mybatis-cache model
Posted siye1989
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mybatis-cache model相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 概述
本文,我们来分享 MyBatis 的缓存模块,对应 cache 包。如下图所示:
在 《精尽 MyBatis 源码解析 —— 项目结构一览》 中,简单介绍了这个模块如下:
在优化系统性能时,优化数据库性能是非常重要的一个环节,而添加缓存则是优化数据库时最有效的手段之一。正确、合理地使用缓存可以将一部分数据库请求拦截在缓存这一层。
MyBatis 中提供了一级缓存和二级缓存,而这两级缓存都是依赖于基础支持层中的缓 存模块实现的。这里需要读者注意的是,MyBatis 中自带的这两级缓存与 MyBatis 以及整个应用是运行在同一个 JVM 中的,共享同一块堆内存。如果这两级缓存中的数据量较大, 则可能影响系统中其他功能的运行,所以当需要缓存大量数据时,优先考虑使用 Redis、Memcache 等缓存产品。
本文涉及的类如下图所示: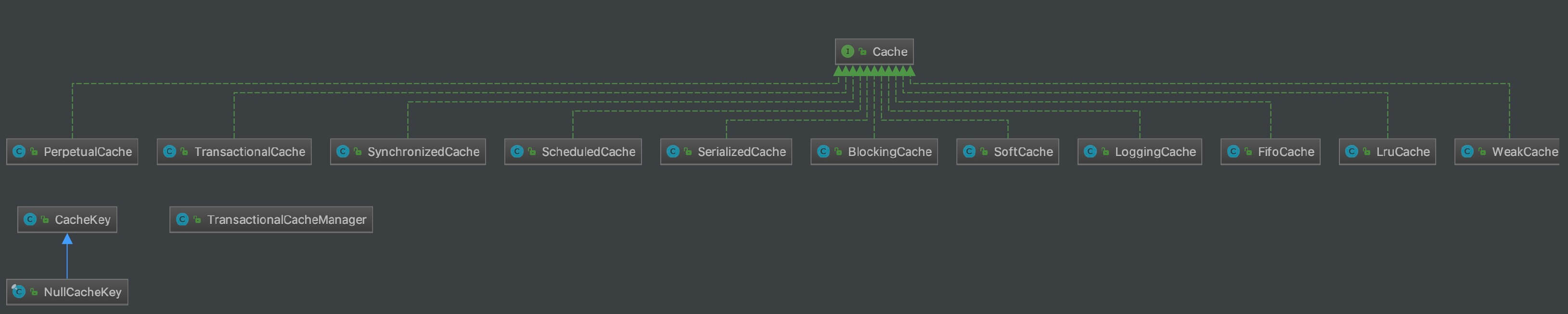
下面,我们就一起来看看具体的源码实现。另外,如果你对 MyBatis 的 Cache 机制不是很了解,可以简单阅读下 《MyBatis 文档 —— 缓存》 。
2. Cache
org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache ,缓存容器接口。注意,它是一个容器,有点类似 HashMap ,可以往其中添加各种缓存。代码如下:
// Cache.java
|
- 方法比较简单。
Cache 基于不同的缓存过期策略、特性,有不同的实现类。下面,我们来逐个来看。可以组合多种 Cache ,实现特性的组合。这种方式,就是常见的设计模式,《【设计模式读书笔记】装饰者模式》 。
2.1 PerpetualCache
org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl.PerpetualCache ,实现 Cache 接口,永不过期的 Cache 实现类,基于 HashMap 实现类。代码如下:
// PerpetualCache.java
|
- 比较简单,胖友自己瞅瞅。
2.2 LoggingCache
org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.LoggingCache ,实现 Cache 接口,支持打印日志的 Cache 实现类。代码如下:
// LoggingCache.java
|
delegate属性,被装饰的 Cache 对象。- 在
#getObject(Object key)方法,增加了requests和hits的计数,从而实现命中比率的统计,即#getHitRatio()方法。
2.3 BlockingCache
org.apache.ibatis.cache.decoratorsBlockingCache ,实现 Cache 接口,阻塞的 Cache 实现类。
这里的阻塞比较特殊,当线程去获取缓存值时,如果不存在,则会阻塞后续的其他线程去获取该缓存。
为什么这么有这样的设计呢?因为当线程 A 在获取不到缓存值时,一般会去设置对应的缓存值,这样就避免其他也需要该缓存的线程 B、C 等,重复添加缓存。
代码如下:
// BlockingCache.java |