this != &src)
{
delete[] this->element;
deepCopy(src);
}
return *this;
}
Grid(const Grid& src)
{
deepCopy(src);
}
Grid<ValueType> operator +(const Grid<ValueType> & m1);
Grid<ValueType> operator *(const Grid<ValueType>& m1);
ValueType& operator()(int row, int col);
void print() const;
public:
class iterator : public std::iterator<std::input_iterator_tag,ValueType>
{
public:
iterator(const Grid* gp,int index)
{
this->gp = gp;
this->index = index;
}
//拷贝构造函数
iterator(const iterator& it)
{
this->gp = it.gp;
this->index = it.index;
}
iterator& operator++()
{
index++;
return *this;
}
iterator operator++(int)
{
iterator copy(*this);
operator++();
return copy;
}
bool operator==(const iterator& rhs)
{
return (rhs.gp == this->gp) && (rhs.index == this->index);
}
bool operator!=(const iterator& rhs)
{
return !(*this == rhs);
}
ValueType& operator*()
{
return gp->element[index];
}
ValueType* operator->()
{
return &gp->element[index];
}
private:
const Grid* gp; //指向cosnt Grid的指针,让编译器知道迭代器的操作不能改变Grid对象本身
int index;
};
iterator begin() const
{
return iterator(this, 0);
}
iterator end() const
{
return iterator(this, this->m_icol * this->m_irow);
}
private:
/*定义一个嵌套类*/
class GridRow
{
friend class Grid;
public:
ValueType& operator[](int col)
{
if (gp->inBounds(row,col))
{
return gp->element[row * gp->m_icol + col];
}
//else 情况下没有返回值!
}
ValueType operator[](int col) const
{
if (gp->inBounds(row, col))
{
return gp->element[row * gp->m_icol + col];
}
}
private:
GridRow(const Grid* girdRef, int index)
{
gp = const_cast<Grid*>(girdRef);
row = index;
}
GridRow(Grid* girdRef, int index)
{
gp = girdRef;
row = index;
}
Grid* gp;
int row;
};
friend class GridRow;
private:
int m_irow;
int m_icol;
ValueType* element;
};
template<typename ValueType>
Grid<ValueType>::Grid()
{
this->element = NULL;
this->m_irow = 0;
this->m_icol = 0;
}
template<typename ValueType>
Grid<ValueType>::Grid(int row, int col):m_irow(row),m_icol(col)
{
if (row < 0 || col < 0)
{
//error
}
this->element = NULL;
resize(this->m_irow,this->m_icol);
}
template<typename ValueType>
Grid<ValueType>::~Grid()
{
if (this->element != NULL)
{
delete []this->element; //这里恐怕会出错
}
}
template<typename ValueType>
void Grid<ValueType>::resize(int row, int col)
{
if (this->element != NULL)
{
delete[]this->element;
}
this->element = new ValueType[row * col];
this->m_icol = col;
this->m_irow = row;
for (int i = 0;i < row * col;i++)
{
this->element[i] = ValueType();
}
}
template<typename ValueType>
inline bool Grid<ValueType>::inBounds(int row, int col) const
{
/*对row 和 col 的上下边界都有进行检查*/
return (row >= 0 && col >= 0) && (row < this->m_irow && col < this->m_icol);
}
template<typename ValueType>
int Grid<ValueType>::numRows() const
{
return this->m_irow;
}
template<typename ValueType>
int Grid<ValueType>::numCols() const
{
return this->m_icol;
}
template<typename ValueType>
ValueType Grid<ValueType>::get(int row, int col)
{
if (row > this->m_irow || col > this->m_icol || row < 0 || col < 0)
{
//error
}
return this->element[row * this->m_irow + col];
}
template<typename ValueType>
const ValueType & Grid<ValueType>::get(int row, int col) const
{
if (row > this->m_irow || col > this->m_icol || row < 0 || col < 0)
{
//error
}
return this->element[row * this->m_irow + col];
}
template<typename ValueType>
void Grid<ValueType>::set(int row, int col, ValueType value)
{
if (this->element == NULL)
{
//error
}
this->element[row * this->m_icol + col] = value;
}
template<typename ValueType>
typename Grid<ValueType>::GridRow Grid<ValueType>::operator[](int row)
{
std::cout << typeid(this).name() << std::endl;
return GridRow(this,row);
}
template<typename ValueType>
const typename Grid<ValueType>::GridRow Grid<ValueType>::operator[](int row) const
{
std::cout << typeid(this).name() << std::endl;
return GridRow(this,row);
}
template<typename ValueType>
Grid<ValueType> Grid<ValueType>::operator+(const Grid<ValueType>& m1)
{
//TODO:确定m1和this的大小相同 若不相同 error
Grid<ValueType> result(m1.m_irow,m1.m_icol);
int grid_size = m1.m_icol * m1.m_irow;
for (int i = 0;i < grid_size;i++)
{
result.element[i] = this->element[i] + m1.element[i];
}
return result;
}
template<typename ValueType>
Grid<ValueType> Grid<ValueType>::operator*(const Grid<ValueType>& m1)
{
//TODO:两个矩阵相乘
//Grid<ValueType> result(this->m_irow,m1.m_icol);
//for (int i = 0;i < result.m_irow;i++)
//{
// for (int j = 0;j < result.m_icol;j++)
// {
// result.set(i,j,0);
// for (int k = 0; k < this->m_icol;k++)
// {
// //result
// }
// }
//}
}
template<typename ValueType>
ValueType& Grid<ValueType>::operator()(int row, int col)
{
return this->element[row * this->m_irow + this->m_icol];
//return this->get(row, col);
}
template<typename ValueType>
void Grid<ValueType>::print() const
{
int col = this->m_icol;
int grid_size = this->m_icol * this->m_irow;
for (int i = 0; i < grid_size; ++i)
{
if (i % col == 0)
{
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << this->element[i] << " ";
}
}
测试代码:
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "grid.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Grid<double> grid1; //声明一个double类型的数组
Grid<int> grid(2,2);
cout << "row = " << grid.numRows() << endl;
cout << "col = " << grid.numCols() << endl;
grid.resize(3, 3);
cout << "row = " << grid.numRows() << endl;
cout << "col = " << grid.numCols() << endl;
grid.set(0, 0, 1);
grid.set(0, 1, 2);
grid.set(0, 2, 3);
grid.set(1, 0, 4);
grid.set(1, 1, 1);
grid.set(1, 2, 2);
grid.set(2, 0, 3);
grid.set(2, 1, 4);
grid.set(2, 2, 4);
cout << "单个读取元素:" << endl;
cout << grid.get(0, 0)
<< grid.get(0, 1)
<< grid.get(0, 2) << endl;
cout << "[][]的测试" << endl;
cout << grid[0][0]
<< grid[0][1]
<< grid[0][2] << endl;
grid[0][0] = 5;
cout << grid[0][0] << endl;
grid.print();
if (grid.inBounds(4,4))
{
cout << "\\ngrid中(4,4)存在元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "\\ngrid中(4,4)不存在元素" << endl;
}
cout << "grid中(0,2)元素为 " << grid.get(0, 2) << endl;
const Grid<int> grid2(grid); //调用拷贝构造函数
const Grid<int>* a;
a = &(grid2);
cout << "单个读取元素:" << endl;
cout << grid.get(2, 0)
<< grid.get(2, 1)
<< grid.get(2, 2) << endl;
//grid2.print();
cout << "[][]的测试" << endl;
cout << grid2[0][0]
<< grid2[0][1]
<< grid2[0][2] << endl;
Grid<int>::iterator it = grid.begin();
cout << *(it) << endl;
it++;
cout << *(it) << endl;
Grid<int>::iterator it1 = grid2.begin();
if (it != it1)
{
cout << "it != it1" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
测试的方法是“单元测试”,尽量把每一个函数功能都测试到,上述测试代码的运行截图:
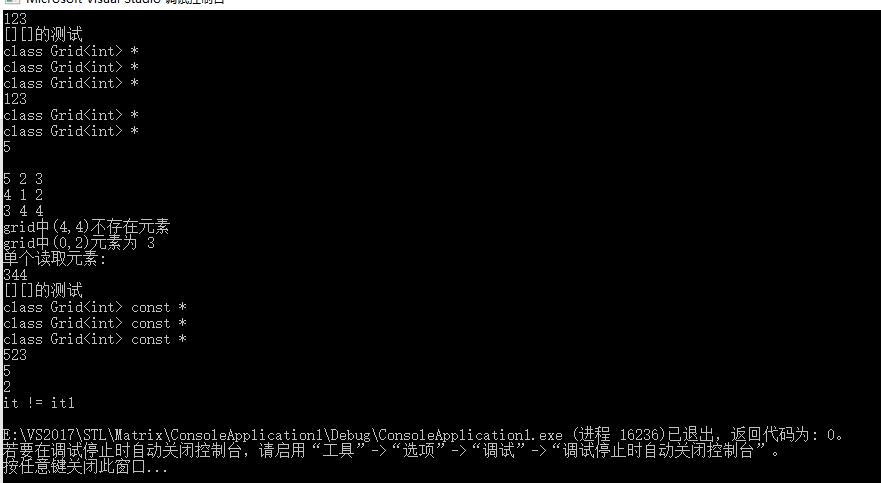
- 上述代码的不足与问题:
1 测试代码并没有把所有的函数功能都测试到。
2 矩阵相乘的函数没有实现完整。
3 Grid类中的get(),set(),operator [ ](int row)等函数需要做输入参数的检查,当输入的row或col超出范围时应有错误提示。
4 Grid类中的迭代器实现的功能不足。
以下为在调试代码中遇到的错误:
- 错误的复现
在VS2017中
const int num = 10;
int *p = # //编译器报错
必须要把上面的代码修改为:
const int num = 10;
const int *p = #
在今天的测试代码中,有如下一行代码,声明了一个const Grid
const Grid<int> grid2(grid); //调用拷贝构造函数
然后测试运算符[][],测试代码如下:
cout << grid2[0][0]
<< grid2[0][1]
<< grid2[0][2] << endl;
此时VS2017编译器报错:
错误 C2440 无法从“initializer list”转换为“Grid
::GridRow”
这个错误很奇怪,根据错误提示:初始化列表无法转换为Grid< int >::GridRow。把这段代码放到gcc中编译调试也会报错。
- 错误的分析
加断点调试,上述测试代码会首先跳到下面的代码里:
template<typename ValueType>
typename Grid<ValueType>::GridRow Grid<ValueType>::operator[](int row)
{
std::cout << typeid(this).name() << std::endl;
return GridRow(this,row);
}
template<typename ValueType>
const typename Grid<ValueType>::GridRow Grid<ValueType>::operator[](int row) const
{
std::cout << typeid(this).name() << std::endl;
return GridRow(this,row);
}
接下来追到GridRow()这个构造函数里,函数实现如下:
GridRow(Grid* girdRef, int index)
{
gp = girdRef;
row = index;
}
函数调用的流程大致如上分析。下面看错误的具体分析
声明了const Grid< int > grid2的类型,由于grid2是const object,所以系统调用的应该是下面这个函数:
template<typename ValueType>
const typename Grid<ValueType>::GridRow Grid<ValueType>::operator[](int row) const
{
std::cout << typeid(this).name() << std::endl;
return GridRow(this,row);
}
在这个函数里,this的类型应该是class Grid< int > const *, 调用GridRow()函数,但是这个函数的第一个参数是Grid * 类型的,也就是说把Grid< int > const * 转换为Grid< int > *,这个时候编译器就会报错。
- 错误的解决
给GridRow类声明两个构造函数,这两个构造函数分别如下:
GridRow(const Grid* girdRef, int index)
{
gp = const_cast<Grid*>(girdRef);
row = index;
}
GridRow(Grid* girdRef, int index)
{
gp = girdRef;
row = index;
}
这样class Grid < int > const*就会调用第一个构造函数,因此也不会报错。
- 参考资料:
1 《C++程序设计 基础,编程抽象与算法策略》
2 《Essential C++》