数据结构----二叉搜索树
Posted hywhyme
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构----二叉搜索树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
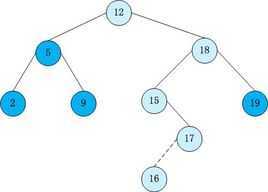
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),(又:二叉搜索树,二叉排序树)它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。 百度百科
- 函数Insert将X插入二叉搜索树BST并返回结果树的根结点指针;
- 函数Delete将X从二叉搜索树BST中删除,并返回结果树的根结点指针;如果X不在树中,则打印一行Not Found并返回原树的根结点指针;
- 函数Find在二叉搜索树BST中找到X,返回该结点的指针;如果找不到则返回空指针;
- 函数FindMin返回二叉搜索树BST中最小元结点的指针;
函数FindMax返回二叉搜索树BST中最大元结点的指针。
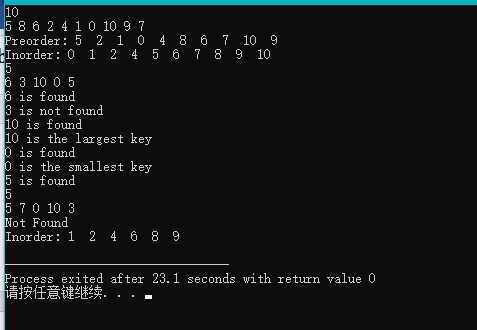
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 5 6 7 8 typedef int ElementType; 9 10 typedef struct TNode * Position; 11 12 typedef Position BinTree; 13 14 struct TNode 15 16 ElementType Data; 17 BinTree Left; 18 BinTree Right; 19 ; 20 21 void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT ) 22 if(BT) 23 printf(" %d ",BT->Data); 24 PreorderTraversal(BT->Left); 25 PreorderTraversal(BT->Right); 26 27 28 void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT ) 29 if(BT) 30 InorderTraversal(BT->Left); 31 printf(" %d ",BT->Data); 32 InorderTraversal(BT->Right); 33 34 35 /* 中序遍历,由裁判实现,细节不表 */ 36 37 BinTree Insert( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) 38 //printf("插入%d\\n",X); 39 BinTree new_node = NULL; 40 if(BST==NULL) 41 //printf("建立根\\n"); 42 BST = (Position)malloc(sizeof(struct TNode)); 43 BST->Data = X; 44 BST->Left = NULL; 45 BST->Right = NULL; 46 else 47 //printf("有根了\\n"); 48 if(X < BST->Data) 49 //printf("在根的左边\\n"); 50 if(BST->Left) 51 Insert(BST->Left,X); 52 else 53 BinTree new_node = (Position)malloc(sizeof(struct TNode)); 54 new_node->Data = X; 55 new_node->Left = NULL; 56 new_node->Right = NULL; 57 BST->Left = new_node; 58 59 else if(X > BST->Data) 60 //printf("在根的右边%d --- %d \\n",X,BST->Data); 61 if(BST->Right) 62 Insert(BST->Right,X); 63 else 64 BinTree new_node = (Position)malloc(sizeof(struct TNode)); 65 new_node->Data = X; 66 new_node->Left = NULL; 67 new_node->Right = NULL; 68 BST->Right = new_node; 69 70 71 72 return BST; 73 74 75 76 Position Find( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) 77 if(BST==NULL) 78 return NULL; 79 80 if(BST->Data==X) 81 return BST; 82 else if(X < BST->Data) 83 return Find(BST->Left,X); 84 else if(X > BST->Data) 85 return Find(BST->Right,X); 86 87 88 Position FindMin( BinTree BST ) 89 if(BST==NULL) 90 return NULL; 91 92 else if(BST->Left==NULL) 93 return BST; 94 95 else 96 return (FindMin(BST->Left)); 97 98 99 Position FindMax( BinTree BST ) 100 if(BST==NULL) 101 return NULL; 102 103 else if(BST->Right==NULL) 104 return BST; 105 106 else 107 return (FindMax(BST->Right)); 108 109 110 111 //删除节点 112 BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) 113 Position temp; 114 if(BST==NULL) 115 printf("Not Found\\n"); 116 return BST; 117 118 else if(X < BST->Data) 119 BST->Left = Delete(BST->Left,X); 120 else if(X > BST->Data) 121 BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right,X); 122 else 123 if(BST->Left && BST->Right) 124 temp = FindMax(BST->Left); 125 BST->Data = temp->Data; 126 BST->Left = Delete(BST->Left,BST->Data); 127 else 128 temp = BST; 129 if(BST->Left) 130 BST = BST->Left; 131 else 132 BST = BST->Right; 133 134 free(temp); 135 136 return BST; 137 138 139 140 141 int main() 142 143 BinTree BST, MinP, MaxP, Tmp; 144 ElementType X; 145 int N, i; 146 BST = NULL; 147 scanf("%d", &N); 148 for ( i=0; i<N; i++ ) 149 scanf("%d", &X); 150 //printf("%d",X); 151 BST = Insert(BST, X); 152 153 printf("Preorder:"); PreorderTraversal(BST); printf("\\n"); 154 printf("Inorder:"); InorderTraversal(BST); printf("\\n"); 155 MinP = FindMin(BST); 156 MaxP = FindMax(BST); 157 scanf("%d", &N); 158 for( i=0; i<N; i++ ) 159 scanf("%d", &X); 160 Tmp = Find(BST, X); 161 if (Tmp == NULL) printf("%d is not found\\n", X); 162 else 163 printf("%d is found\\n", Tmp->Data); 164 if (Tmp==MinP) printf("%d is the smallest key\\n", Tmp->Data); 165 if (Tmp==MaxP) printf("%d is the largest key\\n", Tmp->Data); 166 167 168 scanf("%d", &N); 169 for( i=0; i<N; i++ ) 170 scanf("%d", &X); 171 BST = Delete(BST, X); 172 173 printf("Inorder:"); InorderTraversal(BST); printf("\\n"); 174 return 0; 175
以上是关于数据结构----二叉搜索树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章