BP神经网络及异或实现
Posted thsss
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了BP神经网络及异或实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
BP神经网络是最简单的神经网络模型了,三层能够模拟非线性函数效果。

难点:
- 如何确定初始化参数?
- 如何确定隐含层节点数量?
- 迭代多少次?如何更快收敛?
- 如何获得全局最优解?
1 ‘‘‘ 2 neural networks 3 4 created on 2019.9.24 5 author: vince 6 ‘‘‘ 7 import math 8 import logging 9 import numpy 10 import random 11 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 12 13 ‘‘‘ 14 neural network 15 ‘‘‘ 16 class NeuralNetwork: 17 18 def __init__(self, layer_nums, iter_num = 10000, batch_size = 1): 19 self.__ILI = 0; 20 self.__HLI = 1; 21 self.__OLI = 2; 22 self.__TLN = 3; 23 24 if len(layer_nums) != self.__TLN: 25 raise Exception("layer_nums length must be 3"); 26 27 self.__layer_nums = layer_nums; #array [layer0_num, layer1_num ...layerN_num] 28 self.__iter_num = iter_num; 29 self.__batch_size = batch_size; 30 31 def train(self, X, Y): 32 X = numpy.array(X); 33 Y = numpy.array(Y); 34 35 self.L = []; 36 #initialize parameters 37 self.__weight = []; 38 self.__bias = []; 39 self.__step_len = []; 40 for layer_index in range(1, self.__TLN): 41 self.__weight.append(numpy.random.rand(self.__layer_nums[layer_index - 1], self.__layer_nums[layer_index]) * 2 - 1.0); 42 self.__bias.append(numpy.random.rand(self.__layer_nums[layer_index]) * 2 - 1.0); 43 self.__step_len.append(0.3); 44 45 logging.info("bias:%s" % (self.__bias)); 46 logging.info("weight:%s" % (self.__weight)); 47 48 for iter_index in range(self.__iter_num): 49 sample_index = random.randint(0, len(X) - 1); 50 logging.debug("-----round:%s, select sample %s-----" % (iter_index, sample_index)); 51 output = self.forward_pass(X[sample_index]); 52 g = (-output[2] + Y[sample_index]) * self.activation_drive(output[2]); 53 logging.debug("g:%s" % (g)); 54 for j in range(len(output[1])): 55 self.__weight[1][j] += self.__step_len[1] * g * output[1][j]; 56 self.__bias[1] -= self.__step_len[1] * g; 57 58 e = []; 59 for i in range(self.__layer_nums[self.__HLI]): 60 e.append(numpy.dot(g, self.__weight[1][i]) * self.activation_drive(output[1][i])); 61 e = numpy.array(e); 62 logging.debug("e:%s" % (e)); 63 for j in range(len(output[0])): 64 self.__weight[0][j] += self.__step_len[0] * e * output[0][j]; 65 self.__bias[0] -= self.__step_len[0] * e; 66 67 l = 0; 68 for i in range(len(X)): 69 predictions = self.forward_pass(X[i])[2]; 70 l += 0.5 * numpy.sum((predictions - Y[i]) ** 2); 71 l /= len(X); 72 self.L.append(l); 73 74 logging.debug("bias:%s" % (self.__bias)); 75 logging.debug("weight:%s" % (self.__weight)); 76 logging.debug("loss:%s" % (l)); 77 logging.info("bias:%s" % (self.__bias)); 78 logging.info("weight:%s" % (self.__weight)); 79 logging.info("L:%s" % (self.L)); 80 81 def activation(self, z): 82 return (1.0 / (1.0 + numpy.exp(-z))); 83 84 def activation_drive(self, y): 85 return y * (1.0 - y); 86 87 def forward_pass(self, x): 88 data = numpy.copy(x); 89 result = []; 90 result.append(data); 91 for layer_index in range(self.__TLN - 1): 92 data = self.activation(numpy.dot(data, self.__weight[layer_index]) - self.__bias[layer_index]); 93 result.append(data); 94 return numpy.array(result); 95 96 def predict(self, x): 97 return self.forward_pass(x)[self.__OLI]; 98 99 100 def main(): 101 logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO, 102 format = ‘%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s‘, 103 datefmt = ‘%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S‘); 104 105 logging.info("trainning begin."); 106 nn = NeuralNetwork([2, 2, 1]); 107 X = numpy.array([[0, 0], [1, 0], [1, 1], [0, 1]]); 108 Y = numpy.array([0, 1, 0, 1]); 109 nn.train(X, Y); 110 111 logging.info("trainning end. predict begin."); 112 for x in X: 113 print(x, nn.predict(x)); 114 115 plt.plot(nn.L) 116 plt.show(); 117 118 if __name__ == "__main__": 119 main();
具体收敛效果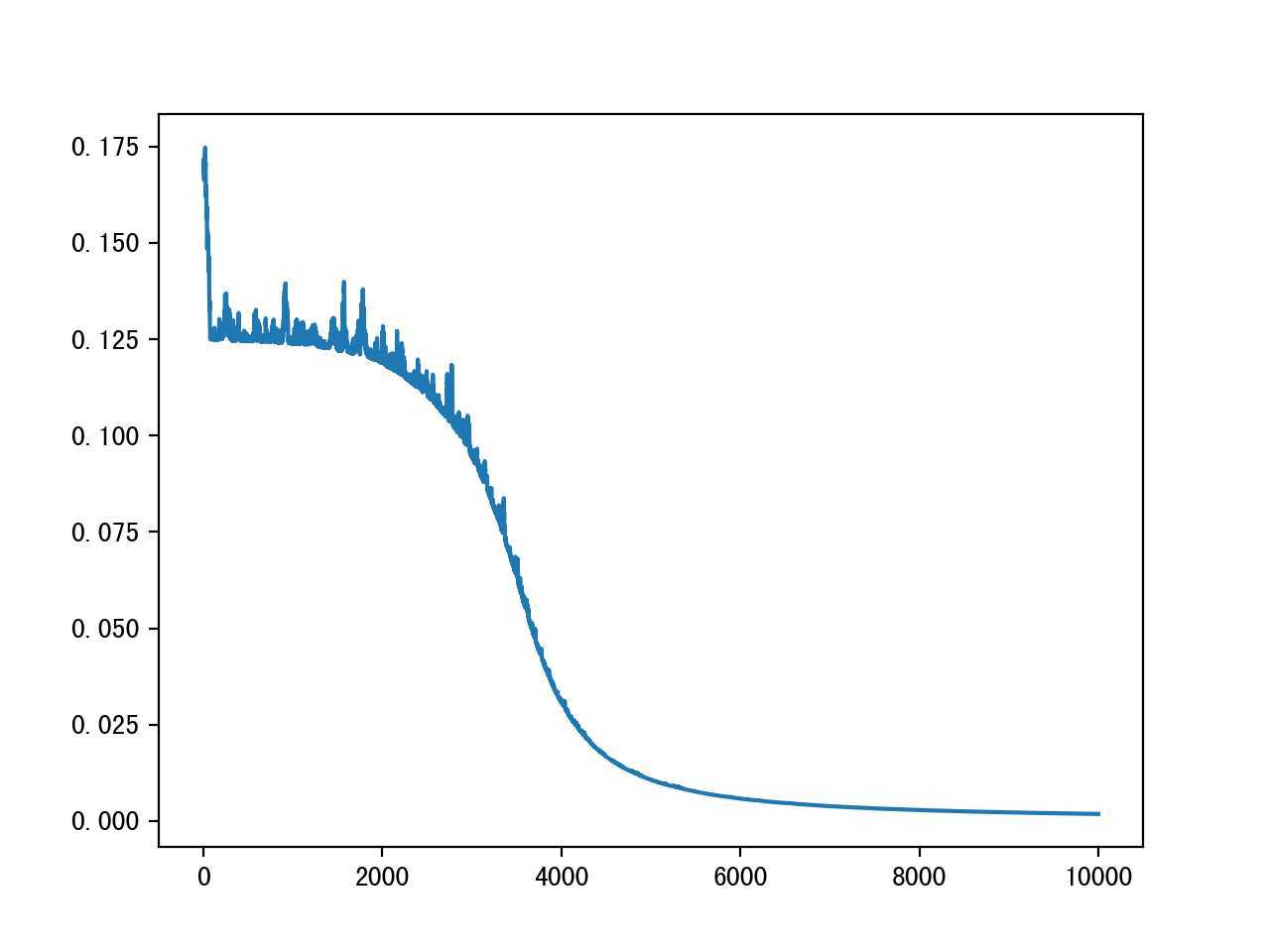
以上是关于BP神经网络及异或实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章