机器学习:逻辑回归
Posted zhuchengchao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习:逻辑回归相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
逻辑回归
理论分析
概述
? Logistic回归在本质上是线性回归,只是在特征到结果的映射中加入了一层函数映射,即先把特征线性求和,然后使用函数\\(g(z)\\)将上述结果映射到0-1上。
优点:计算代价不高,易于理解和实现
缺点:容易欠拟合,分类精度不高
适用数据:数值型和标称型
映射函数
sigmoid
- 函数表示
\\[ g(z)=\\frac11+e^-z \\]
\\[ z = \\theta_0+\\theta_1x_1+\\theta_2x_2+...+\\theta_nx_n \\]
- 导函数:
\\[ g^'(z)=g(z)(1-g(z)) \\]
- 函数图像
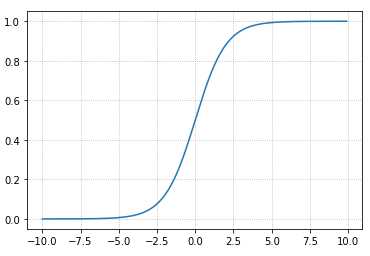
如下代码:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.arange(-10,10,0.1) y = 1./(1.+np.exp(-x)) plt.grid(b=True, ls=':') plt.plot(x, y)
逻辑回归及似然函数
首先假设:
\\[
P(y=1|x;θ)=h_θ(x)
\\]
\\[ P(y=0|x;θ)=1-h_θ(x) \\]
\\[ P(y|x;θ)=(h_θ(x))^y(1-h_θ(x))^1-y \\]
根据似然函数如下:
\\[
L(θ)=P(Y|X;θ)=\\prod_i=1^mp(y^i|x^i;θ)
\\]
取对数,为对数似然函数:
\\[
l(θ)=\\log L(θ)=\\sum_i=1^my^ilog(h_\\theta(x^i))+(1-y^i)log(1-h_\\theta(x^i))
\\]
注:\\(h_θ(x^i)=g(θ^Tx^i)\\)
损失函数
由上述的对数似然函数出以下结论:在取某θ时,数似然函数取最大值,表面此时的参数为最优;
由此将似然函数取反,定义完整的损失函数如下:
\\[ loss(h_\\theta(x),y)=-\\sum_i=1^my^ilog(h_\\theta(x^i))+(1-y^i)log(1-h_\\theta(x^i)) \\]
\\[ J(\\theta)=\\frac1m\\sum_i=1^mloss(h_\\theta(x^(i),y^(i))) \\]
\\[ minJ(\\theta) \\]
? 通过梯度下降对J(θ)进行求解,结果如下:
\\[
\\frac?J(\\theta)?\\theta_j=\\frac1m\\sum_i=1^m(g(θ^Tx^i)-y^i)x_j^i
\\]
? 更新参数
\\[
\\theta_j=\\theta_j - \\alpha\\frac?J(\\theta)?\\theta_j
\\]
正则化
同线性回归中梯度下降的正则化
实际应用
sklearn中API介绍
sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression(penalty=‘l2’, C = 1.0)
# Logistic回归分类器
# coef_:回归系数
# 注:默认使用了l2正则化案例——肿瘤良性、恶性预测
# 导入必要的库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# 读取数据
# 构造列标签名字
column = ['Sample code number','Clump Thickness', 'Uniformity of Cell Size','Uniformity of Cell Shape','Marginal Adhesion', 'Single Epithelial Cell Size','Bare Nuclei','Bland Chromatin','Normal Nucleoli','Mitoses','Class']
# 读数据
data = pd.read_csv("./breast-cancer-wisconsin.data", names=column)
# print(data)
# 对缺失值进行处理
data = data.replace(to_replace="?", value=np.nan)
# 丢弃缺失值
data = data.dropna()
# 对数据进行分割
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data[column[1:10]], data[column[10]], test_size=0.25)
# 进行标准化处理
std = StandardScaler()
x_train = std.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std.transform(x_test)
# 逻辑回归预测
lg = LogisticRegression(C=1.0)
lg.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(lg.coef_)
# [[1.18661055 0.37775507 0.77048383 0.72337353 0.40801567 1.31255209 0.72011434 0.52286549 0.69823535]]
# 模型评估
y_predict = lg.predict(x_test)
# 准确率
print("准确率为:", lg.score(x_test, y_test))
# 准确率为: 0.9649122807017544
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
# 召回率
print("召回率为:", classification_report(y_test, y_predict, labels=[2, 4], target_names=["良性", "恶性"]))
# 召回率为: precision recall f1-score support
#
# 良性 0.97 0.97 0.97 116
# 恶性 0.95 0.95 0.95 55
#
# avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 171- 其他参考代码,例如乳腺癌分类/鸢尾花数据分类,放置GitHub下:
https://github.com/zhuChengChao/ML-LogisticsRegression
以上是关于机器学习:逻辑回归的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章